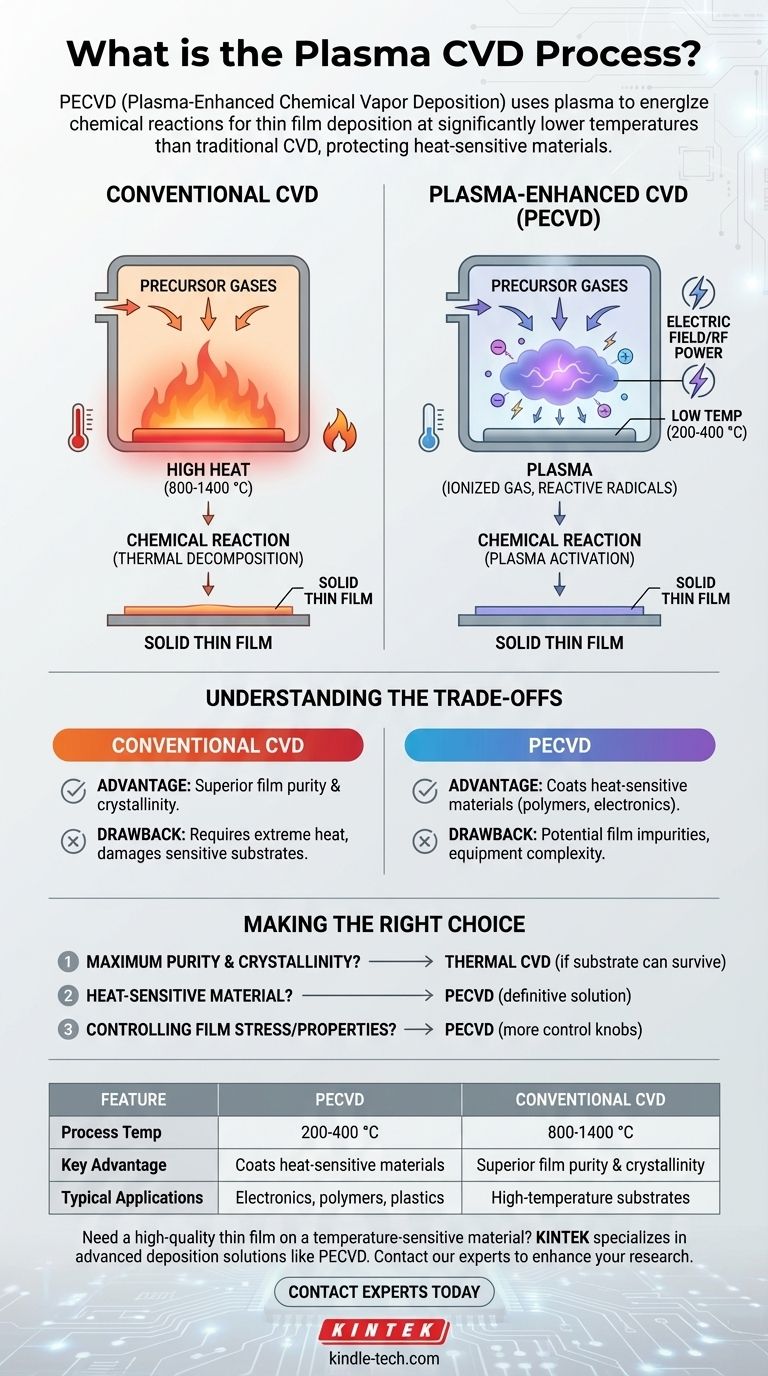
In short, the Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) process is a method for depositing thin films onto a surface using a plasma to energize the chemical reaction. Unlike traditional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) which relies on very high temperatures to break down gases, PECVD uses an ionized gas (a plasma) to create highly reactive molecules. This allows the film deposition to occur at significantly lower temperatures.
The core advantage of using plasma is that it replaces the need for extreme heat. This fundamental difference allows PECVD to coat materials, such as plastics or complex electronic components, that would be damaged or destroyed by the high temperatures of conventional CVD.
