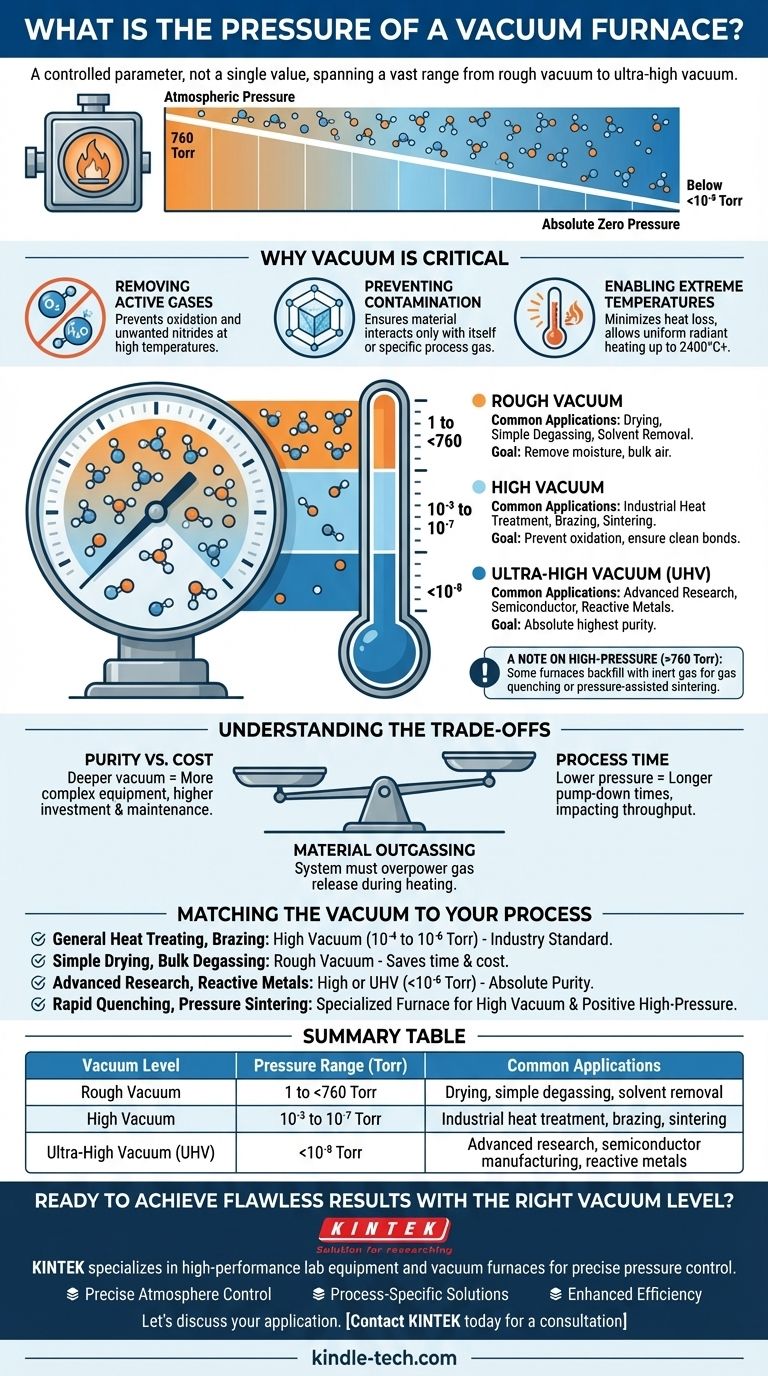
The pressure of a vacuum furnace is not a single value but a highly controlled operational parameter. It spans a vast range, from a rough vacuum just below atmospheric pressure (around 760 Torr) to an ultra-high vacuum near absolute zero pressure (below 10⁻⁸ Torr). The precise pressure required is dictated entirely by the material and the specific thermal process, such as sintering, brazing, or degassing.
The level of vacuum in a furnace is a tool to control the purity of the internal environment. Lowering the pressure removes reactive gases like oxygen and water vapor, preventing contamination and unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures, which is the fundamental reason for using a vacuum in the first place.

Why Vacuum is the Critical Variable
A vacuum furnace's primary job is to create a controlled, stable atmosphere. Removing air and other gases is the most effective way to achieve this, directly influencing the quality and properties of the final product.
Removing Active Gases
The air we breathe is composed of gases—primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and water vapor—that become highly reactive at elevated temperatures. These gases can cause oxidation, form unwanted nitrides, and introduce impurities into the material being processed. A vacuum physically removes these molecules from the chamber.
Preventing Contamination
By creating a near-empty environment, a vacuum ensures that the material being heated only interacts with itself or with a specific, intentionally introduced process gas. This is critical for applications in medical, aerospace, and electronics, where even microscopic levels of contamination can lead to component failure.
Enabling Extreme Temperatures
In a normal atmosphere, heat transfers through convection. By removing the air, a vacuum furnace minimizes heat loss and allows for more efficient and uniform radiant heating. This is essential for reaching the ultra-high temperatures (up to 2400°C or higher) required for advanced ceramics and alloys.
