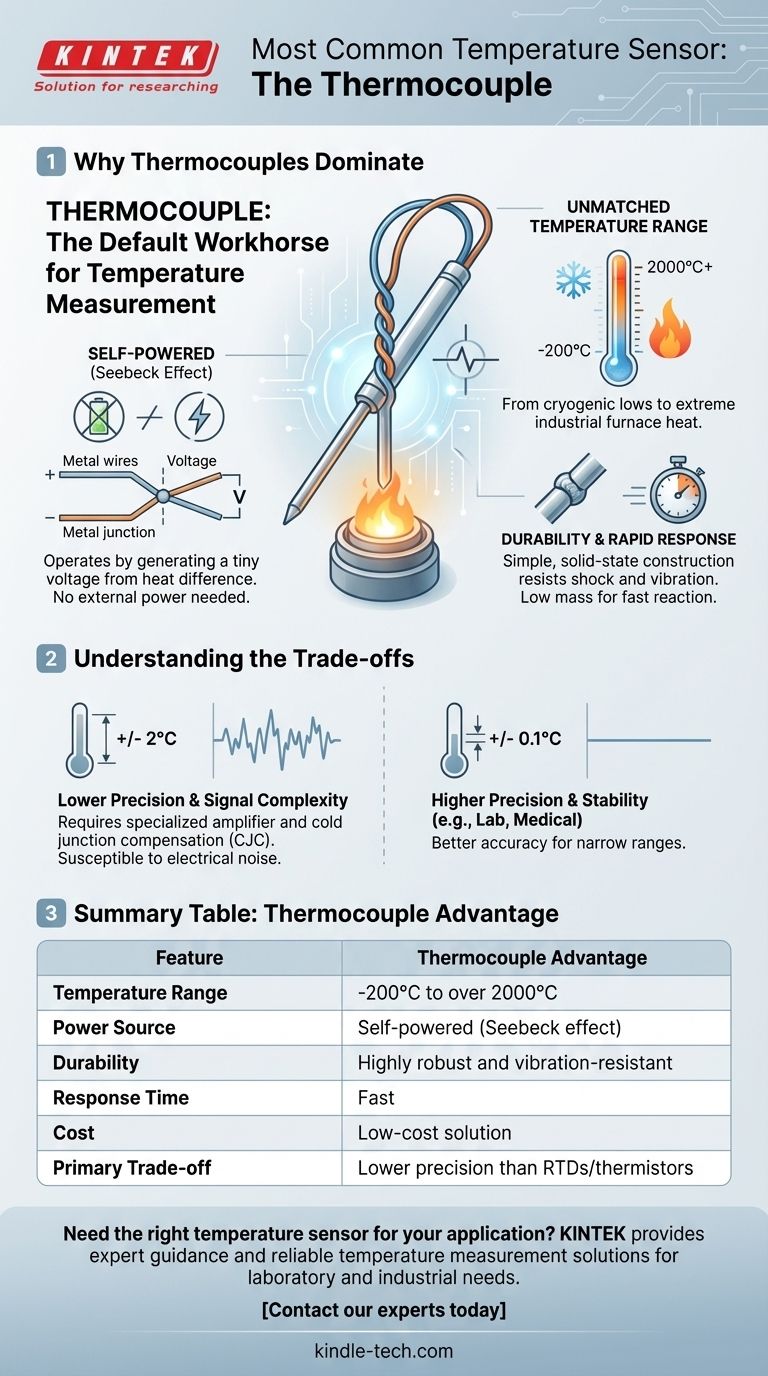
By a significant margin, the most common type of temperature sensor used across industrial, automotive, and consumer applications is the thermocouple. Its widespread adoption is due to a powerful combination of features: thermocouples are self-powered, operate over an exceptionally wide temperature range, offer a rapid response time, and are remarkably durable.
The core reason for the thermocouple's dominance is its unmatched versatility. While other sensors may offer higher precision in specific conditions, no other sensor provides such a robust, low-cost, and wide-ranging solution, making it the default workhorse for temperature measurement.

What Makes Thermocouples the Default Choice?
To understand why thermocouples are so prevalent, we must look at their fundamental design and the unique advantages that result from it.
The Seebeck Effect: Self-Powered Operation
A thermocouple operates on a principle called the Seebeck effect. It is constructed from two different types of metal wires joined together at one end—the sensing junction.
When this junction is heated or cooled, a tiny, predictable voltage is generated across the two wires. This means the sensor is self-powered and requires no external power source or "excitation" to function, drastically simplifying its implementation.
Unmatched Temperature Range
Thermocouples can measure a massive range of temperatures, a capability unmatched by most other sensor types.
Depending on the specific metals used (e.g., Type K, J, T), they can accurately measure everything from cryogenic lows (-200°C) to the extreme heat of jet engine exhaust or industrial furnaces (over 2000°C).
Durability and Rapid Response
At its core, a thermocouple is simply two wires welded together. This simple, solid-state construction makes them incredibly robust and resistant to vibration and mechanical shock.
Because the sensing junction has very little mass, it can also react to temperature changes very quickly, giving it a fast response time that is critical for process control and safety applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While versatile, the thermocouple is not the ideal choice for every situation. Its primary advantages come with inherent trade-offs in precision and signal complexity.
The Challenge of Precision and Stability
Thermocouples are generally less accurate than other sensors like Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTDs) or thermistors. While excellent for measuring a wide range, they may only be accurate to within ±1°C or ±2°C.
For applications requiring precision to a fraction of a degree, such as in laboratory or medical equipment, an RTD is often a better choice.
The Need for Signal Conditioning
The voltage produced by a thermocouple is very small (microvolts per degree Celsius) and is not perfectly linear.
To get a useful reading, you need a sensitive amplifier and specialized circuitry to perform cold junction compensation (CJC) and linearize the signal. This adds a layer of complexity compared to some other sensors.
Susceptibility to Electrical Noise
Because the signal is a tiny analog voltage, the wires of a thermocouple can act like an antenna, making them susceptible to electromagnetic interference (EMI) from nearby motors or power lines. Proper shielding and installation are critical in noisy environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a sensor is about matching its characteristics to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is a wide temperature range, low cost, and durability: The thermocouple is the clear and correct choice for industrial processes, engines, ovens, and general-purpose monitoring.
- If your primary focus is high precision and stability in a narrow range: An RTD or a thermistor will provide better accuracy for applications like climate control, medical devices, or scientific instrumentation.
Understanding these core strengths and weaknesses empowers you to select the right tool for your specific measurement task.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermocouple Advantage |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | -200°C to over 2000°C |
| Power Source | Self-powered (Seebeck effect) |
| Durability | Highly robust and vibration-resistant |
| Response Time | Fast |
| Cost | Low-cost solution |
| Primary Trade-off | Lower precision than RTDs/thermistors |
Need the right temperature sensor for your application?
Choosing between a versatile thermocouple, a highly precise RTD, or another sensor is critical for your process accuracy and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert guidance and reliable temperature measurement solutions for laboratory and industrial needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and ensure optimal performance for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Bomb Type Probe for Steelmaking Production Process
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- Will stainless steel work as a crucible? The Surprising Dangers of Using the Wrong Material
- What is the function of a glassy carbon crucible in LiF–NaF–KF salt melts? Enhance Purification with Dual-Action Design
- Can you melt steel in a graphite crucible? Understand the critical risks of carbon contamination.
- What is the most accurate temperature sensor? Why RTDs Lead in Precision and Stability
- Why are glassy carbon crucibles selected for high-temperature molten salt corrosion? Achieve Unmatched Data Accuracy

















