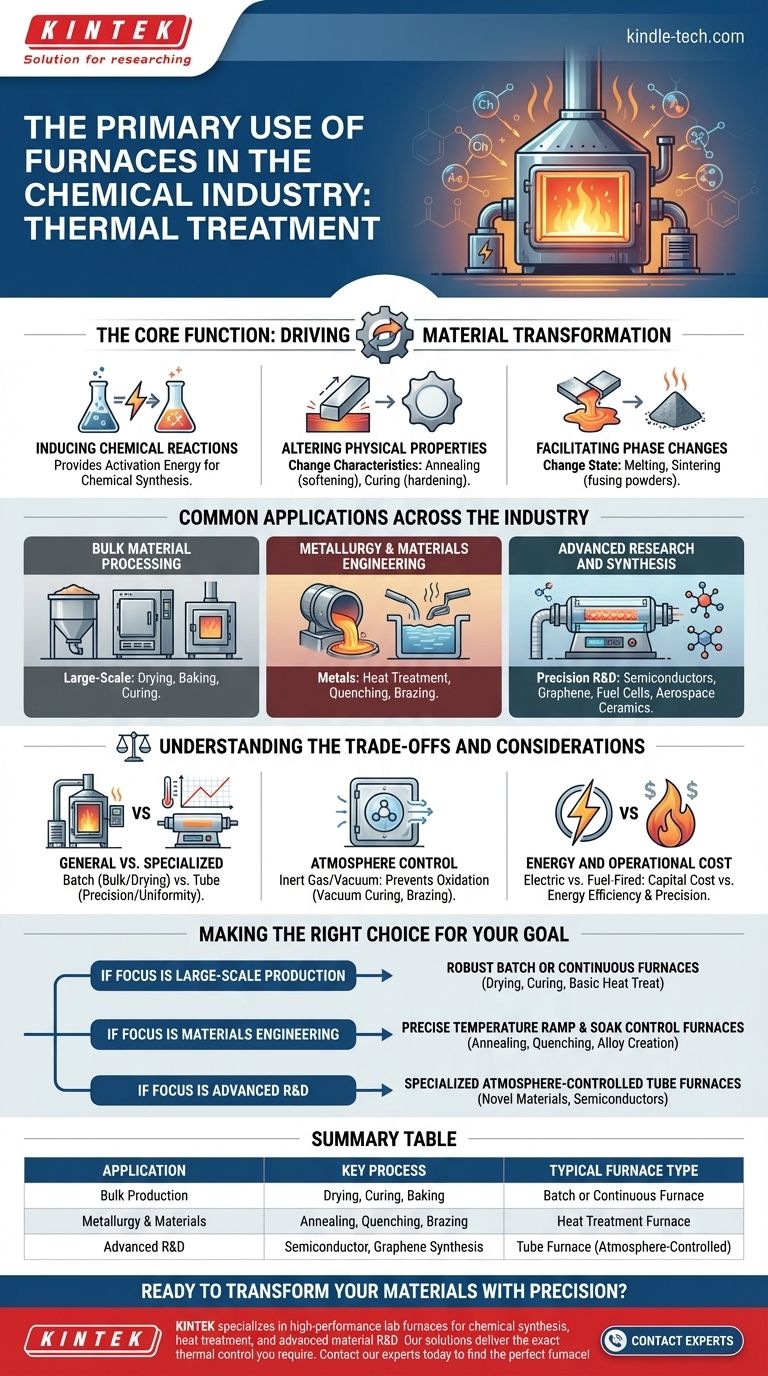
In the chemical industry, the primary use of a furnace is for thermal treatment. This is the process of applying high, controlled heat to raw materials, intermediate compounds, or finished products to deliberately induce specific and predictable physical and chemical changes.
The role of a furnace extends far beyond simple heating. It is a precise engineering tool used to fundamentally alter a material's structure and properties, enabling everything from basic chemical synthesis to the creation of advanced materials like semiconductors and aerospace alloys.

The Core Function: Driving Material Transformation
A furnace is the workhorse for any process that requires thermal energy to initiate a change. This application of heat is rarely crude; it is a carefully controlled process designed to achieve a specific outcome.
