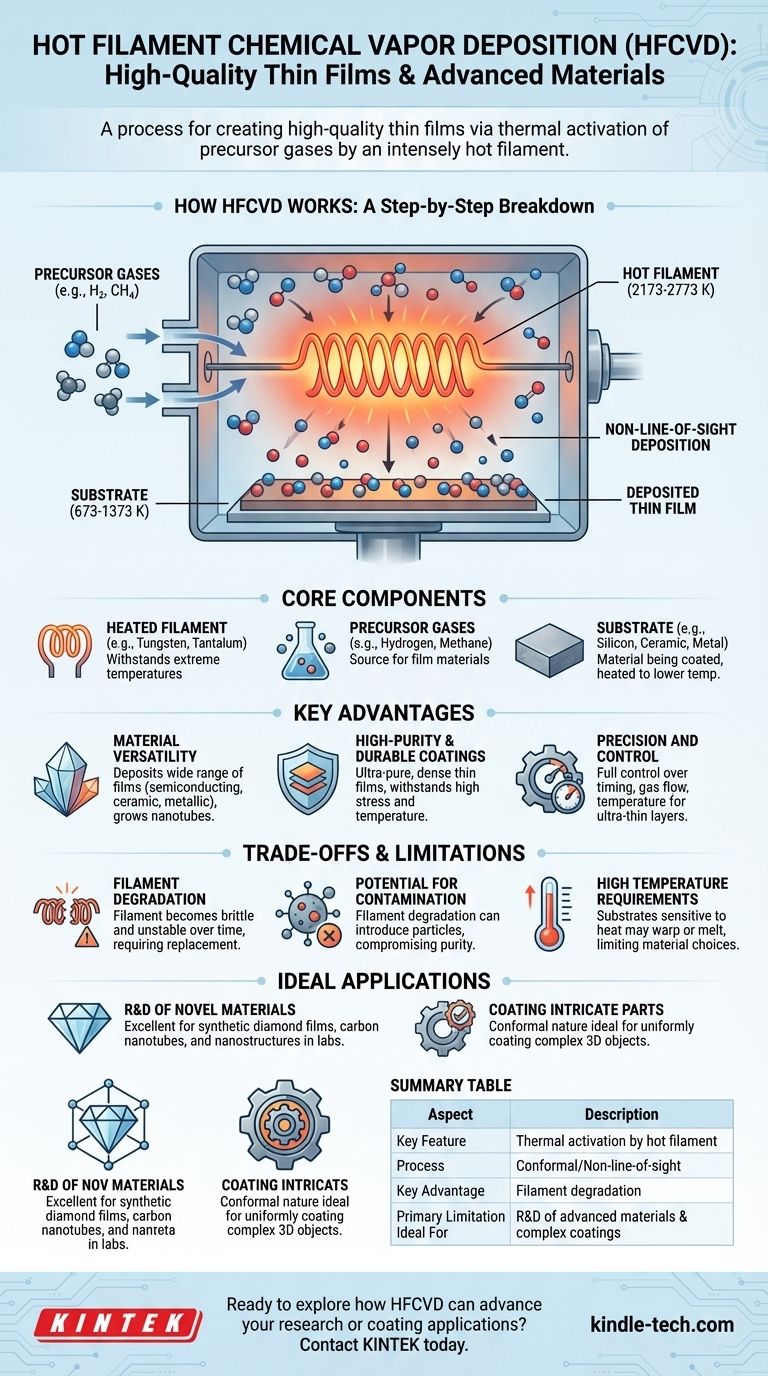
At its core, Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition (HFCVD) is a process for creating high-quality thin films. It works by passing precursor gases, such as hydrogen and methane, over a very hot filament inside a reaction chamber. This intense heat breaks the gases down into reactive chemical species, which then deposit onto a nearby substrate to form a solid, uniform coating.
HFCVD is a powerful and versatile method for growing highly pure materials like synthetic diamond and carbon nanotubes. Its primary advantage is the ability to precisely control the creation of durable, uniform coatings, but this comes with the critical trade-off of filament degradation over time.
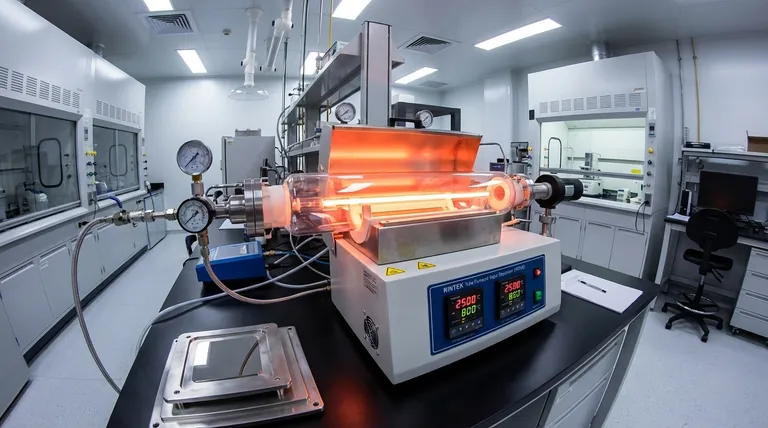

How HFCVD Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
To understand HFCVD, it's best to visualize it as a controlled chemical reaction occurring on a surface, activated by intense heat. The process relies on three key elements working in concert.
