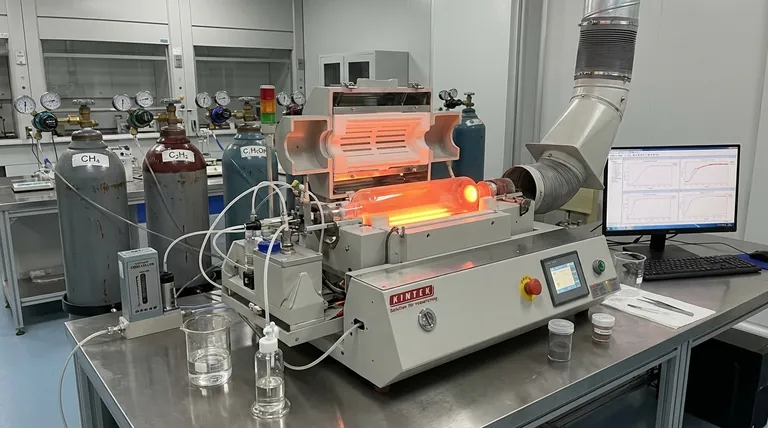
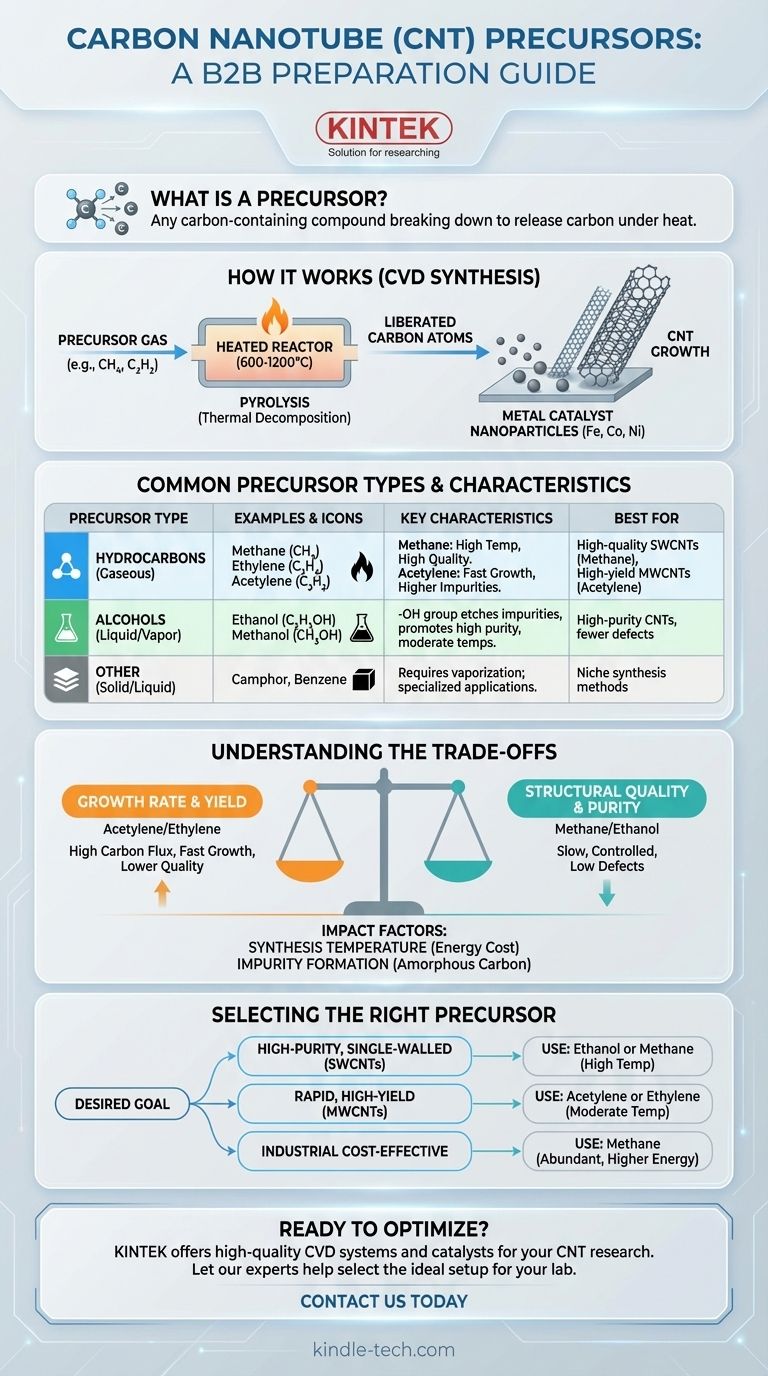
In essence, the precursor for Carbon Nanotube (CNT) preparation is any carbon-containing compound that can be broken down to release carbon atoms under specific reaction conditions. The most common precursors are simple hydrocarbons like methane, ethylene, and acetylene, or alcohols like ethanol. These substances are typically introduced in a gaseous state into a high-temperature reactor, where they decompose and form the building blocks for CNTs.
The choice of a carbon precursor is not merely about supplying a source of carbon. It is a critical process parameter that directly influences the quality, structure, yield, and synthesis temperature of the final Carbon Nanotubes.

