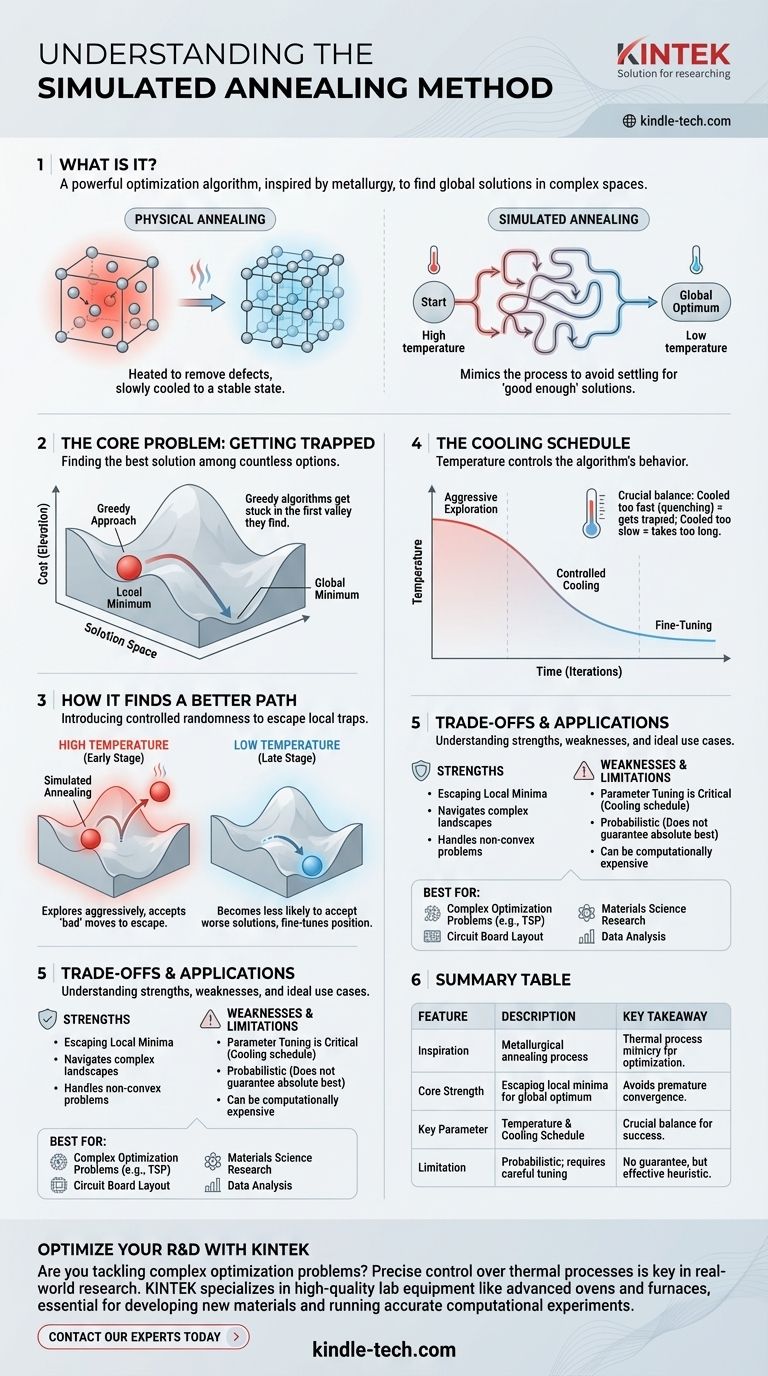
In short, simulated annealing is a powerful optimization algorithm used to find a good (and often global) solution in a vast and complex search space. It is directly inspired by the metallurgical process of annealing, where a material is heated and then slowly cooled to remove defects and reach a stable, low-energy crystalline state. The algorithm mimics this physical process to solve abstract computational problems.
At its core, simulated annealing avoids the common trap of settling for a "good enough" solution by mimicking the physical process of annealing metal. It starts by exploring a wide range of possibilities (high temperature) and gradually narrows its focus to a high-quality, stable solution (low temperature).
The Core Problem: Getting Trapped
To understand simulated annealing, you must first understand the problem it solves: finding the best possible solution among countless options, a task known as optimization.
The Landscape of Solutions
Imagine every possible solution to your problem is a point on a vast, hilly landscape. The elevation of each point represents its "cost"—the lower the elevation, the better the solution. Your goal is to find the lowest point on the entire map, the global minimum.
