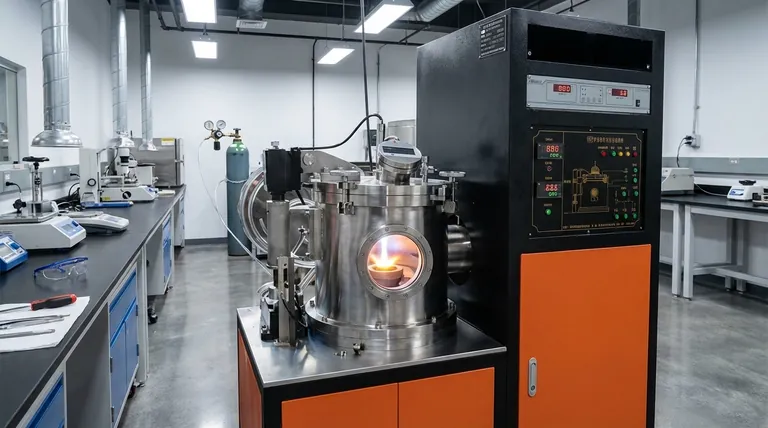
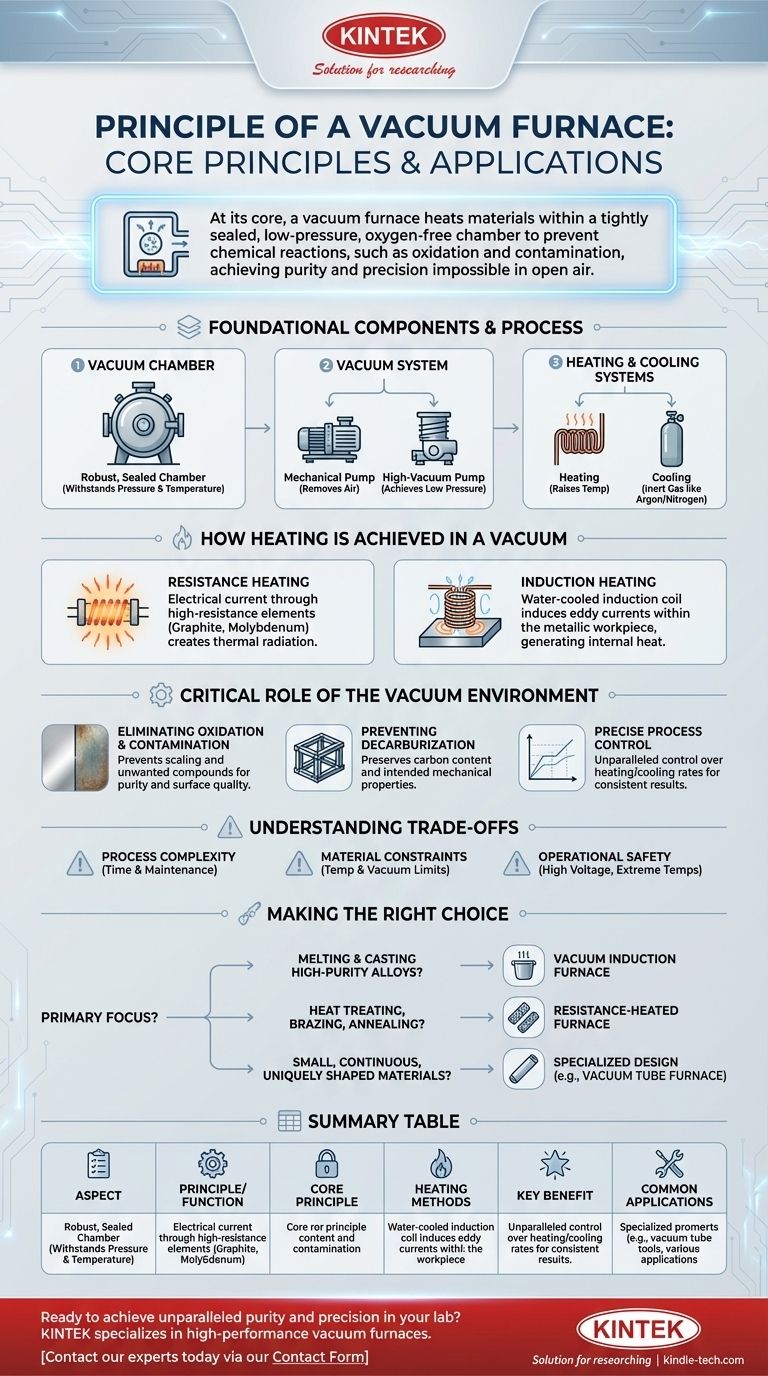
At its core, the principle of a vacuum furnace is to heat materials within a tightly sealed chamber from which the air and other gases have been removed. This low-pressure, oxygen-free environment prevents the chemical reactions, such as oxidation and contamination, that would normally occur when heating materials in a conventional atmosphere. The furnace integrates a vacuum system to create this environment and a heating system to achieve the desired temperature.