The Foundation: Understanding Conventional CVD
To understand what makes the plasma variant unique, we must first understand the fundamental principles of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The Basic Ingredients
The CVD process begins with a few key components. You need a substrate, which is the material you want to coat, and one or more precursor gases, which contain the atoms that will form the final film.
The Deposition Environment
These materials are placed inside a sealed reaction chamber. The chamber's environment, including pressure and temperature, is precisely controlled. For conventional thermal CVD, the substrate is heated to very high temperatures, often between 800 °C and 1400 °C.
The Chemical Reaction
When the precursor gases are introduced into the hot chamber, the thermal energy causes them to react or decompose on the substrate's surface. This chemical reaction results in the formation of a solid thin film on the substrate, while any waste gases are removed from the chamber.
How Plasma Changes the Process
Plasma-Enhanced CVD follows the same general principle but introduces a powerful new tool to drive the reaction: plasma.
What is a Plasma?
A plasma is often called the fourth state of matter. It is a gas that has been energized, typically by a strong electric or electromagnetic field (like microwaves), causing its atoms to break apart into a mix of charged ions and highly reactive free radicals.
The Role of Plasma in Deposition
In PECVD, this plasma is used to break down the precursor gases. The energetic radicals and ions created within the plasma are extremely reactive, far more so than the stable gas molecules at room temperature.
Because these plasma-generated radicals are already so reactive, they don't need extreme heat to form a film on the substrate. They readily react and bond to the surface even at much lower temperatures, typically 200-400 °C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between conventional thermal CVD and PECVD involves a critical trade-off between process temperature and final film quality.
Advantage: Lower Temperature Processing
The most significant benefit of PECVD is its low operating temperature. This opens the door to depositing high-quality films on temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers, plastics, and complex semiconductor devices with existing metallic layers that would melt at thermal CVD temperatures.
Drawback: Potential Film Impurities
The lower temperature and the use of hydrogen-containing precursors (like silane, SiH₄) mean that PECVD films can sometimes contain a higher concentration of impurities, particularly hydrogen. This can affect the film's density, stress, and electrical properties compared to a film grown at high temperature.
Drawback: Equipment Complexity
Generating and sustaining a stable plasma requires additional equipment, such as RF power supplies and matching networks. This makes PECVD systems more complex and potentially more expensive than some simpler thermal CVD setups.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use PECVD or another method depends entirely on the requirements of your substrate and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is maximum film purity and crystallinity: Thermal CVD is often the superior choice, provided your substrate can survive the extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is depositing a film on a heat-sensitive material: PECVD is the definitive and necessary solution, as it avoids thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is controlling film stress or mechanical properties: PECVD offers more control knobs (like plasma power and frequency) to tune the final film characteristics.
Ultimately, understanding the role of plasma is key to selecting the correct manufacturing tool for the specific task at hand.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Conventional Thermal CVD |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | 200-400 °C | 800-1400 °C |
| Key Advantage | Coats heat-sensitive materials | Superior film purity & crystallinity |
| Typical Applications | Electronics, polymers, plastics | High-temperature substrates |
Need to deposit a high-quality thin film on a temperature-sensitive material?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing solutions for advanced deposition processes like PECVD. Our expertise can help you select the right system to enhance your research and development, ensuring precise film properties and protecting delicate substrates.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PECVD can benefit your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is the working principle of PECVD? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition work? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Is DLC a good coating? Unlock Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Parts
- What is Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapour Deposition (PECVD)? High-Quality Film Coating at Low Temperatures
- What are the properties of DLC material? Achieve Superior Surface Performance
- What is the plasma source? A Guide to Generating and Controlling Ionized Gas for Industrial Applications
- What are the disadvantages of DLC coating? Key Limitations to Consider Before Application
- How do pole plate spacing and reaction chamber size affect PECVD? Optimize Your Film Uniformity and Throughput



















