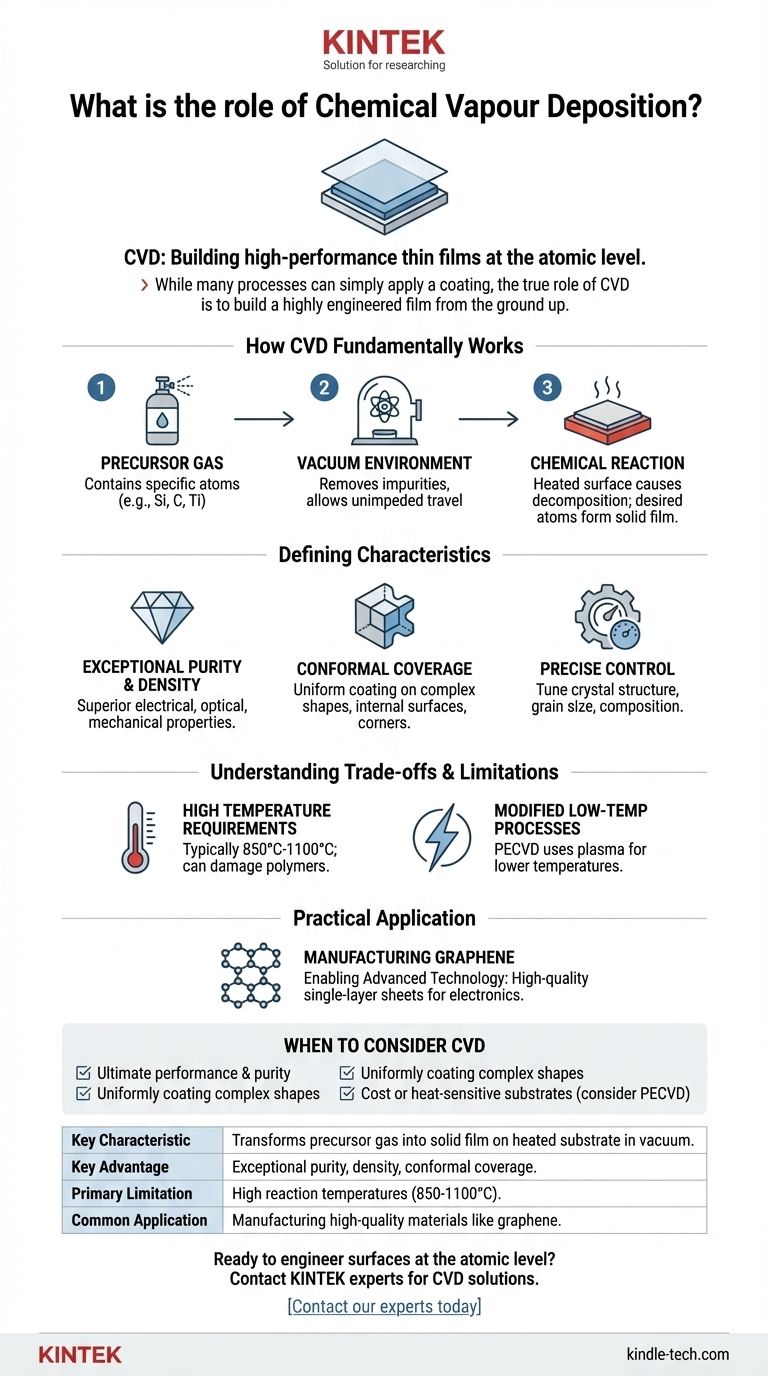
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a sophisticated manufacturing process for creating high-performance, ultra-thin solid films on a surface. It works by introducing a precursor gas into a vacuum chamber, where it reacts and decomposes upon heating, depositing a precisely engineered coating, atom by atom, onto a target material, known as a substrate.
While many processes can simply apply a coating, the true role of CVD is to build a highly engineered film from the ground up. It enables the creation of surfaces with precisely controlled purity, structure, and performance that are often impossible to achieve with simpler methods.

How CVD Fundamentally Works
The CVD process can be understood as a three-step sequence that transforms a gas into a high-performance solid coating.