How Precursors Form Carbon Nanotubes
The most prevalent method for synthesizing CNTs is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The precursor's role in this process is straightforward but crucial.
The Principle of Thermal Decomposition
In a CVD reactor, the precursor gas is heated to a very high temperature, typically between 600°C and 1200°C. This intense heat provides the energy to break the chemical bonds within the precursor molecules.
This process, known as pyrolysis or thermal decomposition, "cracks" the precursor and liberates individual carbon atoms or small carbon-containing radicals.
The Role of the Catalyst
These newly freed carbon atoms are highly reactive. They diffuse towards and dissolve into tiny nanoparticles of a metal catalyst, most commonly iron, cobalt, or nickel.
Once the catalyst particle becomes supersaturated with carbon, the carbon atoms begin to precipitate out. They self-assemble into the stable, hexagonal lattice structure that forms the wall of a Carbon Nanotube, which then grows outwards from the catalyst particle.
Common Carbon Precursors and Their Characteristics
Different precursors have distinct chemical stabilities and compositions, which makes them suitable for different synthesis goals.
Hydrocarbons (Gaseous)
Methane (CH4) is a highly stable molecule. It requires very high temperatures (typically >900°C) to decompose, but this slow and controlled carbon release often results in high-quality, well-structured CNTs with fewer defects.
Ethylene (C2H4) and Acetylene (C2H2) are less stable than methane. They decompose at lower temperatures, leading to a faster CNT growth rate and higher yield. However, this rapid decomposition can sometimes produce more amorphous carbon impurities that coat the nanotubes.
Alcohols (Liquid/Vapor)
Ethanol (C2H5OH) and Methanol (CH3OH) are excellent precursors. The presence of the hydroxyl (-OH) group is particularly beneficial.
At high temperatures, this group can form water vapor or other oxygen-containing species. These act as a mild etching agent, selectively removing the less-stable amorphous carbon and helping to prolong the life of the catalyst. This often results in very high-purity CNTs.
Other Precursor Types
While less common in standard laboratory setups, solid sources like camphor or other liquid hydrocarbons like benzene and xylene can also be used. These materials are either vaporized or sublimated into a gas before being introduced into the reactor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a precursor involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" precursor, only the most appropriate one for a specific application.
Quality vs. Growth Rate
There is often an inverse relationship between growth rate and structural quality.
Reactive precursors like acetylene provide a very high carbon flux, enabling rapid growth. The downside is a higher likelihood of defects and byproduct formation. In contrast, stable precursors like methane offer slower, more controlled growth, which is conducive to forming highly crystalline, low-defect CNTs.
Synthesis Temperature
The chemical stability of the precursor directly dictates the required process temperature. This has significant implications for energy costs and the types of substrates that can be used.
For example, a process requiring methane at 1000°C is far more energy-intensive than one using acetylene at 700°C.
Impurity Formation
The primary impurity in CNT synthesis is amorphous carbon, a disordered, non-graphitic form of carbon. Precursors that decompose too quickly can deposit a thick layer of this soot-like material, which is difficult to remove and degrades the final product's properties.
Selecting the Right Precursor for Your Goal
Your choice should be guided by the desired properties of the final CNT material and your process constraints.
- If your primary focus is high-purity, single-walled CNTs (SWCNTs): Consider using ethanol or methane at high temperatures, as these conditions favor cleaner growth with fewer defects.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-yield production of multi-walled CNTs (MWCNTs): A more reactive hydrocarbon like acetylene or ethylene at moderate temperatures is often the most efficient choice for maximizing output.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and quality for industrial scale-up: Methane is often preferred due to its low cost and abundance, despite requiring higher energy input for decomposition.
Ultimately, mastering CNT synthesis begins with understanding that the carbon precursor is not just an ingredient, but a critical control variable for tuning the final product.
Summary Table:
| Precursor Type | Common Examples | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocarbons (Gaseous) | Methane (CH₄), Ethylene (C₂H₄), Acetylene (C₂H₂) | Methane: High temp, high quality. Acetylene: Fast growth, higher impurities. | High-quality SWCNTs (Methane) or high-yield MWCNTs (Acetylene). |
| Alcohols (Liquid/Vapor) | Ethanol (C₂H₅OH), Methanol (CH₃OH) | -OH group etches impurities, promotes high-purity CNTs, moderate temperatures. | High-purity CNTs with fewer defects. |
| Other (Solid/Liquid) | Camphor, Benzene, Xylene | Requires vaporization; used in specialized applications. | Niche synthesis methods. |
Ready to Optimize Your CNT Synthesis Process?
The right precursor is key to achieving your specific Carbon Nanotube goals—whether it's high purity, rapid yield, or cost-effective scale-up. KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including CVD systems and catalysts, needed to master your CNT preparation.
Let our experts help you select the ideal setup for your research or production needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What are nanotubes drawbacks? The 4 Major Hurdles Limiting Their Real-World Use
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- How do nanotubes affect the environment? Balancing Low Carbon Footprint with Ecological Risks
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance
- Are all lab grown diamonds CVD? Understanding the Two Main Methods



















