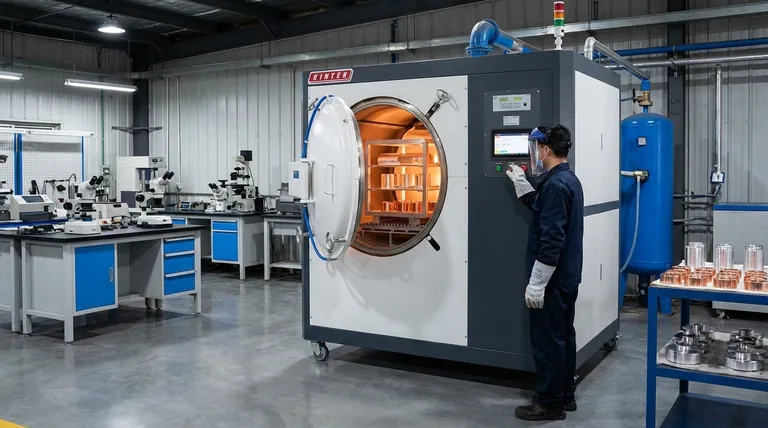
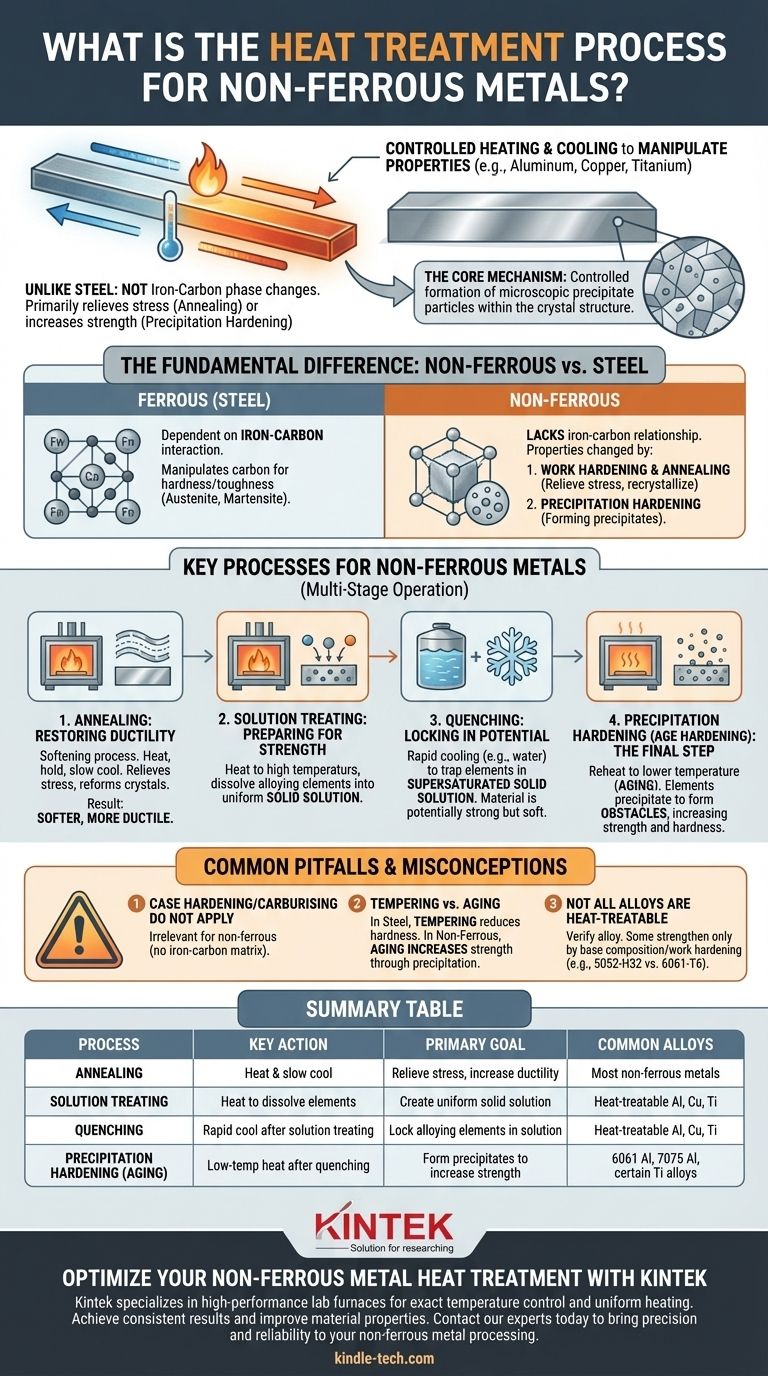
In short, the heat treatment of non-ferrous metals like aluminum, copper, or titanium is a process of controlled heating and cooling designed to manipulate their physical properties. Unlike steel, which relies on iron-carbon phase changes, non-ferrous treatments primarily work by relieving internal stresses through annealing or by increasing strength and hardness through a process called precipitation hardening.
The fundamental mistake is to apply the logic of steel heat treatment to non-ferrous metals. The core mechanism for strengthening most heat-treatable non-ferrous alloys is not carbon-based hardening, but the controlled formation of microscopic precipitate particles within the metal's crystal structure.

The Fundamental Difference: Why Non-Ferrous is Not Steel
Understanding how to properly heat treat non-ferrous metals begins with understanding why they are fundamentally different from their ferrous (iron-based) counterparts.