The Precursor Gas
The process begins with a carefully selected chemical precursor in a gaseous state. This gas contains the specific atoms (like silicon, carbon, or titanium) that will form the final coating.
The Vacuum Environment
This precursor gas is injected into a chamber under vacuum. The vacuum is critical as it removes impurities and allows the precursor molecules to travel unimpeded to the substrate surface.
The Chemical Reaction
The substrate is heated to a specific reaction temperature. This thermal energy causes the precursor gas to decompose or react on the hot surface, shedding its unwanted components and leaving behind only the desired atoms, which then bond to the substrate to form a dense, solid film.
The Defining Characteristics of a CVD Coating
The value of CVD lies in the unique and superior qualities of the films it produces. These characteristics are what distinguish it from other coating techniques.
Exceptional Purity and Density
Because the process occurs in a controlled vacuum and is built from a purified gas source, the resulting films are exceptionally pure and dense. This leads to superior electrical, optical, and mechanical properties.
Conformal Coverage (Wrap-Around)
Unlike line-of-sight processes like spraying, the precursor gas in CVD envelops the entire substrate. This results in a perfectly uniform, or "conformal," coating that covers even the most complex shapes, internal surfaces, and sharp corners without thinning.
Precise Control Over Material Properties
By adjusting parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas composition, engineers have fine-grained control over the final product. This allows for the precise tuning of the film's crystal structure, grain size, and chemical composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No process is universally ideal. Objectivity requires acknowledging where CVD may not be the best fit.
High Temperature Requirements
The most significant limitation of traditional CVD is its high reaction temperature, typically between 850°C and 1100°C. Many potential substrate materials, such as polymers or certain metal alloys, cannot withstand this heat without being damaged.
Modified Low-Temperature Processes
To overcome this, specialized versions like plasma-assisted CVD (PECVD) have been developed. These techniques use plasma to energize the precursor gas, allowing the deposition reaction to occur at much lower temperatures.
Process and Material Constraints
The CVD process is dependent on the availability of a suitable volatile precursor chemical for the desired coating material. Additionally, the equipment and process control are inherently more complex than simpler coating methods.
A Practical Application: Manufacturing Graphene
The production of high-quality graphene for advanced electronics is a perfect example of CVD's role.
The Need for Atomic Perfection
For applications in high-performance sensors and electronics, graphene sheets must have a low defect count and excellent uniformity. A single flaw at the atomic level can compromise the performance of an entire device.
Enabling Advanced Technology
CVD is the leading method for this task because it can grow large, high-quality, single-layer sheets of graphene. This capability is essential for manufacturing the next generation of flexible displays, ultra-fast transistors, and sensitive biosensors.
When to Consider Chemical Vapor Deposition
Choosing the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your specific technical and material goals.
- If your primary focus is ultimate performance and purity: CVD is the premier choice for creating films with superior electrical, mechanical, or optical properties.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating a complex shape: The exceptional conformal nature of CVD makes it ideal for components with intricate geometries that other methods cannot cover evenly.
- If your primary focus is cost or you are using a heat-sensitive substrate: You should carefully evaluate if the high temperatures of traditional CVD are acceptable or if a lower-temperature variant like PECVD is required.
Ultimately, the role of Chemical Vapor Deposition is not just to coat a surface, but to fundamentally transform its performance at the atomic level.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Process | Transforms precursor gas into a solid film on a heated substrate in a vacuum chamber. |
| Key Advantage | Exceptional purity, density, and uniform "conformal" coverage on complex shapes. |
| Primary Limitation | High reaction temperatures (850-1100°C), which can damage some substrates. |
| Common Application | Manufacturing high-quality materials like graphene for advanced electronics and sensors. |
Ready to engineer surfaces at the atomic level?
Chemical Vapor Deposition is key to creating high-performance coatings with superior purity and uniformity. If your project demands exceptional material properties for electronics, optics, or complex components, KINTEK's expertise in lab equipment and consumables can help you achieve it.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our CVD solutions can transform your materials' performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- How do PECVD systems improve DLC coatings on implants? Superior Durability and Biocompatibility Explained



















