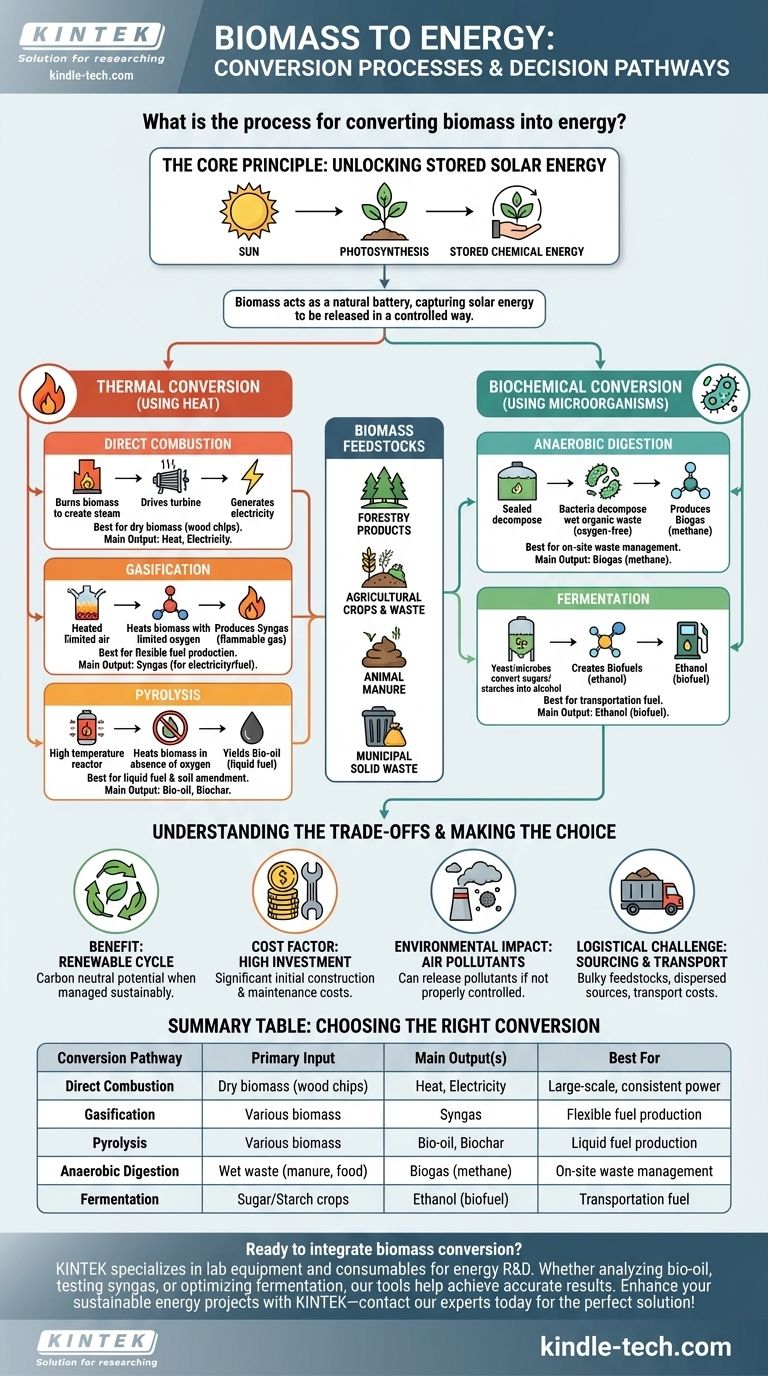
At its core, the process for converting biomass into energy involves unlocking the solar energy stored in organic matter. The most common method is direct combustion, where materials like wood or agricultural waste are burned to produce heat, which then creates steam to spin turbines and generate electricity. However, this is just one of several distinct pathways.
The central challenge isn't simply if biomass can be converted to energy, but how to choose the right conversion technology—thermal, chemical, or biochemical—that best matches the specific type of organic material and the desired energy output, whether it's heat, electricity, or liquid fuel.

The Core Principle: Unlocking Stored Solar Energy
From Photosynthesis to Fuel
All biomass, from trees to agricultural waste, is essentially a natural battery for solar energy. Plants capture the sun's energy through photosynthesis, converting carbon dioxide and water into complex carbohydrates.
The process of creating bioenergy is about releasing this stored chemical energy in a controlled way.
What Qualifies as Biomass?
Biomass is a broad term for any organic material derived from plants or animals. Common feedstocks include:
- Forestry products: Wood chips, sawdust, and dead trees.
- Agricultural crops and waste: Corn, sugarcane, straw, and crop residues.
- Animal manure and human sewage.
- Municipal solid waste: Paper, food scraps, and yard trimmings.
