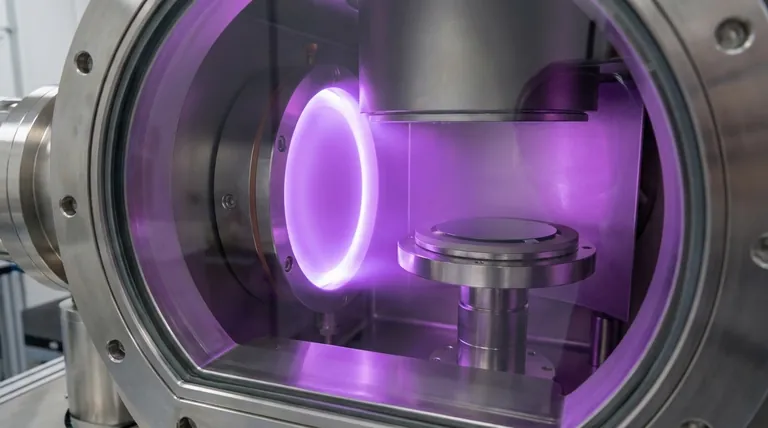
In short, argon is the indispensable process gas used to create a plasma for bombarding a material target. These energized argon ions act like an atomic-scale sandblaster, physically knocking atoms off the target material, which then deposit onto a substrate to form a high-purity thin film.
The core function of argon in sputtering is to serve as a stable, non-reactive projectile. It is chosen because it can be easily ionized to create a plasma, has an ideal atomic weight for efficiently ejecting most target materials, and is cost-effective.
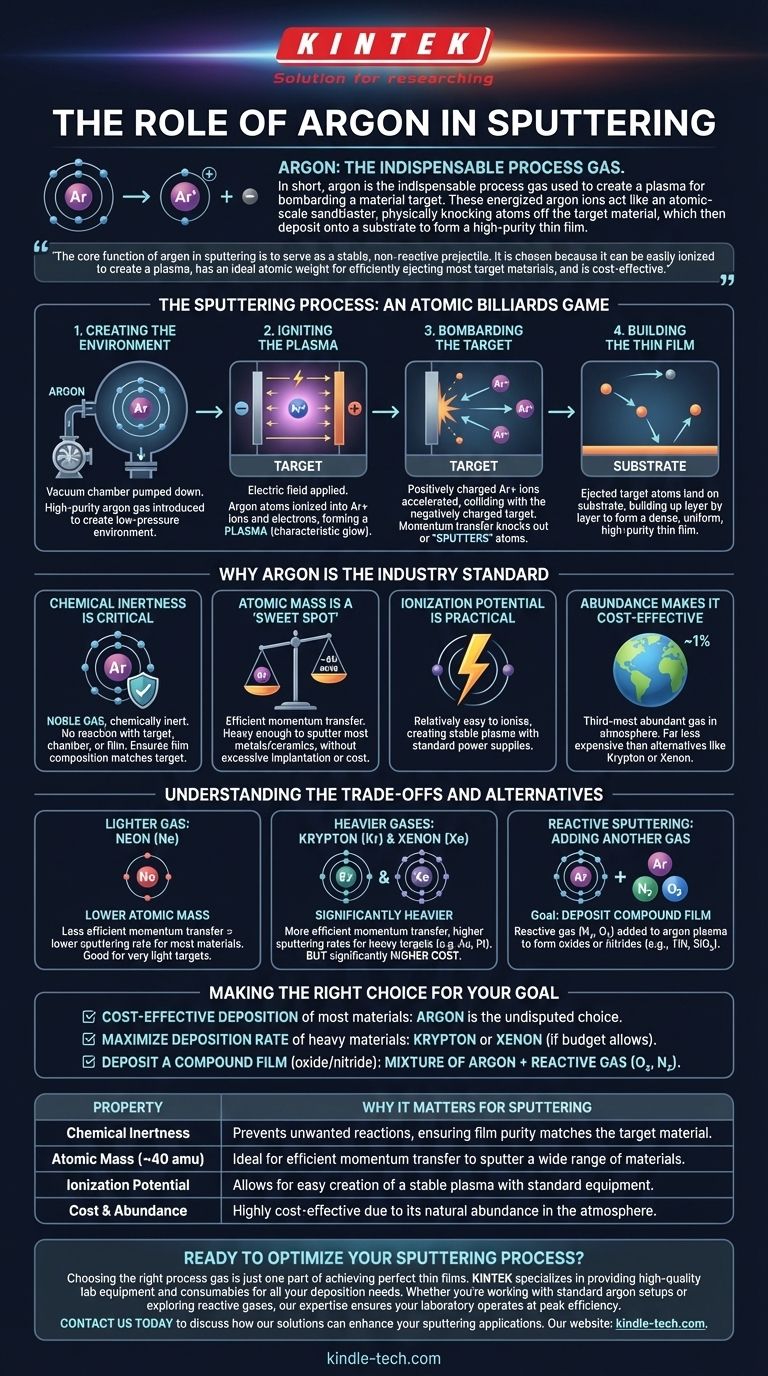
The Sputtering Process: An Atomic Billiards Game
To understand argon's role, you must first understand the fundamental goal of sputtering: to move atoms from a source (the target) to a destination (the substrate) in a highly controlled vacuum environment.