The Role of Carbon in Steel
The vast majority of heat treatment processes for steel—like case hardening, carburising, quenching, and tempering—are entirely dependent on the interaction between iron and carbon.
These processes manipulate the carbon within steel's crystalline structure, forcing transitions between phases like austenite and martensite to achieve hardness and toughness.
Non-Ferrous Strengthening Mechanisms
Non-ferrous metals lack this iron-carbon relationship. Their properties are changed through two primary mechanisms:
- Work Hardening & Annealing: Physically deforming the metal (work hardening) makes it harder but more brittle. Annealing reverses this by using heat to relieve stress and recrystallize the grain structure, restoring softness and ductility.
- Precipitation Hardening: Alloying elements are first dissolved into the base metal at high temperature, then "frozen" in place by rapid cooling (quenching). A final, lower-temperature heating cycle (aging) causes these elements to form extremely fine particles, or precipitates, that dramatically increase strength.
Key Processes for Non-Ferrous Metals
For heat-treatable non-ferrous alloys, particularly aluminum, the strengthening process is a multi-stage operation.
Annealing: Restoring Ductility
Annealing is a softening process. The metal is heated to a specific temperature, held there, and then slowly cooled.
This process allows the internal crystal structure, which may be stressed from manufacturing or forming, to relax and reform. The primary result is a softer, more ductile, and less brittle material, making it easier to form.
Solution Treating: Preparing for Strength
This is the first step of the strengthening process. The alloy is heated to a high temperature where the alloying elements (like copper or silicon in aluminum) dissolve completely into the base metal, creating a uniform solid solution.
Think of this as dissolving sugar in hot water—everything is mixed into a single, uniform liquid.
Quenching: Locking in Potential
Immediately after solution treating, the metal is rapidly cooled, typically in water. This quench does not have time for the dissolved alloying elements to escape the solution.
The goal is to trap these elements in what is called a supersaturated solid solution. The potential for strength is now locked in, but the material is often still relatively soft.
Precipitation Hardening (Age Hardening): The Final Step
This is the crucial strengthening step. The quenched material is reheated to a much lower temperature and held for a specific time.
This gentle heating, or aging, gives the trapped alloying elements just enough energy to "precipitate" out of the solution, forming countless microscopic particles. These particles act as obstacles that prevent the metal's crystal planes from slipping, making the material significantly harder and stronger.
Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions
Applying terminology from steel treatment to non-ferrous metals is the most common source of error.
"Case Hardening" and "Carburising" Do Not Apply
These processes involve diffusing carbon into the surface of steel to create a hard outer shell. Since non-ferrous metals like aluminum or titanium have no iron-carbon matrix to manipulate, these terms are irrelevant and the processes are inapplicable.
"Tempering" vs. "Aging"
In steel, tempering is a process that reduces the hardness of a freshly quenched part to increase its toughness.
In non-ferrous alloys, the process of heating after a quench is called aging, and its purpose is to increase hardness and strength through precipitation. Using the term "tempering" causes significant confusion as the metallurgical goal is the opposite.
Not All Alloys Are Heat-Treatable
A critical fact is that many non-ferrous alloys cannot be strengthened by heat treatment. Their strength comes purely from their base composition and from work hardening.
For example, 6061-T6 aluminum is precipitation hardened, while 5052-H32 aluminum is a strain-hardened alloy that cannot be strengthened further by aging.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct process requires a clear understanding of your desired outcome and your specific alloy.
- If your primary focus is maximum formability or stress relief: Annealing is the correct process to make the material softer and more ductile.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and hardness: The full sequence of solution treating, quenching, and precipitation aging is required, but only on designated heat-treatable alloys.
- If you are working with an unknown alloy: Never assume it is heat-treatable. Always verify the alloy designation, as attempting to precipitation harden a non-treatable alloy will have no effect or may ruin the material.
Ultimately, mastering the properties of non-ferrous metals comes from recognizing their unique metallurgy and applying the correct principles to achieve your engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Action | Primary Goal | Common Alloys |
|---|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Heat & slow cool | Relieve stress, increase ductility | Most non-ferrous metals |
| Solution Treating | Heat to dissolve alloying elements | Create uniform solid solution | Heat-treatable aluminum, copper, titanium |
| Quenching | Rapid cool after solution treating | Lock alloying elements in solution | Heat-treatable aluminum, copper, titanium |
| Precipitation Hardening (Aging) | Low-temperature heat after quenching | Form precipitates to increase strength & hardness | 6061 aluminum, 7075 aluminum, certain titanium alloys |
Optimize Your Non-Ferrous Metal Heat Treatment with KINTEK
Mastering the precise thermal cycles for annealing, solution treating, and precipitation hardening is critical to achieving the desired material properties in your non-ferrous components. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for exact temperature control and uniform heating, essential for successful heat treatment of aluminum, copper, titanium, and other non-ferrous alloys.
Our equipment helps you:
- Achieve consistent results with precise temperature uniformity
- Execute complex thermal cycles for precipitation hardening
- Improve material strength, ductility, and performance
- Avoid common pitfalls in non-ferrous heat treatment
We serve: Research laboratories, metallurgical facilities, aerospace manufacturers, and automotive engineers who require reliable thermal processing solutions.
Ready to enhance your heat treatment capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can bring precision and reliability to your non-ferrous metal processing.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- What is the structure of a vacuum furnace? A Guide to Its Core Components & Functions
- What are the advantages of vacuum hardening? Achieve Superior Precision and Cleanliness for Critical Components
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















