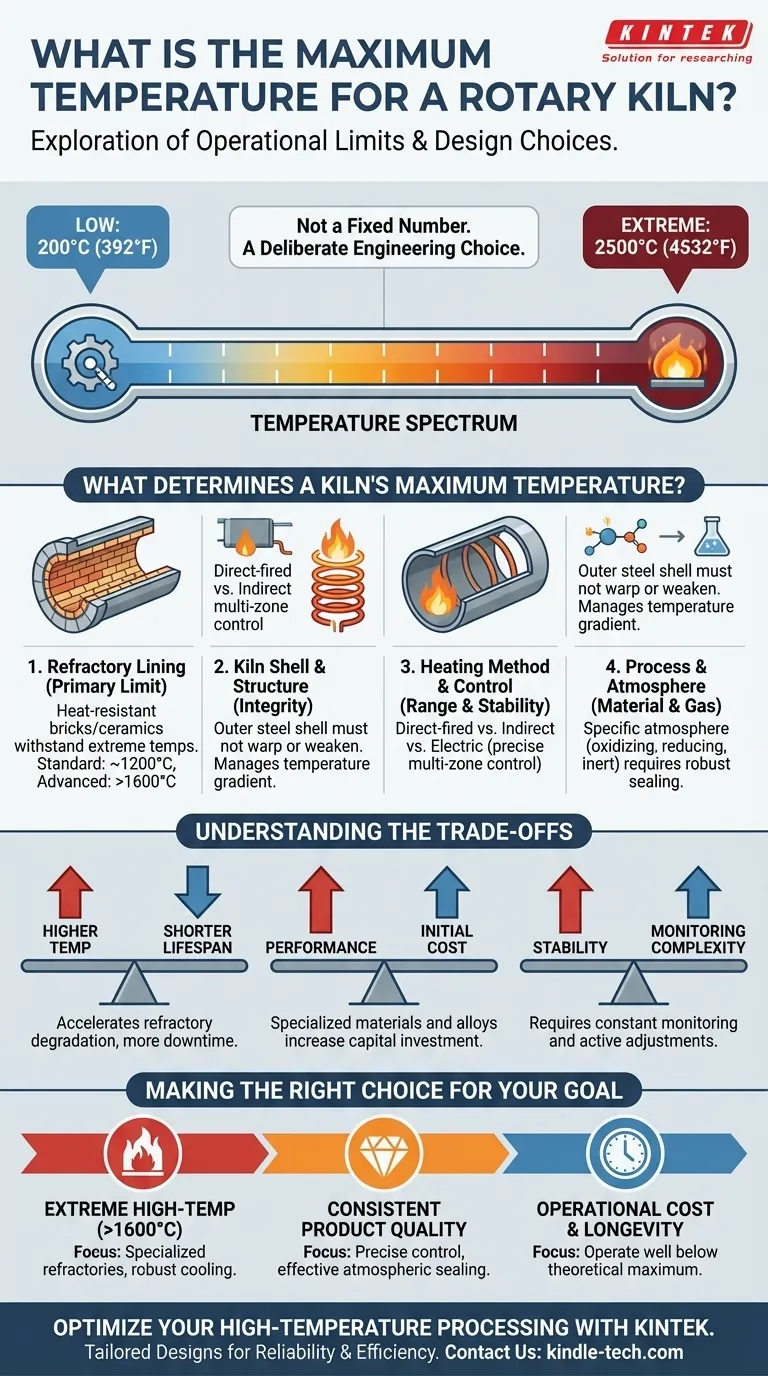
At its upper limit, a highly specialized rotary kiln can be designed to operate at temperatures as high as 2500°C (4532°F). However, this figure represents the extreme end of a wide operational spectrum that begins as low as 200°C (392°F). The actual maximum temperature for any given kiln is not a fixed number but is determined by its specific design, construction materials, and the process it is built for.
The key takeaway is that a kiln's maximum temperature is less about a universal limit and more about a deliberate engineering choice. The practical ceiling is dictated by the thermal tolerance of its refractory lining and steel shell, making material selection the most critical factor in defining its high-temperature capabilities.
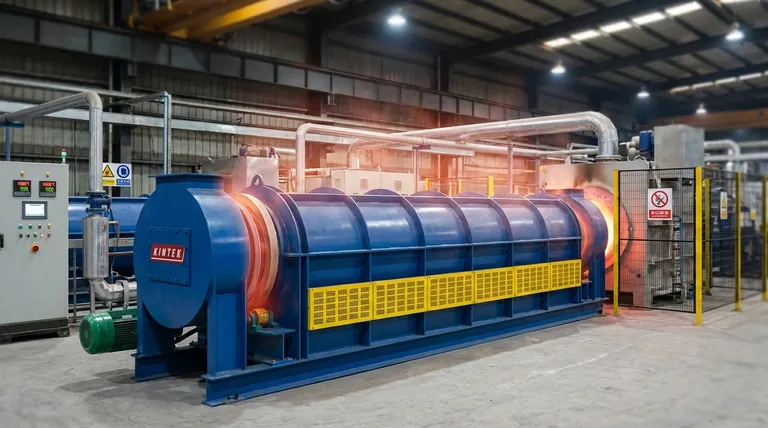

What Determines a Kiln's Maximum Temperature?
