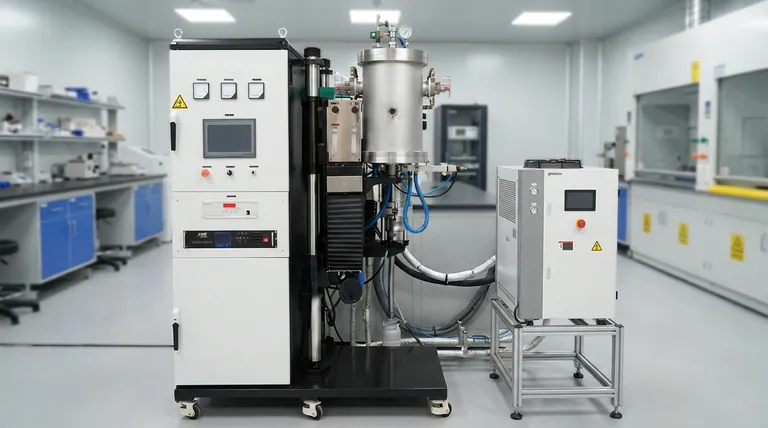
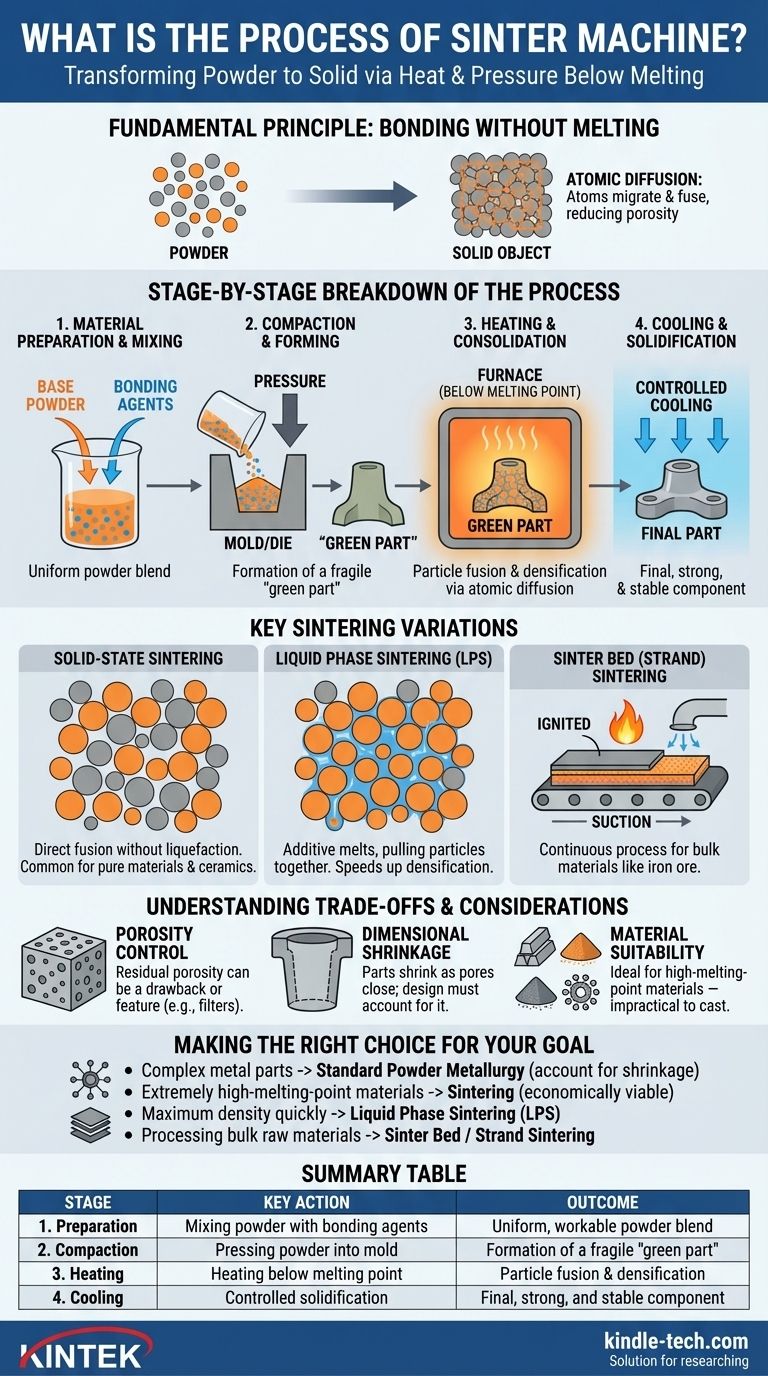
At its core, the sintering process is a method for transforming a powdery material into a solid, dense mass. This is achieved by first compacting the powder into a desired shape, often called a "green part," and then heating it in a furnace to a temperature just below its melting point. This precise application of heat and pressure causes the individual particles to fuse, reducing porosity and creating a strong, unified component without fully liquefying the material.
Sintering is a thermal process that bonds particles together to create a solid object. It's the key to manufacturing strong components from powders, especially with materials that have extremely high melting points, by using atomic diffusion to fuse them instead of fully melting them.

