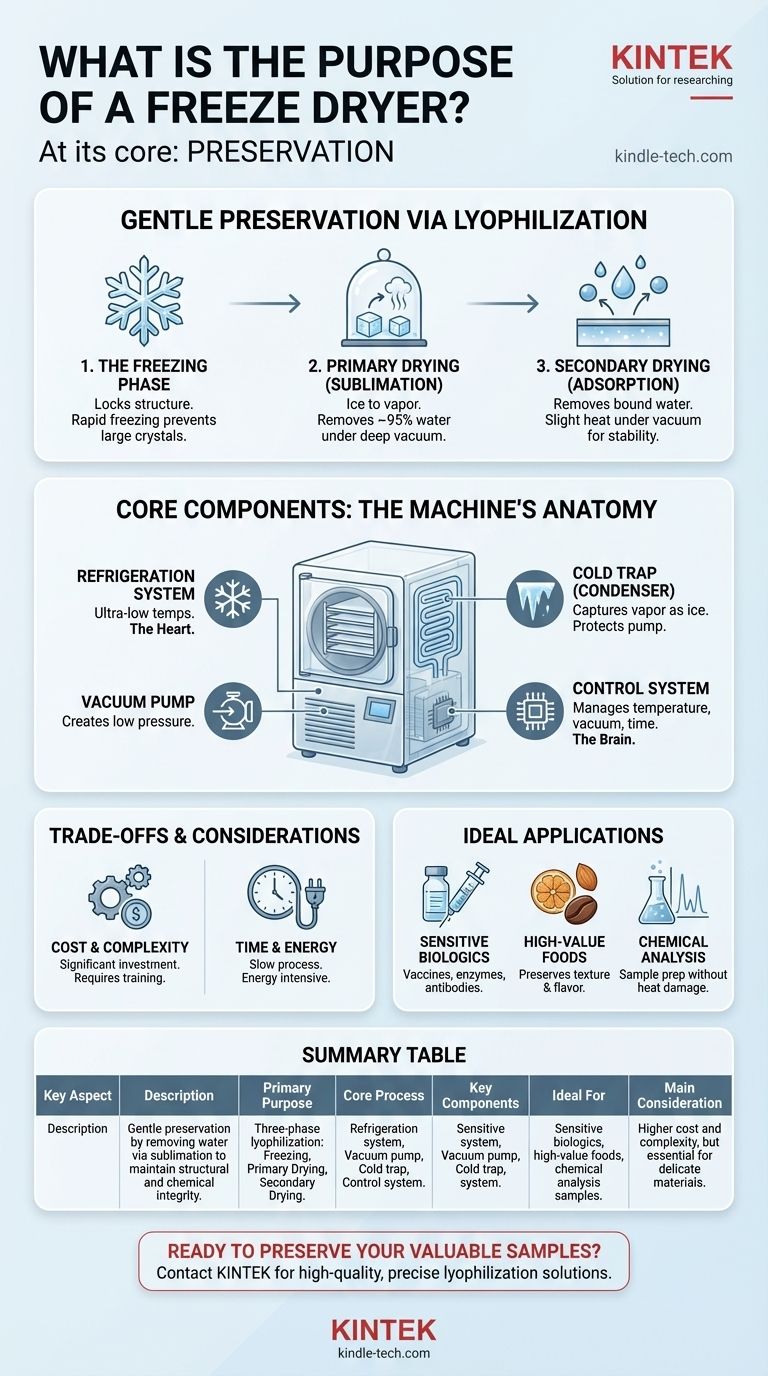
At its core, the purpose of a freeze dryer is preservation. It removes water from a perishable material to dramatically extend its shelf life and make it more convenient for transport. Unlike simple dehydration, this process—formally known as lyophilization—is specifically designed to maintain the material's original physical structure and chemical integrity, making it essential for sensitive items like vaccines, enzymes, and pharmaceuticals.
A freeze dryer is not just about removing water; it's about removing water gently. By freezing the material first and then turning the ice directly into vapor under a vacuum, it bypasses the damaging liquid phase, making it the gold standard for preserving delicate biological and chemical structures.

The Principle of Lyophilization: Gentle Dehydration
The unique value of a freeze dryer comes from its three-phase process, which is fundamentally different from using heat to evaporate water.
Step 1: The Freezing Phase
The material is first frozen, often rapidly. This step is critical because it locks the product's structure in place, converting the water into a stable, solid state. Proper freezing prevents the formation of large ice crystals that could damage the cellular or molecular structure of the sample.
