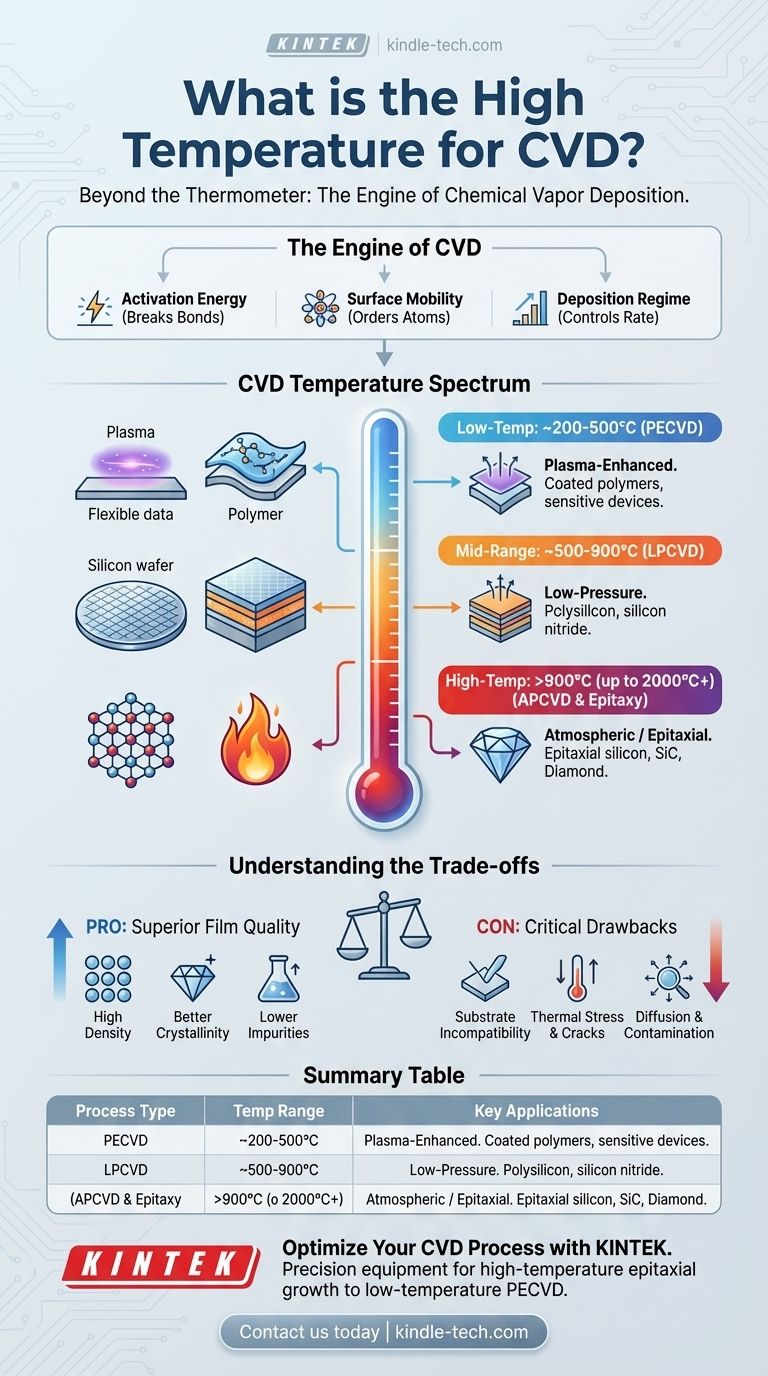
For conventional thermal processes, a "high temperature" for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is generally considered to be anything above 600°C (1112°F). However, this is not a universal rule, as the required temperature is dictated entirely by the specific materials and chemical reactions involved, with some specialized processes for materials like diamond or silicon carbide exceeding 1200°C or even 2000°C.
The critical insight is that temperature in CVD is not just about being "hot"; it is the primary tool used to provide the specific activation energy required to break down precursor gases and form a high-quality, dense thin film on a substrate. The "right" temperature is therefore a function of chemistry, not a fixed number.

Why Temperature is the Engine of CVD
Temperature is arguably the most critical parameter in any thermal CVD process. It directly controls the chemical reactions that define the film's properties, from its structure to its purity.
