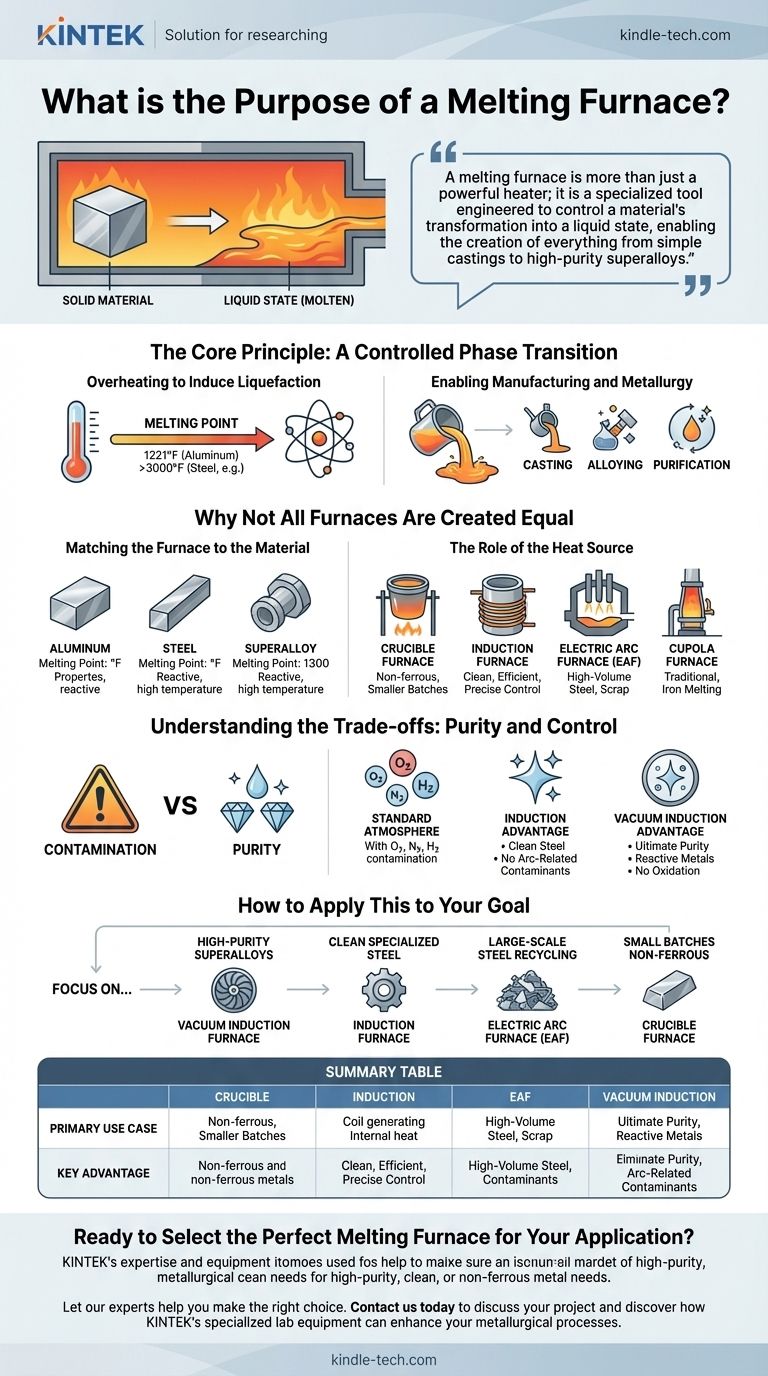
The fundamental purpose of a melting furnace is to apply enough heat to a solid material to change its phase from solid to liquid. By overcoming the material's melting point, the furnace breaks down its physical structure, making it possible to cast, alloy, or refine it for a vast range of industrial and manufacturing applications.
A melting furnace is more than just a powerful heater; it is a specialized tool engineered to control a material's transformation into a liquid state, enabling the creation of everything from simple castings to high-purity superalloys.
