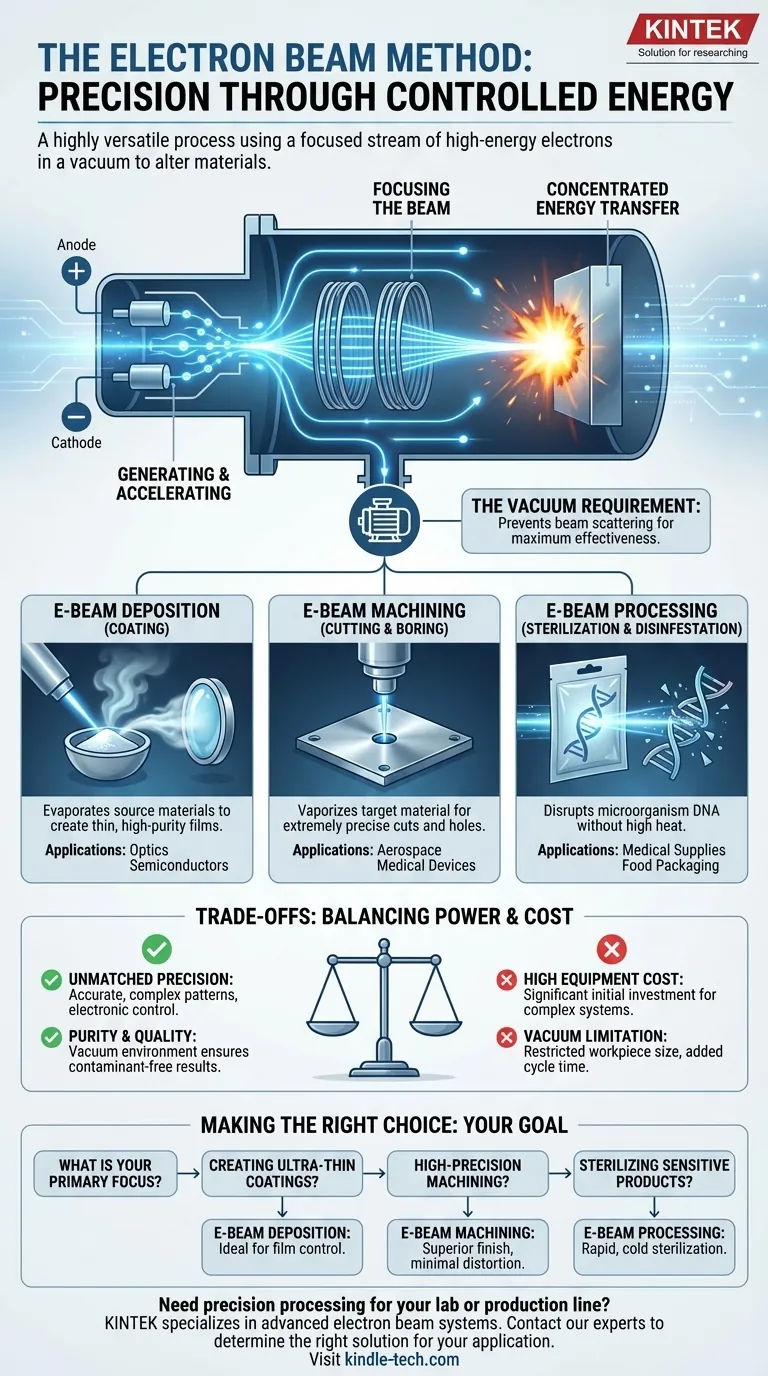
At its core, the electron beam method is a highly versatile process that uses a focused stream of high-energy electrons within a vacuum to precisely alter materials. This controlled energy transfer is adapted for vastly different outcomes, from vaporizing materials for advanced coatings and cutting through metals with surgical precision to sterilizing medical equipment.
The defining characteristic of any electron beam method is its ability to deliver a highly concentrated and controllable dose of energy to a specific point on a target. The specific application—whether it's coating, cutting, or sterilizing—is determined entirely by how that energy is manipulated and the effect it has on the material.

The Fundamental Principle: How an Electron Beam Works
An electron beam (E-beam) system operates on a simple but powerful principle of controlled energy transfer. The process can be broken down into a few key stages.