Understanding Vacuum Pressure Levels
The term "vacuum" describes any pressure below the normal atmosphere. Furnaces are designed to operate at different vacuum levels, each suited for specific tasks. Pressure is commonly measured in Torr, where 760 Torr is standard atmospheric pressure.
Rough Vacuum (1 to <760 Torr)
This is the first stage of vacuum, where the bulk of the air is removed from the chamber. A rough vacuum is often sufficient for processes like drying, solvent removal, and simple degassing, where the primary goal is to remove moisture and the majority of atmospheric oxygen.
High Vacuum (10⁻³ to 10⁻⁷ Torr)
This is the workhorse range for most industrial heat treatment, brazing, and sintering applications. This level of vacuum provides a very pure environment, preventing oxidation and ensuring clean, strong bonds in brazing or full densification in sintering.
Ultra-High Vacuum (<10⁻⁸ Torr)
Reserved for the most sensitive applications, UHV creates an environment with extremely few gas molecules. It is essential for advanced scientific research, semiconductor manufacturing, and processes involving materials that are exceptionally reactive or require the absolute highest purity.
A Note on High-Pressure Operation (>760 Torr)
Confusingly, some vacuum furnaces are also designed for high-pressure operation. After pulling a vacuum to purify the environment, the furnace can be backfilled with an inert gas (like Argon) to a positive pressure. This technique is used for gas quenching to cool parts rapidly or for pressure-assisted sintering to achieve maximum density.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving a lower pressure (a deeper vacuum) is not always better. The required vacuum level is a balance between process requirements, cost, and time.
Purity vs. Cost
Deeper vacuum levels require more complex and expensive equipment. While a simple mechanical pump can achieve a rough vacuum, reaching high and ultra-high vacuums requires additional pumps (like turbomolecular or cryogenic pumps) working in series. This significantly increases the initial investment and maintenance costs.
Process Time
The time it takes to pump down the chamber to the target pressure is a major factor in production throughput. Achieving a rough vacuum can take minutes, while pumping down to an ultra-high vacuum can take many hours. Choosing the appropriate vacuum level is critical for operational efficiency.
Material Outgassing
As materials are heated, they release trapped gases and moisture—a phenomenon called outgassing. This process works against the vacuum pumps, and the system must be powerful enough to remove these released gases to maintain the target pressure throughout the heating cycle.
Matching the Vacuum to Your Process
Choosing the right furnace begins with a clear understanding of your process requirements. The goal is to use the level of vacuum that achieves the desired material properties in the most cost-effective and timely manner.
- If your primary focus is general heat treating, annealing, or brazing: A high vacuum in the 10⁻⁴ to 10⁻⁶ Torr range is the industry standard, providing an excellent balance of cleanliness and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is simple drying or bulk degassing: A rough vacuum may be entirely sufficient, saving significant time and equipment cost.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research or processing highly reactive metals: You will likely require a high or ultra-high vacuum (below 10⁻⁶ Torr) to ensure absolute purity.
- If your process involves rapid gas quenching or pressure-assisted sintering: You need a specialized furnace capable of both high vacuum and positive high-pressure operation.
Ultimately, the correct vacuum pressure is the one that reliably and cost-effectively achieves your specific material processing goal.
Summary Table:
| Vacuum Level | Pressure Range (Torr) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Rough Vacuum | 1 to <760 Torr | Drying, simple degassing, solvent removal |
| High Vacuum | 10⁻³ to 10⁻⁷ Torr | Industrial heat treatment, brazing, sintering |
| Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) | <10⁻⁸ Torr | Advanced research, semiconductor manufacturing, reactive metals |
Ready to Achieve Flawless Results with the Right Vacuum Level?
Choosing the correct vacuum pressure is critical for the success of your sintering, brazing, or heat treatment process. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including vacuum furnaces designed to deliver the precise pressure control your materials demand.
We provide the tools for:
- Precise Atmosphere Control: Prevent oxidation and contamination for superior material properties.
- Process-Specific Solutions: From rough vacuum for drying to UHV for advanced research.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Optimize cycle times and achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Let's discuss your application. Our experts will help you select the ideal furnace to meet your specific vacuum and temperature requirements.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and take control of your thermal processing environment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is vacuum needed in physical vapour deposition? Achieve Purity and Precision in Thin-Film Coatings
- How hot does a vacuum furnace get? Discover the Right Temperature for Your Process
- What is the relationship between temperature and pressure in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Optimal Vacuum Performance
- What are the three most important factors in material heat treatment? Master Temperature, Time, and Cooling for Superior Properties
- Why is a vacuum oven required for UIO-66 crystal treatment? Maximize MOF Activation and Surface Area
- What is the significance of vacuum heating for Li-IL in MOFs? Ensure Deep Dehydration & Battery Stability
- What is the overview of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Alloys
- What is the temperature of the electric arc furnace? Key Insights for Efficient Steel Production



















