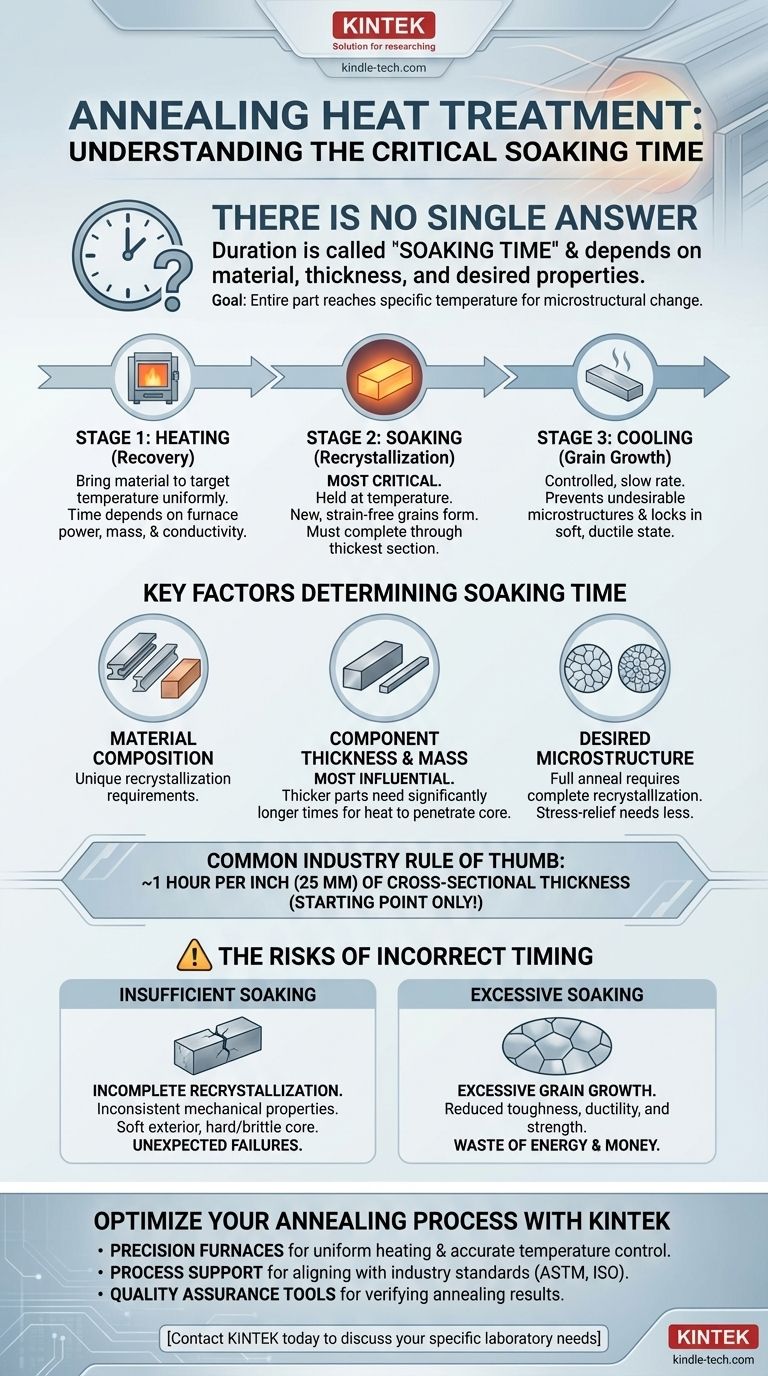
Critically, there is no single answer to the length of time heat is applied during annealing. The duration, more accurately known as the soaking time, is entirely dependent on the material's composition, its thickness, and the specific properties you aim to achieve. The process is not about a fixed time but about ensuring the entire part reaches and holds a specific temperature long enough for its internal structure to change.
The core principle of annealing is not just heating, but holding the material at a specific temperature until the desired microstructural transformation, known as recrystallization, is complete throughout its entire cross-section. This "soaking" duration is the critical variable, not the initial heating time.

The Three Stages of the Annealing Cycle
To understand the time component, you must first understand that annealing is a three-part process. The "heating" phase is just the beginning.