Step 2: Primary Drying (Sublimation)
Once frozen, the material is placed under a deep vacuum. This low-pressure environment allows the ice to transition directly into water vapor without first melting into a liquid. This process, called sublimation, is the heart of freeze-drying and removes the vast majority (around 95%) of the water.
Step 3: Secondary Drying (Adsorption)
After the ice is gone, a small amount of water molecules remains bound to the material's surface. The temperature is then slightly increased (while still under vacuum) to break these bonds and remove the final traces of moisture. This ensures maximum long-term stability.
Deconstructing the Machine: Core Components
A laboratory freeze dryer is a sophisticated system where each part plays a crucial role in enabling the lyophilization process.
The Refrigeration System
Often called the "heart of the freeze dryer," this system is responsible for achieving the ultra-low temperatures needed for both the initial freezing of the sample and for operating the cold trap. It is a complex assembly including a compressor, refrigerant, and heat exchangers.
The Vacuum Pump
The vacuum pump creates the extremely low-pressure environment inside the drying chamber. This vacuum is what makes sublimation possible at low temperatures, preventing the sample from melting and being damaged by heat.
The Cold Trap (Condenser)
The cold trap is an extremely cold surface (colder than the sample) located between the drying chamber and the vacuum pump. Its sole purpose is to capture the water vapor that sublimates off the sample, turning it back into ice. This protects the vacuum pump from being damaged by moisture.
The Control System
This is the brain of the operation. The control system manages the temperature, vacuum levels, and timing of each of the three phases. For sensitive materials, a precise control system is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, freeze-drying is not a universal solution. It involves specific trade-offs that are important to understand.
Cost and Complexity
Freeze dryers are a significant investment and are more complex to operate than simple dehydrators or ovens. They require proper training to use effectively and safely.
Time and Energy Consumption
The lyophilization process is inherently slow, often taking hours or even days to complete. It is also an energy-intensive process due to the power required for the refrigeration and vacuum systems.
Matching the Machine to the Mission
Not all freeze dryers are created equal. The required cold trap temperature, vacuum level, and level of temperature control depend entirely on the material you are preserving. Choosing a unit with unnecessary features adds cost, while choosing one that is under-spec'd can ruin samples.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right preservation method depends entirely on the nature of your material and your ultimate goal.
- If your primary focus is the long-term stability of sensitive biologics (vaccines, enzymes, antibodies): You need a laboratory-grade freeze dryer with precise temperature controls and a deep vacuum to guarantee the preservation of biological activity.
- If your primary focus is preserving food texture and flavor for high-value products: The core principle of sublimation is essential for superior quality compared to heat dehydration, though a less complex commercial unit may suffice.
- If your primary focus is sample preparation for chemical analysis: Freeze-drying is superior to oven-drying, as it removes water without using heat that could alter or destroy the compounds you intend to measure.
By understanding this principle of gentle water removal, you can effectively leverage freeze-drying to protect the integrity and extend the life of your most valuable materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Gentle preservation by removing water via sublimation to maintain structural and chemical integrity. |
| Core Process | Three-phase lyophilization: Freezing, Primary Drying (sublimation), and Secondary Drying. |
| Key Components | Refrigeration system, Vacuum pump, Cold trap (condenser), and Control system. |
| Ideal For | Sensitive biologics (vaccines, enzymes), high-value foods, and chemical analysis samples. |
| Main Consideration | Higher cost and complexity than other drying methods, but essential for delicate materials. |
Ready to Preserve Your Most Valuable Samples?
Choosing the right freeze dryer is critical for protecting the integrity of sensitive materials like pharmaceuticals, biologics, and research samples. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including freeze dryers designed for precise temperature and vacuum control to ensure your materials are preserved gently and effectively.
Let our experts help you select the perfect lyophilization solution for your laboratory's specific needs. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our reliable equipment can enhance your preservation workflow.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 35L 50L 90L for Lab Use
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Small Lab Rubber Calendering Machine
- Single Punch Tablet Press Machine and Mass Production Rotary Tablet Punching Machine for TDP
People Also Ask
- How can budgetary constraints be managed when purchasing a lab freeze dryer? A Strategic Guide to Cost-Effective Investment
- What are the benefits of freeze-drying for sensitive samples? Preserve Delicate Materials with Unmatched Quality
- Why is manufacturer reputation important when selecting a lab freeze dryer? Ensure Long-Term Reliability for Your Samples
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- What are the key factors that influence the price of a lab freeze dryer? A Guide to Capacity, Performance & Features



