Step 1: Creating the Environment
The process begins in a vacuum chamber, which is pumped down to remove contaminants like oxygen and water vapor.
A small, precisely controlled amount of high-purity argon gas is then introduced into the chamber, creating a low-pressure environment.
Step 2: Igniting the Plasma
A strong electric field is applied within the chamber, typically between the target (which acts as the cathode) and the chamber walls or a dedicated anode.
This electrical energy strips electrons from the argon atoms, creating a mixture of positively charged argon ions (Ar+) and free electrons. This ionized gas is known as a plasma, often visible as a characteristic glow.
Step 3: Bombarding the Target
The positively charged argon ions are powerfully accelerated by the electric field, causing them to slam into the negatively charged target material.
This collision is purely physical. The momentum transfer from the heavy argon ion is sufficient to knock out, or "sputter," atoms from the target's surface.
Step 4: Building the Thin Film
The ejected target atoms travel through the vacuum chamber and land on the substrate (e.g., a silicon wafer, glass, or metal part), which is strategically placed to intercept them.
Over time, these atoms build up layer by layer, forming a dense, uniform, and high-purity thin film.
Why Argon is the Industry Standard
While other noble gases can be used, argon provides the best balance of performance, cost, and practicality for the vast majority of sputtering applications.
Its Chemical Inertness is Critical
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically inert. It will not react with the target material, the chamber components, or the growing film.
This property is non-negotiable for ensuring the deposited film has the exact same chemical composition as the target material.
Its Atomic Mass is a "Sweet Spot"
The efficiency of the sputtering process depends heavily on the momentum transfer between the ion and the target atom. Argon's atomic mass (≈ 40 amu) is a perfect middle-ground.
It is heavy enough to effectively sputter most metals and ceramics, but not so heavy that it causes excessive implantation into the substrate or becomes prohibitively expensive.
Its Ionization Potential is Practical
Argon is relatively easy to ionize, allowing for the creation and maintenance of a stable plasma using standard, reliable power supplies.
Its Abundance Makes it Cost-Effective
Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere (≈ 1%). This natural abundance makes it far less expensive than other suitable noble gases like Krypton (Kr) or Xenon (Xe).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While argon is the workhorse, certain specialized applications call for different gases. Understanding why reveals the underlying physics.
Lighter Gas: Neon (Ne)
Neon has a lower atomic mass than argon. This results in less efficient momentum transfer and therefore a lower sputtering rate for most materials. However, it can be useful for sputtering very light target elements where argon might be too destructive.
Heavier Gases: Krypton (Kr) & Xenon (Xe)
Krypton and Xenon are significantly heavier than argon. This allows for much more efficient momentum transfer, leading to higher sputtering rates, especially for heavy target materials like gold or platinum. The primary drawback is their significantly higher cost.
Reactive Sputtering: Adding Another Gas
Sometimes, the goal is to deposit a compound film, not a pure one. In reactive sputtering, a gas like nitrogen or oxygen is added to the argon.
The argon plasma still does the sputtering, but the reactive gas combines with the sputtered target atoms mid-flight or on the substrate to form compounds like titanium nitride (TiN) or silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice of process gas is dictated entirely by the desired outcome and budget.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective deposition of most metals and materials: Argon is the undisputed and correct choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing the deposition rate of heavy materials like gold or platinum: Krypton or Xenon are superior options, provided the budget allows for their high cost.
- If your primary focus is depositing a compound film like an oxide or nitride: A mixture of argon and a reactive gas (O₂ or N₂) is the required approach.
Ultimately, argon's unique combination of chemical stability, ideal mass, and low cost makes it the foundational element of modern physical vapor deposition.
Summary Table:
| Property | Why It Matters for Sputtering |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents unwanted reactions, ensuring film purity matches the target material. |
| Atomic Mass (~40 amu) | Ideal for efficient momentum transfer to sputter a wide range of materials. |
| Ionization Potential | Allows for easy creation of a stable plasma with standard equipment. |
| Cost & Abundance | Highly cost-effective due to its natural abundance in the atmosphere. |
Ready to Optimize Your Sputtering Process?
Choosing the right process gas is just one part of achieving perfect thin films. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your deposition needs. Whether you're working with standard argon setups or exploring reactive gases, our expertise ensures your laboratory operates at peak efficiency.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your sputtering applications and deliver superior results for your research or production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between CVD and PECVD? Choose the Right Thin-Film Deposition Method
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is PECVD used for? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Performance Thin Films
- What is PECVD silicon deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Films
- What is plasma in CVD process? Lowering Deposition Temperatures for Heat-Sensitive Materials



