Understanding the maximum temperature of a rotary kiln requires looking beyond a single number and examining the components that collectively define its thermal limits. The final figure is a result of several interdependent design considerations.
The Critical Role of Refractory Lining
The material you are processing never directly touches the kiln's steel shell. It interacts with an inner lining of refractory materials—heat-resistant bricks or castable ceramics designed to withstand extreme temperatures.
This refractory lining is the first and most important limiting factor. Standard materials may handle temperatures up to 1200°C, while advanced ceramics like high-purity alumina or magnesia are required for processes pushing above 1600°C and beyond.
The Kiln Shell and Structural Integrity
While the refractory lining takes the brunt of the heat, the outer steel shell must maintain its structural integrity. The kiln is a massive, rotating piece of machinery, and excessive heat transfer can cause the steel to warp or weaken.
The design must manage the temperature gradient between the hot interior and the cooler exterior. Components like riding rings, trunnion wheels, and the drive assembly are all susceptible to heat-related stress and failure if the kiln operates beyond its engineered thermal limits.
The Heating Method and Control
How the kiln is heated directly influences its operational range and stability. Direct-fired kilns, where a flame is introduced into the cylinder, create a different thermal environment than indirectly heated kilns.
Modern electric rotary kilns offer exceptionally precise temperature control. By using heater elements placed around the kiln's circumference, they provide even heat transmission and allow for specific temperature profiles with distinct pre-heating and high-temperature zones.
Process Requirements and Atmosphere
The material being processed and the desired chemical reaction often set the required temperature. Furthermore, maintaining a specific atmosphere—whether oxidizing, reducing, or inert—is critical at high temperatures.
This requires robust sealing measures at the feed and discharge ends to prevent air from leaking in or process gases from escaping. The effectiveness of these seals can be a limiting factor in high-temperature, atmosphere-controlled applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting or operating a kiln at its maximum temperature involves significant trade-offs that impact cost, lifespan, and efficiency.
Higher Temperature vs. Shorter Lifespan
Operating a kiln consistently at or near its maximum design temperature will dramatically accelerate the degradation of the refractory lining. This leads to more frequent and costly downtime for relining and maintenance, directly impacting production availability.
Performance vs. Initial Cost
The materials required for extreme-temperature operation are substantially more expensive. High-performance refractories, specialized metal alloys for the kiln shell, and advanced sealing systems all add to the initial capital investment. Pushing for a higher temperature rating means committing to a higher budget.
Stability vs. Monitoring Complexity
Achieving a stable temperature in a high-temperature kiln is not a "set and forget" process. It requires constant monitoring of the temperature profile and active adjustments to kiln speed, feed rate, and energy input. Failure to manage these variables can lead to product quality issues or damage to the kiln itself.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal kiln temperature is not the highest possible; it's the temperature that reliably and economically achieves your process goal. When evaluating a rotary kiln, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is extreme high-temperature calcination or synthesis (>1600°C): You must prioritize a design with specialized, high-purity refractory materials and a robust shell cooling system.
- If your primary focus is consistent product quality: Focus on a system with precise, multi-zone temperature control and effective atmospheric sealing to ensure uniform processing.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and longevity: Operate the kiln well below its theoretical maximum temperature to significantly extend the life of the refractory lining and reduce maintenance cycles.
Ultimately, the right kiln is not the one with the highest temperature rating, but the one engineered to sustainably and efficiently meet your specific process demands.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on Max Temperature |
|---|---|
| Refractory Lining | Primary limit; standard materials handle ~1200°C, advanced ceramics exceed 1600°C |
| Kiln Shell & Structure | Steel integrity must be maintained; excessive heat causes warping/failure |
| Heating Method | Direct-fired, indirect, or electric (for precise control) affects range and stability |
| Process & Atmosphere | Material requirements and gas control (oxidizing, reducing, inert) set operational limits |
| Trade-offs | Higher temps reduce lifespan, increase costs, and require complex monitoring |
Ready to optimize your high-temperature processing? At KINTEK, we specialize in designing and supplying rotary kilns tailored to your exact thermal and operational needs. Whether your lab requires extreme calcination (>1600°C) or consistent, cost-effective heating, our expertise in refractory materials, precise temperature control, and durable construction ensures reliability and efficiency.
Let’s engineer the perfect solution for your goals. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK’s lab equipment can enhance your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- High Temperature Constant Temperature Heating Circulator Water Bath Chiller Circulator for Reaction Bath
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker



















