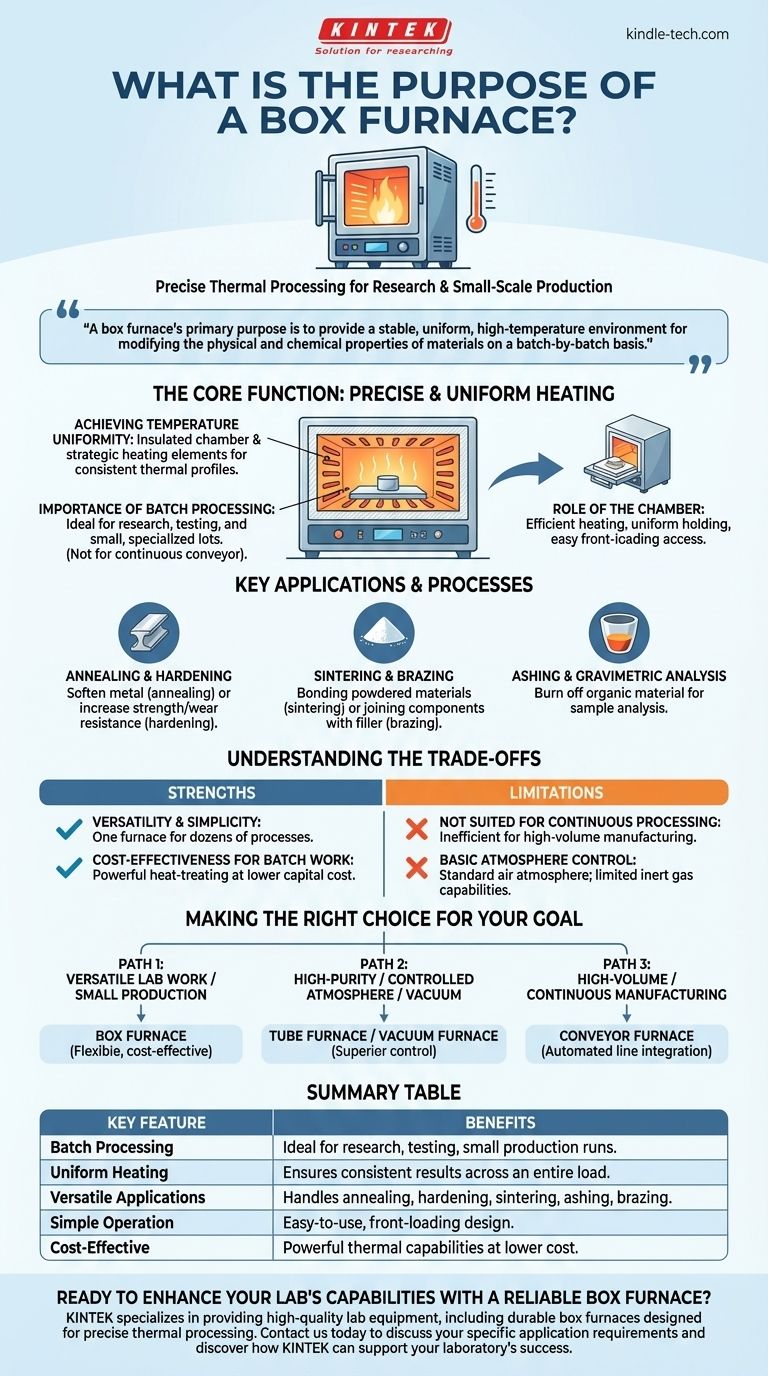
At its core, a box furnace is a high-temperature chamber designed for batch heat-treating materials in a precisely controlled thermal environment. It serves as a versatile workhorse in laboratories and small-scale production for processes like annealing, ashing, hardening, and sintering due to its simple, front-loading design and ability to achieve uniform temperatures.
A box furnace's primary purpose is to provide a stable, uniform, high-temperature environment for modifying the physical and chemical properties of materials on a batch-by-batch basis, making it an essential tool for research, development, and specialized production.

The Core Function: Precise and Uniform Heating
A box furnace, sometimes called a muffle furnace, operates on a straightforward yet powerful principle. Its value comes from creating an extremely predictable and repeatable heating environment for samples placed inside its chamber.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
The furnace's internal chamber is lined with high-grade thermal insulation. Heating elements are strategically placed around the chamber to distribute heat evenly, minimizing hot or cold spots. This ensures that an entire batch of parts experiences the same thermal profile.
The Importance of Batch Processing
Unlike continuous furnaces that process materials on a conveyor, a box furnace is designed for batch work. An operator loads a set of parts, runs a specific heating and cooling cycle (a "recipe"), and then unloads the finished batch. This method is ideal for research, testing new processes, or producing small, specialized lots.
The Role of the Chamber
The "box" is the heart of the unit. The chamber's enclosed, insulated design is critical for reaching high temperatures efficiently and holding them with minimal fluctuation. The front-loading door provides easy access for placing and retrieving materials.
Key Applications and Processes
The versatility of the box furnace makes it indispensable for a wide range of thermal processes across many industries.
Annealing and Hardening
Metals are heated to specific temperatures and then cooled at a controlled rate to alter their properties. Annealing softens metal to make it more workable, while hardening increases its strength and wear resistance.
Sintering and Brazing
Sintering involves heating powdered materials below their melting point until their particles bond together, forming a solid piece. Brazing uses a filler metal to join two separate components. The box furnace provides the stable, high-heat environment needed for both processes.
Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
In laboratory settings, box furnaces are used to burn off organic material from a sample to determine its inorganic content. This process, known as ashing, is a fundamental step in many types of chemical and materials analysis.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly versatile, a box furnace is not the right tool for every job. Understanding its strengths and limitations is key to using it effectively.
Strength: Versatility and Simplicity
The simple design and operation of a box furnace make it an excellent choice for general-purpose applications. A single furnace can be used for dozens of different processes simply by changing the temperature and time settings.
Strength: Cost-Effectiveness for Batch Work
For laboratories, small businesses, or prototyping, the box furnace offers powerful heat-treating capabilities at a relatively low capital cost compared to more specialized or continuous systems.
Limitation: Not Suited for Continuous Processing
The batch-based nature of a box furnace makes it inefficient for high-volume, assembly-line-style manufacturing, where a conveyor or tunnel furnace would be a better fit.
Limitation: Basic Atmosphere Control
A standard box furnace operates with an air atmosphere. While some models can be modified with ports for introducing inert gases, they cannot achieve the high-purity atmosphere or deep vacuum levels of a dedicated tube furnace or vacuum furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your objective.
- If your primary focus is versatile lab work or small, varied production runs: A box furnace is the ideal, cost-effective solution for its flexibility and ease of use.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing in a controlled atmosphere or vacuum: A dedicated tube furnace or vacuum furnace will provide the superior environmental control you require.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous manufacturing: A conveyor furnace is designed for integrating into an automated production line.
Ultimately, the box furnace is an essential tool designed for precise, repeatable thermal modification in a simple and accessible batch format.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Batch Processing | Ideal for research, testing, and small production runs. |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures consistent results across an entire load of parts. |
| Versatile Applications | Handles annealing, hardening, sintering, ashing, and brazing. |
| Simple Operation | Easy-to-use, front-loading design for straightforward operation. |
| Cost-Effective | Provides powerful thermal processing capabilities at a lower cost than specialized systems. |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a reliable box furnace?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including durable box furnaces designed for precise thermal processing. Whether your work involves annealing, sintering, ashing, or material testing, our solutions deliver the uniform heating and repeatable results you need.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing



















