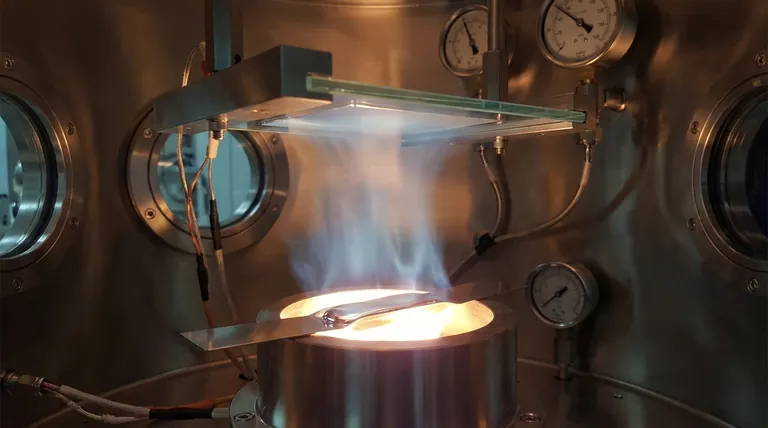
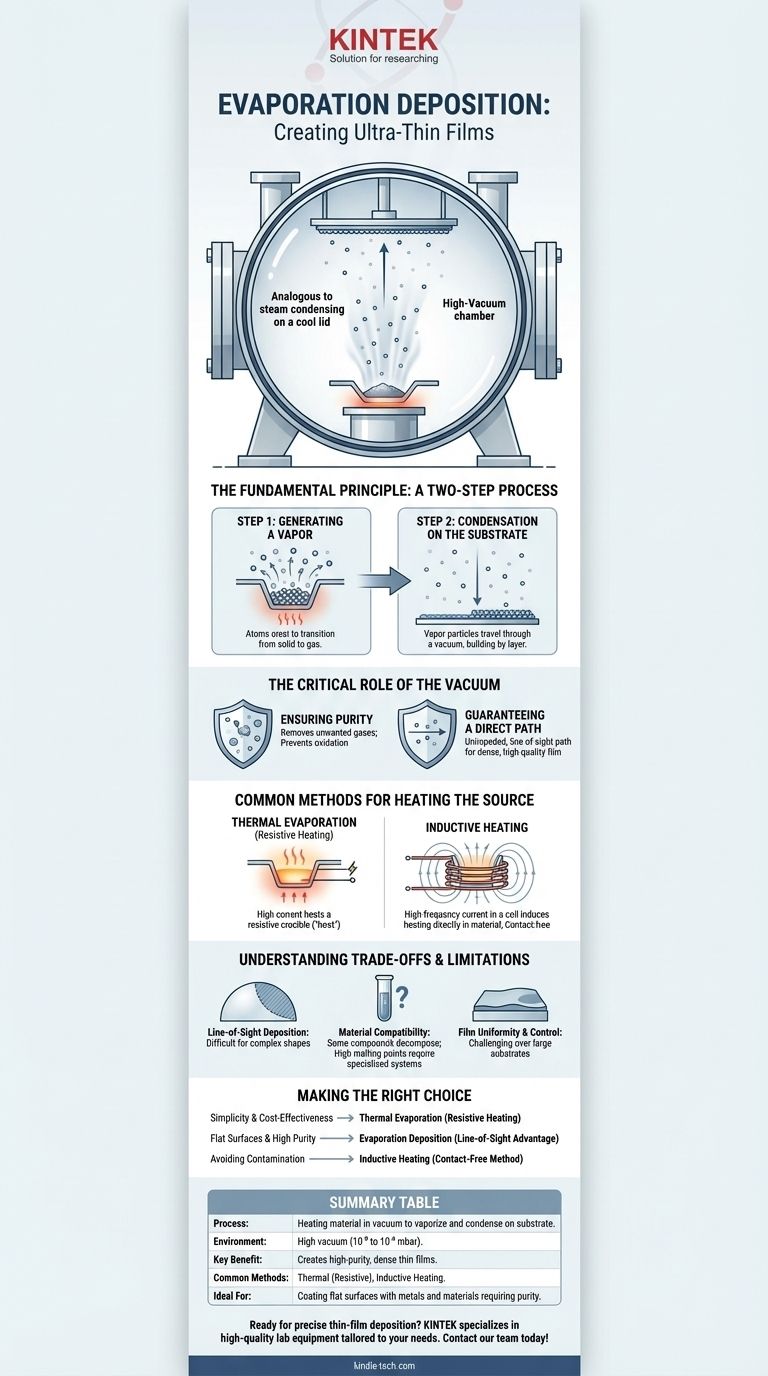
In essence, evaporation deposition is a method for creating ultra-thin films by heating a source material within a high-vacuum chamber until it vaporizes. These vaporized atoms or molecules then travel through the vacuum and condense onto a cooler target surface, known as a substrate. This process meticulously builds a thin, uniform layer of the source material on the substrate.