The "Greedy" Approach and Its Flaw
A simple algorithm, often called hill-climbing, would start at a random point and always move downhill. This is a "greedy" approach because it only accepts moves that yield immediate improvement.
The problem is that this method will get stuck in the first valley it finds—a local minimum. It has no way of knowing if a much deeper valley, the global minimum, exists just over the next hill.
How Simulated Annealing Finds a Better Path
Simulated annealing overcomes this limitation by introducing a controlled element of randomness that allows it to escape these local traps.
The Inspiration: Physical Annealing
In metallurgy, heating a metal gives its atoms enough energy to move around freely, breaking out of suboptimal, defective structures. As the metal is cooled slowly, the atoms have time to settle into a highly ordered, strong crystal lattice—a state of minimum energy.
The Algorithm: Temperature as a Control Knob
Simulated annealing adopts this concept by introducing a temperature parameter. This isn't a physical temperature, but a variable that controls the algorithm's behavior.
The algorithm starts with a high temperature. In this state, it explores the solution landscape aggressively, much like the energetic atoms in hot metal. It has a high probability of accepting moves that are worse than its current position. This is the key: making a "bad" move is what allows it to climb out of a local minimum.
The Cooling Schedule
As the algorithm runs, the temperature is gradually lowered according to a cooling schedule. As the temperature decreases, the algorithm becomes less and less likely to accept a worse solution.
By the end, at a very low temperature, the algorithm behaves like the simple hill-climbing method, only accepting improvements and fine-tuning its position in what is hopefully the global minimum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Like any powerful tool, simulated annealing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for using it effectively.
Strength: Escaping Local Minima
Its primary advantage is its ability to navigate complex, non-convex landscapes with many local minima. For problems where greedy algorithms consistently fail, simulated annealing is an excellent choice.
Weakness: Parameter Tuning is Critical
The algorithm's performance is highly sensitive to the cooling schedule. If cooled too quickly, it can get trapped in a local minimum anyway ("quenching"). If cooled too slowly, it can take an impractical amount of time to find a solution. Finding the right schedule often requires experimentation.
Limitation: It's a Probabilistic Method
Simulated annealing does not guarantee that it will find the absolute best solution (the global minimum). It is a heuristic, meaning it's designed to find a very good solution in a reasonable amount of time. There is always a statistical chance it settles in a suboptimal state.
Making the Right Choice for Your Problem
Use this guidance to decide if simulated annealing is the correct approach for your optimization task.
- If your primary focus is solving a complex problem with many traps (local minima): Simulated annealing is one of the best tools for the job, especially for classic problems like the Traveling Salesperson Problem or circuit board layout.
- If your primary focus is finding a provably optimal solution with maximum speed: You should first check if your problem is simple enough (e.g., convex) to be solved by a faster, deterministic algorithm like linear programming or a standard greedy approach.
Ultimately, simulated annealing provides a robust framework for navigating vast and difficult search spaces to find high-quality solutions where simpler methods fail.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Inspiration | Metallurgical annealing process (heating & slow cooling) |
| Core Strength | Escaping local minima to find a global optimum |
| Key Parameter | Temperature & Cooling Schedule |
| Best For | Complex optimization problems with many local traps |
| Limitation | Probabilistic; requires careful parameter tuning |
Optimize Your Research and Development with KINTEK
Are you tackling complex optimization problems in materials science, chemical engineering, or data analysis? The principles of simulated annealing are inspired by real-world thermal processes, and having precise control over those processes in your lab is crucial.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including advanced ovens and furnaces that provide the uniform heating and controlled cooling essential for research and development. Whether you're developing new materials or running computational experiments, reliable equipment is the foundation of accurate results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect laboratory solution to enhance your optimization workflows and achieve breakthrough results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory shaker in PHA research? Accelerate Extremophile Screening & Bioplastic Development
- What is the function of a laboratory orbital shaker during the Fenton reaction? Optimize Leather Wastewater Treatment
- What critical reaction conditions does a shaking incubator provide? Optimize Cassava Cellulose Enzymatic Hydrolysis
- What role does a laboratory orbital shaker play in silane coupling? Enhance Self-Assembled Monolayer Uniformity
- Why is a high-precision orbital shaker required for chitin adsorption? Achieve Rapid Equilibrium & Precise Data