The Core Components
The HFCVD setup consists of a reaction chamber containing a heated filament, the precursor gases, and a substrate.
The filament is typically made of a refractory metal like tungsten (W), tantalum (Ta), or rhenium (Re) that can withstand extreme temperatures, often between 2173 and 2773 K (1900 to 2500 °C).
The substrate is the material being coated (e.g., silicon, ceramic, metal) and is also heated, though to a much lower temperature, typically 673 to 1373 K (400 to 1100 °C).
Gas Activation and Dissociation
The process begins when precursor gases are introduced into the chamber. The intensely hot filament acts as a thermal activator, breaking down, or dissociating, the gas molecules into highly reactive atoms or radicals.
For example, methane (CH4) breaks down into carbon and hydrogen species, while hydrogen gas (H2) is dissociated into atomic hydrogen. The filament itself often reacts with the gases, forming metal carbides that can help catalyze this dissociation process.
Deposition and Film Growth
These newly created, highly reactive chemical species travel the short distance from the filament to the heated substrate. There, they react on the surface, building up layer by layer to form a solid, dense, and highly pure thin film.
Because this process relies on gas moving throughout the chamber, it is non-line-of-sight. This allows HFCVD to apply an even, conformal coating to parts with complex shapes and intricate surfaces.
Key Advantages of the HFCVD Method
HFCVD inherits many of the powerful benefits of the broader family of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) techniques, making it suitable for a range of advanced applications.
Material Versatility
The fundamental process is based on chemical reactions, making it highly adaptable. HFCVD can be used to deposit a wide variety of films, including semiconducting, ceramic, and metallic layers, and is frequently used to grow advanced materials like carbon nanotubes and gallium nitride nanowires.
High-Purity and Durable Coatings
HFCVD allows for exceptional control over the gas mixture, leading to the creation of ultra-pure thin films. These coatings are dense and durable, capable of withstanding high-stress environments and extreme temperature variations.
Precision and Control
The process gives operators full control over timing, gas flow, and temperature. This precision enables the creation of ultra-thin layers of material, a critical requirement for manufacturing modern electrical circuits and semiconductor devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technical process is without its drawbacks. The primary challenge in HFCVD centers on the very component that makes it work: the filament.
Filament Degradation
The extreme temperatures and reactive chemical environment take a toll on the filament. Prolonged use causes the metal to become brittle and mechanically unstable, eventually leading to failure. This means filaments are a consumable part that requires periodic replacement, introducing downtime and operational costs.
Potential for Contamination
As the filament material (e.g., tungsten) degrades, it can become an unintended source of contamination. Particles from the filament can get incorporated into the growing film, compromising its purity and performance, which is a critical concern in high-purity applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
High Temperature Requirements
The process requires a heated substrate, which can limit the types of materials that can be successfully coated. Substrates that are sensitive to high temperatures may warp, melt, or be otherwise damaged, making them incompatible with the HFCVD process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
HFCVD is a specialized tool, and its suitability depends entirely on your project's specific requirements for material properties, purity, and production scale.
- If your primary focus is research and development of novel materials: HFCVD is an excellent choice for growing high-quality synthetic diamond films, carbon nanotubes, and other advanced nanostructures in a lab setting.
- If your primary focus is creating durable, corrosion-resistant coatings on complex parts: The conformal nature of HFCVD makes it ideal for uniformly coating intricate 3D objects that other line-of-sight methods cannot.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: You must carefully weigh the benefits against the operational costs of filament replacement and potential batch-to-batch inconsistencies caused by filament aging.
Ultimately, HFCVD is a powerful deposition technique that offers exceptional control and quality when its operational parameters align with the application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Feature |
|---|---|
| Process | Thermal activation of gases by a hot filament for deposition. |
| Key Advantage | Conformal, non-line-of-sight coating of complex shapes. |
| Primary Limitation | Filament degradation over time, requiring replacement. |
| Ideal For | R&D of advanced materials (e.g., diamond films) and durable coatings on intricate parts. |
Ready to explore how HFCVD can advance your research or coating applications? KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables you need for precise thin film deposition. Our experts can help you select the right tools for growing high-purity materials like diamond or carbon nanotubes. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and discover the KINTEK difference in laboratory solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What is the process of vacuum vapor deposition? Mastering CVD and PVD Thin-Film Coating
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty



