At its core, evaporation deposition is a process of controlled phase transition. By heating a material in a high vacuum, we allow its atoms to travel in a straight line, unimpeded by air, to precisely coat a target surface.

The Fundamental Principle: A Two-Step Process
Evaporation deposition operates on a simple but highly controlled physical principle. It is analogous to the way steam from a boiling pot condenses as water on a cool lid, but it occurs in a far more controlled environment.
Step 1: Generating a Vapor
The process begins by supplying energy to a source material, causing its atoms or molecules to transition from a solid or liquid state into a gaseous vapor. This happens when the particles gain enough thermal energy to overcome the forces binding them together.
Step 2: Condensation on the Substrate
This vapor then travels through the vacuum chamber. Upon hitting the cooler substrate, the particles lose their energy, condense back into a solid state, and adhere to the surface. This continuous process gradually builds the desired thin film, one layer of atoms at a time.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum
The entire process is performed inside a sealed chamber under a high vacuum, typically at pressures of 10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ mbar. This vacuum environment is not incidental; it is essential for two reasons.
Ensuring Purity
First, the vacuum removes air and other unwanted gases. This prevents the hot source material from reacting with contaminants like oxygen and ensures the deposited film is composed purely of the intended material.
Guaranteeing a Direct Path
Second, the near-absence of air molecules means the vaporized particles can travel directly from the source to the substrate without collision. This unimpeded, line-of-sight path is crucial for creating a high-quality, dense film.
Common Methods for Heating the Source
The primary difference between types of evaporation deposition lies in how the source material is heated to the point of vaporization.
Thermal Evaporation (Resistive Heating)
This is the most straightforward method. A high electrical current is passed through a heat-resistant crucible, "boat," or basket holding the source material. The resistance of the boat causes it to heat up intensely, transferring that thermal energy to the material until it evaporates.
Inductive Heating
In this method, the crucible holding the material is placed inside a coil powered by a high-frequency alternating current. This generates a powerful changing magnetic field, which in turn induces "eddy currents" within the crucible. These currents generate heat directly within the material without any physical contact from the power source, offering a very clean heating process.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, evaporation deposition is not without its challenges. Understanding these is key to its successful application.
Line-of-Sight Deposition
The direct path of vapor particles is a double-edged sword. While it ensures purity, it also means the process cannot easily coat complex, three-dimensional shapes. Areas not in the direct line of sight of the source will receive little to no coating.
Material Compatibility
Not all materials are suitable for evaporation. Some compounds may decompose when heated rather than evaporating cleanly. Others have extremely high melting points that require specialized and expensive heating systems.
Film Uniformity and Control
Achieving a perfectly uniform film thickness across a large substrate can be difficult. Thickness is highly dependent on the geometry of the chamber, the distance from the source to the substrate, and the angle at which the vapor arrives.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your specific goal will determine whether evaporation deposition is the right technique and which heating method to employ.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and cost-effectiveness: Thermal evaporation using resistive heating is often the ideal starting point for depositing many elemental metals.
- If your primary focus is coating a flat surface with a high-purity material: The line-of-sight nature of evaporation deposition is a significant advantage, ensuring a direct and uncontaminated particle path.
- If your primary focus is avoiding any contamination from the heating element: Inductive heating offers a contact-free method that can be critical for depositing highly sensitive or reactive materials.
By mastering these principles, you gain precise control over the creation of materials at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Heating a material in a vacuum to vaporize and condense it onto a substrate. |
| Environment | High vacuum chamber (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁶ mbar). |
| Key Benefit | Creates high-purity, dense thin films. |
| Common Methods | Thermal (Resistive) Evaporation, Inductive Heating. |
| Ideal For | Coating flat surfaces with metals and other materials requiring high purity. |
Ready to achieve precise thin-film deposition in your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including evaporation deposition systems tailored to your research and production needs. Our experts can help you select the right technology—whether thermal or inductive heating—to ensure purity, efficiency, and outstanding results for your specific materials. Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of thermal evaporation deposition? It's Material-Dependent, Not a Fixed Number
- What is a thermal evaporation system? A Guide to Simple, Effective Thin-Film Deposition
- What are thermal evaporation sources? Key Types and How to Choose the Right One
- What are the advantages of e-beam evaporation? Achieve High-Purity, High-Rate Thin Film Deposition
- Is sputtering better than evaporation purity? A Guide to High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- How does electron beam deposition work? Achieve High-Performance Optical & Polymeric Coatings
- Why are high-temperature porcelain boats used for biochar in a tube furnace? Ensure Sample Purity and Thermal Stability
- What is the function of high-purity alumina boats and spacers in S-CO2 corrosion experiments? Ensure Data Precision



















