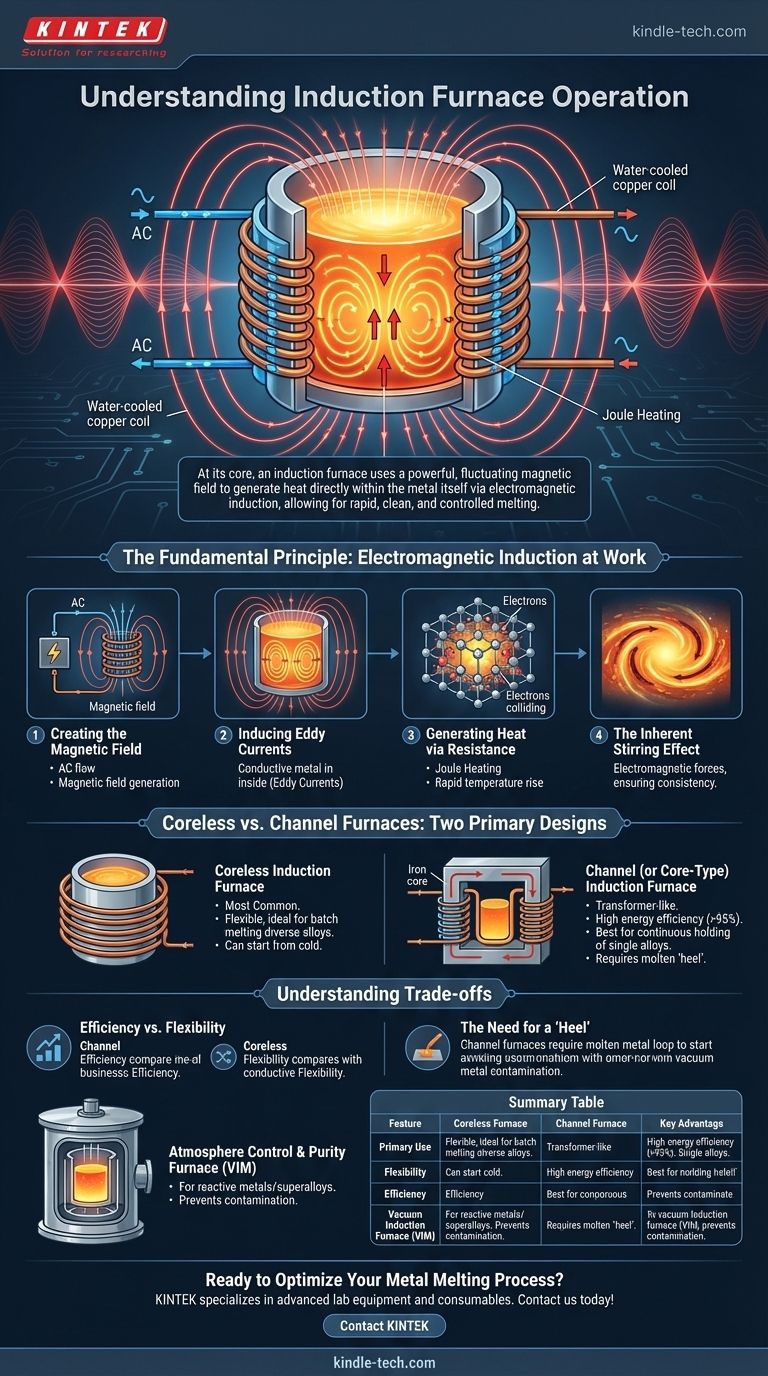
At its core, an induction furnace operates by using a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field to generate heat directly within the metal itself. This process, known as electromagnetic induction, allows for rapid, clean, and controlled melting without any direct contact from a heating element or flame.
The central principle of an induction furnace is the conversion of electrical energy into heat inside the target material. Unlike conventional furnaces that heat from the outside in, an induction furnace essentially turns the metal charge into its own heat source, leading to remarkable efficiency and precision.
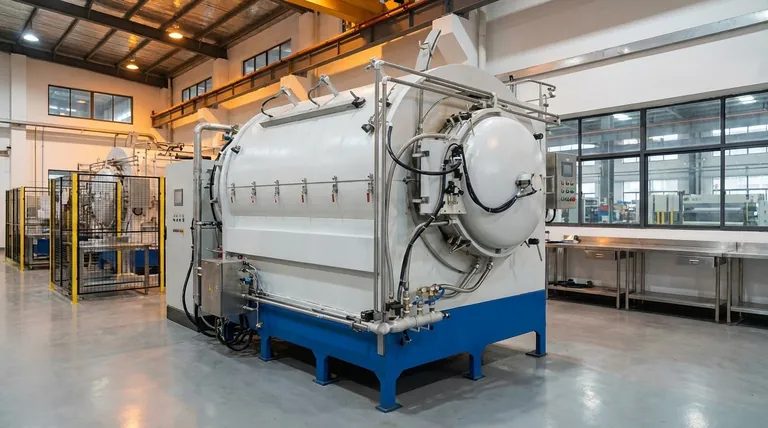

The Fundamental Principle: Electromagnetic Induction at Work
To understand the operation, it's best to break it down into a sequence of events. Each step is a direct consequence of the laws of electromagnetism.