Key Conversion Pathways
While direct burning is the most straightforward method, several more sophisticated processes exist, each suited for different types of biomass and end-use applications. These are broadly categorized as thermal or biochemical.
Thermal Conversion (Using Heat)
This category involves using heat to break down and release the energy in biomass.
Direct Combustion is the oldest and most direct method. Biomass is simply burned in a furnace to produce high-pressure steam. This steam drives a turbine connected to a generator, producing electricity. It is best suited for dry biomass like wood chips.
Gasification is a process that heats biomass with a limited amount of oxygen. Instead of burning completely, the biomass converts into a flammable gas mixture called syngas (synthesis gas). This syngas can then be burned to generate electricity or further processed into liquid fuels.
Pyrolysis involves heating biomass at high temperatures in the complete absence of oxygen. This process yields a liquid fuel called bio-oil (or pyrolysis oil), which can be stored, transported, and later used to power boilers or engines. It also produces solid biochar and syngas as byproducts.
Biochemical Conversion (Using Microorganisms)
This category uses the metabolic action of microorganisms to break down biomass.
Anaerobic Digestion utilizes bacteria to decompose wet organic waste (like manure or food scraps) in an oxygen-free environment. This process produces biogas, a methane-rich gas that can be captured and burned to generate heat and electricity.
Fermentation is the process used to create biofuels like ethanol. It uses yeast and other microbes to convert the sugars found in crops like corn and sugarcane into alcohol. This ethanol is then blended with gasoline for use in vehicles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Biomass is a renewable resource, but its use is not without significant costs and environmental considerations. A clear-eyed view of these trade-offs is essential.
The Benefit: A Renewable Cycle
Unlike fossil fuels, which release ancient carbon into the atmosphere, biomass is part of the current biogenic carbon cycle. The CO2 released during combustion is theoretically offset by the CO2 absorbed by new plant growth, making it a potentially carbon-neutral resource when managed sustainably.
The Cost Factor: High Initial Investment
Biomass power plants require significant capital investment. The costs of construction, production, and ongoing maintenance are often higher than for comparable fossil fuel facilities, which can be a major barrier to adoption.
The Environmental Impact: More Than Just CO2
While potentially carbon-neutral, burning biomass can release other air pollutants, such as particulates and nitrogen oxides, which can impact air quality if not properly controlled. Furthermore, sourcing biomass unsustainably can lead to deforestation and habitat destruction.
The Logistical Challenge: Sourcing and Transport
Biomass feedstocks are often bulky, have a lower energy density than fossil fuels, and are geographically dispersed. The logistics of collecting, transporting, and storing this material represent a significant operational and financial challenge.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal biomass conversion strategy depends entirely on your available resources and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, consistent electricity generation: Direct combustion of low-moisture feedstocks like wood pellets or agricultural residue is the most mature and reliable technology.
- If your primary focus is managing wet organic waste from farms or municipalities: Anaerobic digestion is the ideal solution for converting waste into a valuable source of on-site energy.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid fuel for transportation: Fermentation of sugar or starch crops to produce ethanol is the established pathway, while gasification and pyrolysis offer future routes to advanced biofuels.
By understanding these distinct conversion pathways and their associated trade-offs, you can effectively evaluate how biomass can fit into a modern, sustainable energy strategy.
Summary Table:
| Conversion Pathway | Primary Input | Main Output(s) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Combustion | Dry biomass (wood chips) | Heat, Electricity | Large-scale, consistent power generation |
| Gasification | Various biomass | Syngas (for electricity/fuel) | Flexible fuel production |
| Pyrolysis | Various biomass | Bio-oil, Biochar | Liquid fuel and soil amendment production |
| Anaerobic Digestion | Wet waste (manure, food scraps) | Biogas (methane) | On-site waste management and energy |
| Fermentation | Sugar/Starch crops (corn, sugarcane) | Ethanol (biofuel) | Transportation fuel production |
Ready to integrate biomass conversion into your lab or facility? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for energy research and development. Whether you're analyzing bio-oil, testing syngas, or optimizing fermentation processes, our precise and reliable tools help you achieve accurate results. Enhance your sustainable energy projects with KINTEK—contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- High Performance Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Research and Development
People Also Ask
- Does pressure affect melting and boiling? Master Phase Changes with Pressure Control
- What is the pressure in a batch reactor? A Guide to Dynamic Control and Safety
- How is high pressure generated in an autoclave? Unlock the Science of Sterilization & Synthesis
- What are the analytical used in laboratory? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab's Needs
- Which solvent is normally used in IR spectroscopy? Optimize Your Sample Prep for Clearer Results



















