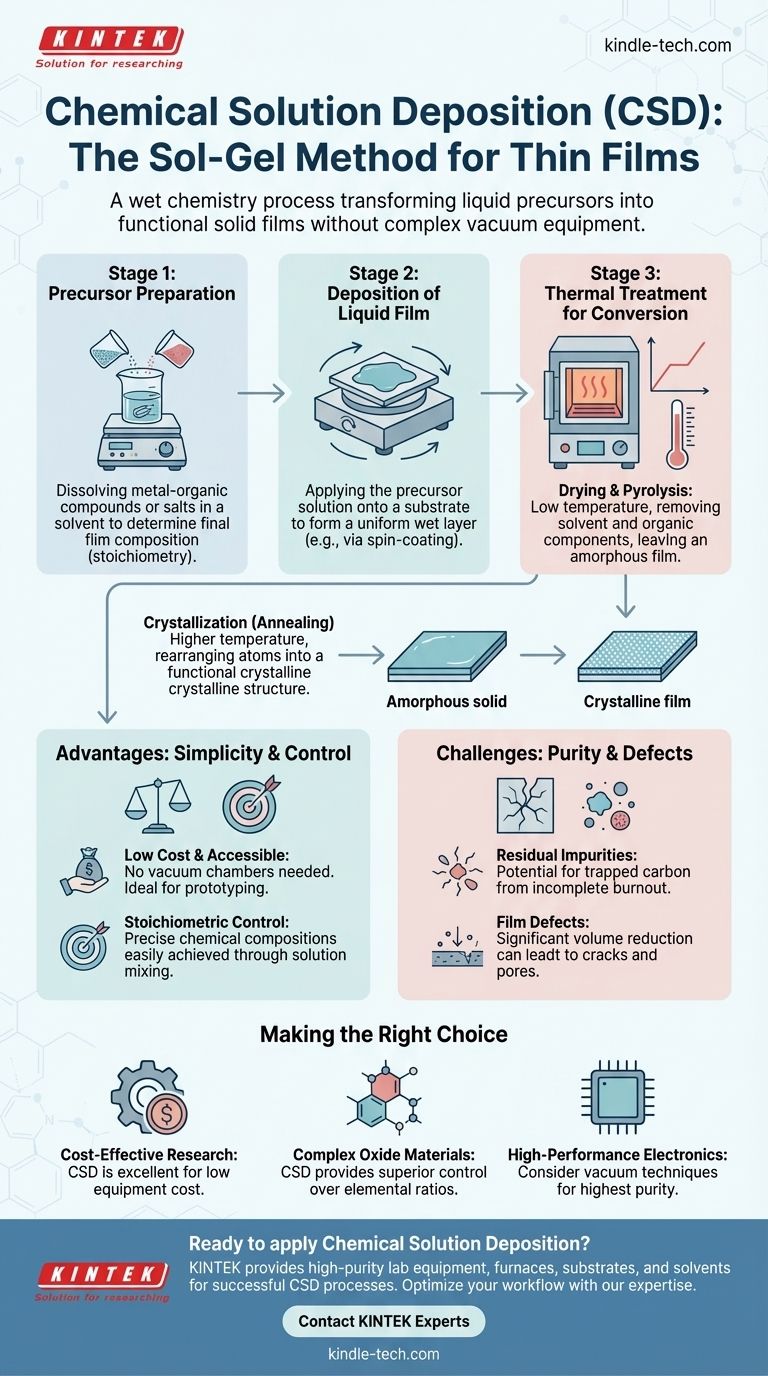
At its core, Chemical Solution Deposition (CSD) is a "wet chemistry" method for creating a thin, solid film on a surface. The process begins with a specially designed liquid precursor, which is applied to a substrate, dried to remove solvents, and then heat-treated to transform the liquid into a final, functional crystalline film. This technique is also commonly known as the sol-gel method.
The central principle of CSD is the controlled chemical transformation of a liquid solution into a solid thin film. It stands out for its simplicity and low cost, offering precise control over the final material's chemical composition without the need for complex vacuum equipment.