The fundamental purpose of a vacuum furnace is not just to heat a material, but to protect and control its integrity during the process. By removing the atmosphere, you eliminate unwanted variables, enabling a level of purity and precision that is impossible to achieve in open air.

The Foundational Components and Process
A vacuum furnace's operation relies on the seamless integration of three critical systems: the chamber, the vacuum pump system, and the heating system. The process follows a controlled sequence to ensure the integrity of the material being treated.
The Vacuum Chamber
The entire process takes place inside a robust, sealed chamber. This vessel is engineered from high-quality materials designed to withstand both the external atmospheric pressure and the extreme internal temperatures generated by the heating elements.
The Vacuum System
Achieving the necessary low-pressure environment is a multi-stage process. An initial mechanical vacuum pump (or "roughing pump") removes the bulk of the air. Once it reaches its limit, a secondary high-vacuum pump, such as a diffusion pump, takes over to achieve the much lower pressures required for high-purity work.
The Heating and Cooling Systems
The heating system raises the material to the target temperature. Once the heating cycle is complete, the cooling process must also be precisely controlled. Often, a high-purity inert gas like argon or nitrogen is introduced and circulated to cool the material quickly and uniformly without causing oxidation.
How Heating is Achieved in a Vacuum
Since there is no air to transfer heat via convection, vacuum furnaces rely on other methods. The specific heating technology used often defines the furnace's primary application.
Resistance Heating
This is a common method where electrical current is passed through high-resistance heating elements made of materials like graphite or molybdenum. These elements glow hot and transfer heat to the workpiece primarily through thermal radiation.
Induction Heating
A vacuum induction furnace uses a powerful, water-cooled induction coil. An alternating current in this coil generates a strong electromagnetic field, which in turn induces powerful electrical eddy currents directly within the metallic workpiece. The metal's own resistance to these currents generates intense, rapid, and clean heat from the inside out.
The Critical Role of the Vacuum Environment
The vacuum is not just a feature; it is the central enabler of the entire process. Its benefits are what justify the complexity of the equipment.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
This is the principal advantage. Without oxygen, nitrogen, and other reactive gases, metals and alloys can be heated to very high temperatures without tarnishing, scaling, or forming unwanted chemical compounds. This ensures the purity and surface quality of the final product.
Preventing Decarburization
For certain steels, heating in an atmosphere can cause carbon to leach from the surface, softening the material. A vacuum environment completely prevents this decarburization, preserving the alloy's intended mechanical properties.
Precise Process Control
The controlled environment allows for unparalleled precision. Heating rates, soak times, and cooling rates can be managed exactly as required by the material's specifications, leading to highly consistent and repeatable results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, vacuum furnaces introduce complexities that are important to acknowledge. Their benefits come with specific operational demands.
Process Complexity
Operating a vacuum furnace is not as simple as a conventional oven. The pump-down cycle takes time, and maintaining a proper vacuum seal requires diligent maintenance and clean components.
Material and Design Constraints
The type of furnace imposes limitations. For instance, a vacuum tube furnace, which heats a ceramic or quartz tube from the outside, is limited by the maximum temperature and vacuum level the tube material itself can withstand.
Operational Safety
These are powerful industrial machines. Operators must adhere to strict safety protocols, as they involve high voltages, extreme temperatures, and the physical risks associated with opening a hot furnace chamber.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The ideal vacuum furnace technology is dictated entirely by your end goal.
- If your primary focus is melting and casting high-purity alloys: A vacuum induction furnace is the superior choice, as its direct, contactless heating method ensures maximum cleanliness and chemical precision.
- If your primary focus is heat treating, brazing, or annealing components: A resistance-heated furnace provides excellent temperature uniformity and control, making it a reliable standard for treating finished or semi-finished parts.
- If your primary focus is processing small, continuous, or uniquely shaped materials: A specialized design like a vacuum tube furnace might be the most efficient solution for your specific application.
Ultimately, a vacuum furnace provides an unparalleled level of environmental control, transforming material processing from a simple act of heating into a precise science.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Principle/Function |
|---|---|
| Core Principle | Heating materials in a sealed, low-pressure chamber to prevent oxidation and contamination. |
| Heating Methods | Resistance Heating (thermal radiation) or Induction Heating (internal eddy currents). |
| Key Benefit | Enables high-purity processing, prevents decarburization, and ensures precise process control. |
| Common Applications | Heat treating, brazing, annealing, and melting high-purity alloys. |
Ready to achieve unparalleled purity and precision in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance vacuum furnaces for all your laboratory needs. Whether you require precise heat treatment, clean brazing, or high-purity melting, our equipment is designed to deliver consistent, contamination-free results.
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss how a KINTEK vacuum furnace can enhance your material processing capabilities and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