Providing Activation Energy
Every chemical reaction needs a certain amount of energy to get started—the activation energy. In thermal CVD, heat provides this energy. It breaks the chemical bonds in the volatile precursor gases, allowing the desired atoms to deposit onto the substrate surface.
Influencing Surface Mobility
Once atoms land on the substrate, they need to be able to move around to find their ideal spot in the crystal lattice. Higher temperatures increase this surface mobility, allowing atoms to form a more ordered, dense, and crystalline film with fewer defects.
Determining the Deposition Regime
The deposition rate's sensitivity to temperature reveals the process's limiting factor. At lower temperatures, the rate is reaction-rate limited; there isn't enough energy for the reaction to happen quickly. At higher temperatures, the process becomes mass-transport limited, meaning the reaction happens so fast that the bottleneck is simply how quickly new precursor gas can get to the surface.
The Spectrum of CVD Temperatures
Because different materials require different activation energies, CVD processes operate across a vast temperature range. We can group them into three general categories.
Low-Temperature CVD: ~200 to 500°C
This range is dominated by Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD). Instead of relying solely on heat, PECVD uses an electric field to create a plasma, which energizes the precursor gases. This allows for deposition at much lower temperatures, making it essential for coating temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers or completed electronic devices with final metal layers.
Mid-Range CVD: ~500 to 900°C
This is the workhorse range for many semiconductor applications, particularly for Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD). Processes for depositing common materials like polycrystalline silicon (polysilicon) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) fall squarely in this window. It offers a good balance between achieving high-quality films and manageable thermal budgets.
High-Temperature CVD: >900°C
These processes are reserved for materials that are either very stable or require a perfect crystalline structure. Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) for growing thick layers of silicon dioxide or specialized processes for growing high-purity epitaxial silicon layers operate well above 1000°C. Synthesizing extremely hard materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or diamond requires even more extreme temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs of High Temperature
Choosing a higher process temperature is a deliberate decision with significant benefits and critical drawbacks.
Pro: Superior Film Quality
Generally, higher temperatures produce films with higher density, better crystallinity, and lower impurity levels. The increased surface mobility helps "heal" defects as the film grows, resulting in superior material properties.
Con: Substrate Incompatibility
This is the most significant limitation. You cannot deposit a film at 1000°C onto a substrate that melts at 600°C or a device that would be damaged by that heat. High temperatures severely restrict the types of materials that can be used as a foundation.
Con: Thermal Stress and Diffusion
When the hot substrate and film cool down, differences in their thermal expansion coefficients can create immense stress, causing the film to crack or peel. Furthermore, high heat can cause atoms from underlying layers to diffuse upwards into the new film, contaminating it and ruining device performance.
Selecting the Right Temperature for Your Goal
The optimal temperature is determined by your end goal. The choice is always a trade-off between the ideal film properties and the physical limitations of your substrate.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with sensitive substrates (like polymers or finished circuits): Your only option is low-temperature PECVD, where plasma provides the energy that heat cannot.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible crystalline quality (like epitaxial silicon for high-performance chips): You must use a high-temperature thermal process above 1000°C and design the entire manufacturing flow around this thermal constraint.
- If your primary focus is a robust, well-understood process for standard materials (like polysilicon or dielectrics): Mid-range LPCVD processes between 600°C and 900°C offer the best balance of film quality, throughput, and thermal budget.
Ultimately, temperature in CVD is a precise tool used to drive specific chemical outcomes and dictate the final properties of the material you create.
Summary Table:
| CVD Process Type | Typical Temperature Range | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temp (PECVD) | ~200°C to 500°C | Coating polymers, final device layers |
| Mid-Range (LPCVD) | ~500°C to 900°C | Polysilicon, silicon nitride deposition |
| High-Temp (APCVD) | >900°C (up to 2000°C+) | Epitaxial silicon, SiC, diamond films |
Ready to optimize your CVD process for superior film quality and substrate compatibility?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing precision lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific CVD needs. Whether you're working with high-temperature epitaxial growth or low-temperature PECVD for sensitive materials, our experts can help you select the right system to achieve optimal results.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What are the tubes in a furnace called? Understanding the Role of the Working Tube
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere



