The Three Foundational Stages of CSD
The entire CSD process can be understood as a clear, three-stage progression. Each stage serves a distinct purpose in converting the initial chemicals into the final, high-quality film.
Stage 1: Precursor Preparation
A precursor solution is the foundation of the CSD process. This liquid contains all the necessary chemical elements for the final film.
Typically, this involves dissolving metal-organic compounds or salts into a specific organic solvent. The precise ratio of these components in the liquid directly dictates the final chemical makeup, or stoichiometry, of the solid film.
Stage 2: Deposition of the Liquid Film
Once the precursor is prepared, it is applied to a substrate to form a uniform wet layer.
While various methods exist, spin-coating is a very common technique. The substrate is spun at high speed, and the centrifugal force spreads the liquid precursor into an even, thin film across its surface.
Stage 3: Thermal Treatment for Conversion
This final stage uses heat to convert the liquid film into a solid, functional material. It involves two critical steps.
First is drying and pyrolysis. A low-temperature heating step removes the solvent and burns off, or pyrolyzes, the organic components of the precursor. This leaves behind an amorphous film of the desired elements.
Second is crystallization, often called annealing. The amorphous film is heated to a higher temperature, which provides the energy for the atoms to arrange themselves into an ordered, crystalline structure, yielding the final desired properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any technical process, CSD has distinct advantages and inherent limitations that make it suitable for some applications but not others.
Key Advantage: Simplicity and Cost
CSD is a relatively inexpensive and simple process. It does not require the expensive high-vacuum chambers and complex equipment associated with methods like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or sputtering.
This low barrier to entry makes it highly accessible for laboratory research and rapid prototyping.
Key Advantage: Stoichiometric Control
Because the process starts with a liquid, achieving precise chemical compositions is straightforward.
Scientists can create complex, multi-element materials simply by mixing the correct proportions of different chemical precursors in the initial solution. This offers a level of compositional flexibility that can be difficult to achieve with other methods.
Common Challenge: Purity and Defects
The primary trade-off for simplicity is the potential for residual impurities. If the organic components from the precursor or solvent do not fully burn off during pyrolysis, they can become trapped in the film as carbon impurities.
Furthermore, the significant volume reduction as the liquid film converts to a solid can sometimes lead to the formation of cracks or pores, which may affect the film's performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technique depends entirely on your project's specific priorities regarding cost, material complexity, and final film quality.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective research or rapid prototyping: CSD is an excellent choice due to its low equipment cost and simple setup.
- If your primary focus is creating complex oxide materials with a specific elemental ratio: CSD provides superior, straightforward control over the film's chemical stoichiometry.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible purity for high-performance electronics: You may need to consider vacuum-based techniques that avoid the potential for solvent and organic residue contamination.
Ultimately, Chemical Solution Deposition provides a powerful and accessible pathway from a simple chemical solution to a highly engineered solid film.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Process | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Precursor Preparation | Dissolving metal-organic compounds in a solvent. | Creates a liquid solution with the correct chemical ratio for the final film. |
| 2. Deposition | Applying the solution to a substrate (e.g., via spin-coating). | Forms a uniform, wet liquid film on the surface. |
| 3. Thermal Treatment | Heating the film to first dry/pyrolyze, then crystallize it. | Transforms the liquid into a solid, functional crystalline film. |
Ready to apply Chemical Solution Deposition in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing the high-purity lab equipment and consumables you need for successful CSD processes, from precise thermal treatment furnaces to reliable substrates and solvents. Our expertise ensures you achieve the stoichiometric control and film quality your research demands.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific thin film requirements and optimize your CSD workflow!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How does PACVD equipment improve DLC coatings? Unlock Low Friction and High Heat Resistance
- What machine is used to make lab-grown diamonds? Discover the HPHT & CVD Technologies
- What is the hot filament chemical vapour deposition of diamond? A Guide to Synthetic Diamond Coating
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- How are reactants introduced into the reaction chamber during a CVD process? Mastering Precursor Delivery Systems



