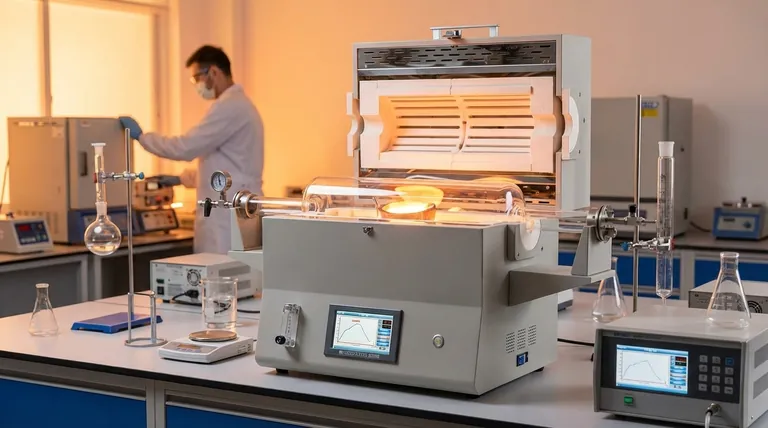

The Core Principle: A Controlled Phase Transition
Overheating to Induce Liquefaction
A melting furnace operates on the principle of phase transition. Every crystalline solid has a specific melting point—the temperature at which its ordered atomic structure breaks down, and it becomes a liquid. The furnace's job is to deliver and maintain energy, typically heat, to exceed this threshold.
Enabling Manufacturing and Metallurgy
Once a material is in its liquid state, it becomes workable. This molten state is the critical starting point for numerous processes, including casting into molds, mixing with other elements to create alloys, or undergoing purification processes to remove unwanted contaminants.
Why Not All Furnaces Are Created Equal
Matching the Furnace to the Material
Materials have vastly different melting points and chemical properties. A furnace designed for aluminum, which melts at 1,221°F (660°3°C), is fundamentally different from one needed for steel or superalloys, which require much higher temperatures and often a controlled atmosphere.
The Role of the Heat Source
The method used to generate heat defines the furnace type and its ideal application. The four major types each serve a different purpose.
- Crucible Furnaces: These are some of the simplest types, where the material is held in a container (the crucible) that is heated from the outside. They are common for smaller batches and non-ferrous metals.
- Induction Furnaces: These use electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal itself. This process is clean, efficient, and offers excellent temperature control.
- Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): These use a high-power electric arc between electrodes to melt the material. EAFs are workhorses for high-volume steel production, especially from scrap metal.
- Cupola Furnaces: A traditional, vertically oriented furnace used for decades, primarily for melting iron.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Purity and Control
The Problem of Contamination
The high-temperature melting process can easily introduce impurities. The atmosphere inside the furnace (oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen) can react with the molten metal, and even the heat source itself can be a source of contamination.
The Induction Advantage for Clean Melting
An induction furnace offers a significant advantage in producing cleaner steel. Because it does not use an electric arc, it avoids introducing excess carbon and atmospheric gases into the melt, resulting in a purer final product.
The Vacuum Advantage for Ultimate Purity
For highly reactive and performance-critical metals like superalloys, nickel, and cobalt, even a standard atmosphere is too reactive. A vacuum induction melting furnace performs the melting under a vacuum to remove these reactive gases, preventing oxidation and ensuring the highest possible purity and alloy integrity.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Choosing the right furnace technology depends entirely on the material and the desired quality of the end product.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity superalloys or reactive metals: A vacuum induction furnace is required to prevent contamination from atmospheric gases.
- If your primary focus is creating specialized steel with low carbon and gas content: A standard induction furnace provides the necessary control for clean melting without arc-related contaminants.
- If your primary focus is large-scale, high-volume steel recycling: An electric arc furnace delivers the raw power and capacity needed for the job.
- If your primary focus is smaller batches of non-ferrous metals: A crucible furnace often provides the most practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is a critical engineering decision that directly determines the quality, purity, and performance properties of the final material.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use Case | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Crucible Furnace | Small batches of non-ferrous metals | Cost-effective, simple operation |
| Induction Furnace | Clean steel, specialized alloys | Excellent temperature control, minimal contamination |
| Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | High-volume steel recycling | High power, large capacity |
| Vacuum Induction Furnace | Superalloys, reactive metals (Ni, Co) | Ultimate purity, prevents oxidation |
Ready to Select the Perfect Melting Furnace for Your Application?
The right furnace technology is critical to achieving the material purity, quality, and performance you require. Whether you are developing high-purity superalloys, producing clean steel, or melting non-ferrous metals, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Let our experts help you make the right choice. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK's specialized lab equipment can enhance your metallurgical processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