Creating the Magnetic Field
An induction furnace uses a specialized power supply to send a high-frequency alternating current (AC) through a large, water-cooled copper coil. This coil wraps around a crucible or vessel containing the metal to be melted. The flow of AC through this coil generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within the coil.
Inducing Eddy Currents
This fluctuating magnetic field penetrates the electrically conductive metal inside the crucible. According to Faraday's law of induction, the changing magnetic field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Generating Heat via Resistance
The metal itself has a natural resistance to the flow of these induced eddy currents. As the eddy currents swirl through the metal, they overcome this resistance and generate immense heat through a process called Joule heating. This heat rapidly raises the metal's temperature to its melting point.
The Inherent Stirring Effect
A secondary benefit of this process is a natural stirring action. The forces created by the powerful magnetic field and the eddy currents cause the molten metal to move and circulate, ensuring a consistent temperature and a homogenous mixture when making alloys.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces: Two Primary Designs
While the principle remains the same, induction furnaces are typically built in one of two main configurations, each suited for different applications.
The Coreless Induction Furnace
This is the most common design. In a coreless furnace, the coil directly surrounds a refractory-lined crucible that contains the charge material. There is no iron core connecting the two.
This design is highly flexible, making it ideal for melting a wide range of metals and alloys in batches. It can be started from cold and completely emptied after each melt.
The Channel (or Core-Type) Induction Furnace
This design operates much like a transformer. It has an iron core with a primary coil, but the secondary "coil" is a closed loop of molten metal contained in a channel at the bottom of the furnace.
Heat generated in this molten metal loop circulates into the main bath of the furnace. This design is extremely energy-efficient but is best used for holding large volumes of a single type of metal molten for long periods, as it must maintain a "heel" of molten metal to operate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing and operating an induction furnace involves balancing key performance characteristics.
Efficiency vs. Flexibility
Channel furnaces boast the highest electrical efficiency (often over 95%) but are inflexible. They are best for continuous, single-alloy operations like holding furnaces in large foundries.
Coreless furnaces are less electrically efficient but offer unparalleled flexibility. Their ability to start cold and melt different materials makes them the standard for foundries that produce a variety of alloys.
The Need for a "Heel"
A major operational difference is that a channel furnace cannot be started from cold. It requires a continuous loop, or "heel," of molten metal to complete the secondary circuit. Draining it completely means it cannot be restarted without a complex and difficult pre-heating process.
Atmosphere Control and Purity
For melting highly reactive metals like titanium or for producing ultra-pure superalloys, the induction process can be enclosed in a vacuum. A Vacuum Induction Furnace (VIM) prevents the molten metal from reacting with oxygen and nitrogen, which would otherwise introduce impurities and compromise the material's properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace type is critical to achieving your operational and metallurgical goals.
- If your primary focus is batch melting diverse alloys: A coreless induction furnace provides the necessary flexibility to switch between different materials and start from a cold charge.
- If your primary focus is holding large volumes of a single metal molten continuously: A channel induction furnace offers the highest energy efficiency and is the most cost-effective solution for this task.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, reactive alloys: A vacuum induction furnace is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and ensure the final material meets strict specifications.
By understanding these core principles, you can leverage induction technology for highly controlled, clean, and efficient metal processing.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Coreless Furnace | Channel Furnace | Vacuum Induction Furnace (VIM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Batch melting diverse alloys | Holding large volumes of a single metal | Melting reactive, high-purity alloys |
| Flexibility | High (can start cold, change alloys) | Low (requires a molten metal 'heel') | High (within vacuum environment) |
| Efficiency | Good | Excellent (>95%) | Good |
| Key Advantage | Versatility for foundries | Energy efficiency for continuous operation | Prevents contamination for ultra-pure metals |
Ready to Optimize Your Metal Melting Process?
Understanding the principles of induction furnace operation is the first step toward achieving superior efficiency and metal quality in your lab or foundry. The right equipment is crucial for your specific application, whether you need the flexibility of a coreless furnace, the holding efficiency of a channel furnace, or the purity control of a vacuum system.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and research facilities. Our expertise can help you select the perfect induction melting solution to enhance your productivity, reduce costs, and ensure consistent, high-quality results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your requirements and discover how our solutions can power your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- Which element made stainless steel difficult to brazed? It's Chromium's Oxide Layer
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What are the advantages of brazing over braze welding? Achieve Stronger, Cleaner, and Repeatable Joints
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining



