The Fundamental Principle: Bonding Without Melting
Sintering is a foundational process in fields like powder metallurgy and ceramics manufacturing. Its primary advantage is the ability to create solid objects from materials that are difficult or impossibly expensive to melt and cast.
What is Sintering?
Sintering, also known as frittage, compacts and forms a solid mass from a loose powder. It relies on high heat and, often, external pressure to force a material's atoms into tighter bonds.
The result is a harder, stronger, and more durable final product than the original powder. It is the go-to method for producing everything from pottery and ceramic components to complex metal parts.
The Atomic Mechanism: Diffusion
The science behind sintering is atomic diffusion. When heated, the atoms within the material's particles become more active. They begin to migrate across the boundaries where particles touch.
This migration fuses the particles together, gradually closing the gaps and pores between them. This process effectively welds the powder into a single, densified piece.
A Stage-by-Stage Breakdown of the Process
While there are many variations, the sintering process generally follows four distinct stages, moving from a loose powder to a finished, solid part.
Stage 1: Material Preparation and Mixing
The process begins with the base powder. This primary material is often mixed with other elements, such as alloys or bonding agents.
These bonding agents, which can include wax or polymers, act as a temporary glue to hold the powder together during the initial shaping phase.
Stage 2: Compaction and Forming
Next, the prepared powder is compacted into its desired shape. This is typically done by filling a mold or die and applying immense pressure.
This step forms a fragile, pre-sintered object known as a "green part." This part has the correct shape but lacks the strength and density of the final product.
Stage 3: Heating and Consolidation
The green part is carefully placed into a sintering furnace with a controlled atmosphere. The temperature is raised significantly, but critically, it remains below the primary material's melting point.
As the part heats up, two things happen. First, any temporary bonding agents are burned away or evaporated. Second, atomic diffusion begins, and the material's particles start to fuse and bond, dramatically increasing the part's density and strength.
Stage 4: Cooling and Solidification
Finally, the component is cooled in a controlled manner. This gradual cooling prevents thermal shock and the formation of internal stresses, ensuring the part solidifies into a stable, unified mass with its final intended properties.
Key Sintering Variations
Not all sintering is the same. The specific mechanism can be adapted based on the material and desired outcome, with two main approaches dominating the field.
Solid-State Sintering
This is the most basic form of sintering, where the bonding occurs entirely in a solid state. The primary material's particles fuse directly through atomic diffusion without any liquefaction. This is a common method for pure materials and ceramics.
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
To accelerate the process, an additive with a lower melting point can be mixed with the primary powder. During heating, this additive melts while the main powder remains solid.
The resulting liquid flows into the pores between the solid particles, pulling them together through capillary action and speeding up the densification process.
Sinter Bed (Strand) Sintering
For processing bulk materials like iron ore, a continuous process is used. Material is spread on a moving conveyor, or "sinter car," and passed under a furnace that ignites the top layer. Suction then pulls hot air down through the bed, causing the lower layers to sinter in succession.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that must be managed to achieve a successful outcome.
Porosity Control
Sintering is designed to reduce or eliminate the empty space (porosity) between particles. However, some residual porosity often remains. This can be a drawback if maximum strength is needed, or it can be a deliberate feature for creating products like self-lubricating bearings or filters.
Dimensional Shrinkage
As the particles fuse and the pores close, the entire component shrinks. This densification is a natural and expected part of the process.
Engineers must precisely calculate this shrinkage and design the initial mold and green part to be proportionally larger than the desired final dimensions.
Material Suitability
The process is ideal for materials that can be readily made into a powder, such as many metals and ceramics. It is especially valuable for materials with extremely high melting points, like tungsten and molybdenum, which are impractical to process via casting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your manufacturing objective will determine which aspect of the sintering process is most critical to your project.
- If your primary focus is creating complex metal parts: Standard powder metallurgy (compaction in a die followed by furnace heating) is the path, but you must precisely account for shrinkage in your design.
- If your primary focus is working with extremely high-melting-point materials: Sintering is one of the few economically viable methods, as it avoids the need to reach the material's full melting temperature.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density quickly: Consider Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS), where a lower-melting-point additive is used to accelerate the particle bonding process.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk raw materials like iron ore: Specialized, continuous methods like sinter bed or strand sintering are designed for high-throughput material preparation.
By understanding these core stages and principles, you can effectively leverage sintering to create robust components from a wide range of powdered materials.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Mixing base powder with bonding agents | Uniform, workable powder blend |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder into a mold under high pressure | Formation of a fragile "green part" |
| 3. Heating | Heating in a furnace below melting point | Particle fusion and densification via atomic diffusion |
| 4. Cooling | Controlled solidification | Final, strong, and stable component |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with precision sintering?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including furnaces essential for the sintering process. Whether you are working with complex metal parts, high-melting-point materials, or require maximum density, our solutions are designed to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve superior results in your powder metallurgy and materials science projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
People Also Ask
- What is sintering reaction? Transform Powders into Dense Solids Without Melting
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- How does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace facilitate the post-treatment of Zirconia coatings?



