Inducing Chemical Reactions
Many chemical reactions require a significant input of energy, known as activation energy, to begin. A furnace provides this energy in a controlled environment, making it a fundamental tool for chemical synthesis.
Altering Physical Properties
Heat can radically change a material's physical characteristics without altering its chemical formula. Processes like annealing soften metals to make them more workable, while curing hardens polymers and ceramics to achieve their final strength.
Facilitating Phase Changes
The most intuitive use of a furnace is to change a material's state. This includes melting solid metals to create alloys or sintering fine powders until they fuse into a solid, dense object, a key process in ceramics and powder metallurgy.
Common Applications Across the Industry
The principle of thermal treatment is applied in a vast range of processes, from bulk production to highly specialized research and development.
Bulk Material Processing
In large-scale production, furnaces are used for foundational steps. This includes drying to remove moisture, baking to set coatings, or curing large batches of composite materials.
Metallurgy and Materials Engineering
Furnaces are essential for creating and refining metals. Key processes include heat treatment to improve strength and durability, quenching (rapid cooling) to lock in a specific crystalline structure, and brazing to join metallic components.
Advanced Research and Synthesis
Specialized furnaces, such as tube furnaces, provide the extreme precision needed for cutting-edge applications. They are critical for creating high-performance materials like semiconductors, solid oxide fuel cells, graphene, and advanced aerospace ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
Selecting a furnace is not a one-size-fits-all decision. The choice depends entirely on the process requirements, as different designs offer distinct advantages and limitations.
General Purpose vs. Specialized Furnaces
A large batch furnace is excellent for drying tons of raw material but lacks the precision for sensitive work. In contrast, a horizontal or rotary tube furnace provides exceptional temperature uniformity and control, which is non-negotiable for producing something like a semiconductor wafer.
Atmosphere Control
Many high-temperature reactions are ruined by exposure to oxygen. Advanced furnaces allow for precise atmosphere control, enabling processes like vacuum curing or brazing in an inert gas. This prevents unwanted oxidation and ensures material purity.
Energy and Operational Cost
Industrial furnaces are incredibly energy-intensive. The decision between an electric furnace and a fuel-fired one involves a complex trade-off between capital cost, energy prices, temperature precision, and environmental regulations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right thermal process is dictated by your end goal. The furnace is merely the tool to execute that process.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production: You will likely use robust batch or continuous furnaces for processes like drying, curing, or basic heat treatment.
- If your primary focus is materials engineering: You require furnaces with precise temperature ramp and soak controls for processes like annealing, quenching, and alloy creation.
- If your primary focus is advanced research and development: Specialized tube furnaces with integrated atmosphere control are essential for synthesizing novel materials like fuel cells, composites, or semiconductors.
Ultimately, the furnace is the primary instrument for transforming the potential of raw materials into the reality of valuable, functional products.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Typical Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Production | Drying, Curing, Baking | Batch or Continuous Furnace |
| Metallurgy & Materials | Annealing, Quenching, Brazing | Heat Treatment Furnace |
| Advanced R&D | Semiconductor, Graphene Synthesis | Tube Furnace (Atmosphere-Controlled) |
Ready to transform your materials with precision? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces for chemical synthesis, heat treatment, and advanced material R&D. Whether you need robust batch furnaces for production or atmosphere-controlled tube furnaces for sensitive research, our solutions deliver the exact thermal control you require. Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace for your chemical industry application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play in the homogenization of CuAlBe alloys? Optimize Shape Memory Performance
- What role does a laboratory oven play during the curing phase of NIPU coatings? Ensure Superior Cross-Linking
- What is the temperature for a furnace? It Depends on Your Material and Process Goal
- What are the three heat treatment processes? Hardening, Annealing, and Tempering Explained
- How does temperature monitoring affect nickel alloys in SPS? Ensure Precision for High-Performance Sintering
- What are the risks of sintering? Managing Dimensional Accuracy, Costs, and Compliance
- What are the properties of sintering materials? How Powder Transforms into High-Performance Parts
- What is the effect of vacuum on heat transfer? Mastering Thermal Control in Extreme Environments



