1. Heating to the Target Temperature (Recovery)
This is the initial phase where the furnace heats the component. The primary goal is to bring the material up to the required annealing temperature as uniformly as possible.
The time for this stage depends on the furnace's power, the component's mass, and its thermal conductivity. It is not the most critical time-dependent variable for metallurgical success.
2. Soaking at the Target Temperature (Recrystallization)
This is the most crucial stage and directly relates to your question. The component is held, or "soaked," at the annealing temperature.
During this hold, new, strain-free grains begin to form and grow within the metal, a process called recrystallization. This is what relieves internal stresses, increases ductility, and softens the material. The goal is to hold it long enough for this process to complete through the component's thickest section.
3. Controlled Cooling (Grain Growth)
After soaking, the component is cooled at a specific, often very slow, rate. The cooling rate is critical for preventing the formation of undesirable microstructures and ensuring the soft, ductile state is locked in. Fast cooling can re-introduce stress or create hardness, defeating the purpose of the anneal.
Key Factors That Determine Soaking Time
The proper soaking time is a calculated engineering decision based on several factors.
Material Composition and Type
Different alloys have vastly different recrystallization temperatures and kinetics. For example, high-carbon steels require more careful control than low-carbon steels, and aluminum alloys have entirely different parameters than copper.
Component Thickness and Mass
This is the single most influential factor. Heat must penetrate to the core of the material. A thick part requires a much longer soaking time than a thin sheet to ensure the center reaches and holds the target temperature.
A common industry rule of thumb is to soak for one hour for every inch (or 25 mm) of thickness of the material's cross-section, but this is only a starting point.
Desired Microstructure
The intended outcome dictates the process. A "full anneal" aims for maximum softness and requires a complete recrystallization. A "process anneal" or "stress-relief anneal" may be performed at a lower temperature or for a shorter time, as the goal is only to relieve stresses from manufacturing, not to achieve maximum softness.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong soaking time has significant consequences, which is why a single, generic answer is impossible.
The Risk of Insufficient Soaking
If the soaking time is too short, the core of the material will not fully recrystallize. This results in a component with inconsistent mechanical properties—a soft exterior with a hard, brittle, and stressed interior. This is a common cause of unexpected failures.
The Danger of Excessive Soaking
Holding the material at temperature for too long can lead to excessive grain growth. While the material will be soft, these large grains can significantly reduce its toughness, ductility, and strength.
Furthermore, excessive time is a direct waste of energy, furnace time, and money, negatively impacting operational efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the correct duration, you must move from seeking a number to defining your objective.
- If your primary focus is establishing a new process: Begin by consulting material data sheets or industry standards (e.g., from ASM, ASTM, or ISO) for your specific alloy.
- If your primary focus is optimizing an existing process: Use the "one hour per inch" rule as a baseline, produce a test part, and verify the outcome with metallurgical analysis and hardness testing (e.g., Rockwell or Brinell).
- If your primary focus is simple stress relieving: Recognize that this is a lower-temperature process than a full anneal and generally requires less soaking time, but is still governed by the part's thickness.
Ultimately, proper annealing time is a function of methodical process engineering, not a fixed recipe.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Soaking Time |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Different alloys (e.g., steel vs. aluminum) have unique recrystallization requirements. |
| Component Thickness | The most critical factor; thicker sections require significantly longer times. |
| Desired Outcome | A full anneal requires more time than a simple stress relief. |
| Common Rule of Thumb | ~1 hour per inch (25 mm) of cross-sectional thickness (as a starting point). |
Optimize Your Annealing Process with KINTEK
Achieving the precise soaking time is critical for consistent material properties and avoiding costly failures from under- or over-annealing. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that support meticulous heat treatment processes.
We help our laboratory customers by providing:
- Precision Furnaces: For uniform heating and accurate temperature control essential for proper soaking.
- Process Support: Guidance on aligning your equipment with industry standards (ASTM, ISO) for your specific alloys.
- Quality Assurance Tools: Hardness testers and metallurgical supplies to verify your annealing results.
Don't leave your material properties to chance. Let our expertise in lab solutions ensure your annealing cycles are efficient and effective.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and how we can support your heat treatment success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular RTP Heating Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is quartz tube heating? Achieve Instant, Targeted Heat with Infrared Radiation
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results



