Generating and Focusing the Beam
Inside a vacuum chamber, free electrons are generated and then accelerated to high velocities using powerful electric fields. Magnetic fields act as lenses, focusing these fast-moving electrons into a narrow, concentrated beam.
Concentrated Energy Transfer
When this high-velocity beam collides with a solid material, the kinetic energy of the electrons is instantly converted into other forms, primarily intense, localized heat. The power and focus of this energy delivery can be adjusted with extreme precision.
The Importance of a Vacuum
The entire process must occur in a vacuum. This is critical because it prevents the electrons from colliding with and scattering off air molecules, which would diffuse the beam and drastically reduce its effectiveness.
Key Applications of Electron Beam Technology
The ability to precisely control this energy transfer allows E-beam technology to be adapted for a wide range of industrial applications.
E-Beam Deposition (Coating)
In this application, the electron beam is aimed at a source material, such as ceramic or metal powders, held in a crucible. The intense heat from the beam causes the material to evaporate. This vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber and condenses as a very thin, uniform film on a target surface, such as an optical lens.
E-Beam Machining (Cutting & Boring)
For machining, a much higher power density beam is used. The energy is so concentrated that it instantly vaporizes the target material, allowing for extremely precise cuts, holes, or complex shapes to be created. This method is valued for producing a superior surface finish and a very narrow cut (kerf width).
E-Beam Processing (Sterilization & Disinfestation)
Here, the goal is not to heat or vaporize the material but to use the beam's energy to break down biological matter. The electrons disrupt the DNA of microorganisms, sterilizing medical products or aseptic food packaging. The same principle is used for disinfestation, eliminating insects from bulk crops without damaging the product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, E-beam technology is not a universal solution. Its advantages are balanced by specific operational requirements and costs.
The Advantage: Unmatched Precision
Because the beam is controlled by electric and magnetic fields, its position, size, and power can be manipulated electronically with incredible speed and accuracy. This allows for complex patterns and extremely fine detail.
The Advantage: Purity and Quality
In deposition and machining, the vacuum environment ensures a high-purity process, free from atmospheric contaminants. This results in higher-quality coatings and cleaner cuts compared to many alternative methods.
The Limitation: High Equipment Cost
The complexity of the electron gun, high-voltage power supplies, and vacuum systems makes the initial capital investment for E-beam equipment significant. This often restricts its use to high-value applications where precision is paramount.
The Limitation: Vacuum Requirement
The need for a vacuum chamber limits the size of the workpiece that can be processed. It also adds time and complexity to the overall manufacturing cycle due to the need to pump down the chamber for each batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating whether an E-beam method is appropriate depends entirely on your specific technical and commercial requirements.
- If your primary focus is creating ultra-thin, high-purity coatings: E-beam deposition offers exceptional control over film thickness and composition, making it ideal for advanced optics and semiconductors.
- If your primary focus is high-precision machining of difficult materials: E-beam machining provides a superior surface finish and minimal thermal distortion, perfect for aerospace and medical device components.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing sensitive products without high heat: E-beam processing is a powerful and rapid method for treating medical supplies, pharmaceuticals, and food packaging.
Ultimately, the electron beam method is a premier tool for applications that demand the highest degree of precision energy delivery in a highly controlled environment.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| E-Beam Deposition | Creating thin films & coatings | High-purity, uniform layers |
| E-Beam Machining | Precision cutting & boring | Superior surface finish, minimal distortion |
| E-Beam Processing | Sterilization & disinfestation | Cold process, no chemical residues |
Need precision processing for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including electron beam systems for high-purity coating, precise machining, and effective sterilization. Our experts can help you determine if this high-precision technology is the right solution for your application. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of thermal evaporation method? Achieve Simple, Fast, and Cost-Effective Thin Films
- What are the uses of evaporation in industry? From Food Concentration to High-Tech Thin Films
- What is the vacuum thermal evaporation deposition technique? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Coating
- What is the source of vacuum evaporation? Energy and Vacuum for High-Purity Coatings
- What are the disadvantages of thermal evaporation method? Key Limitations in Purity and Performance
- What are the applications of electron beams? From Nanoscale Imaging to Industrial Manufacturing
- How thermal evaporation is used to deposit a thin metal film? A Simple Guide to High-Purity Coating
- What is the difference between sputtering and e-beam? Choose the Right Thin Film Deposition Method



















