In aluminum brazing, the critical process occurs in a precise temperature window between 577°C and 600°C (1071°F and 1112°F). At this temperature, the filler metal melts and flows into the joint, while the base metal remains solid. This entire process must happen in a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere to be successful.
The key to understanding brazing temperature is to see it not as a single number, but as the peak of a carefully managed thermal cycle. Each phase of heating and cooling serves a distinct purpose, and success depends on controlling the interplay between temperature, time, and atmosphere.
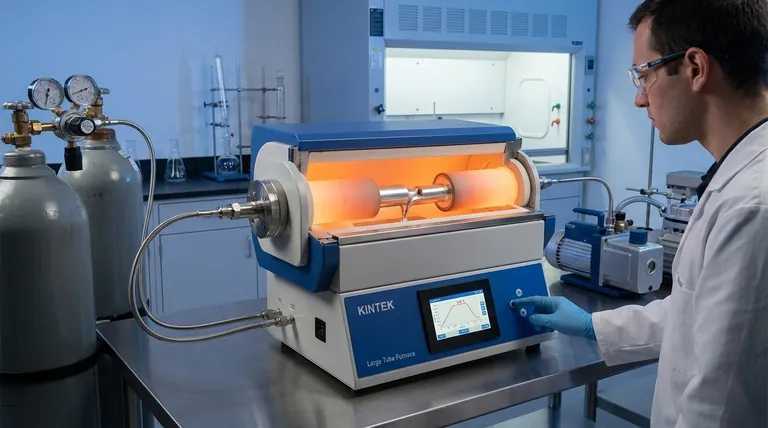

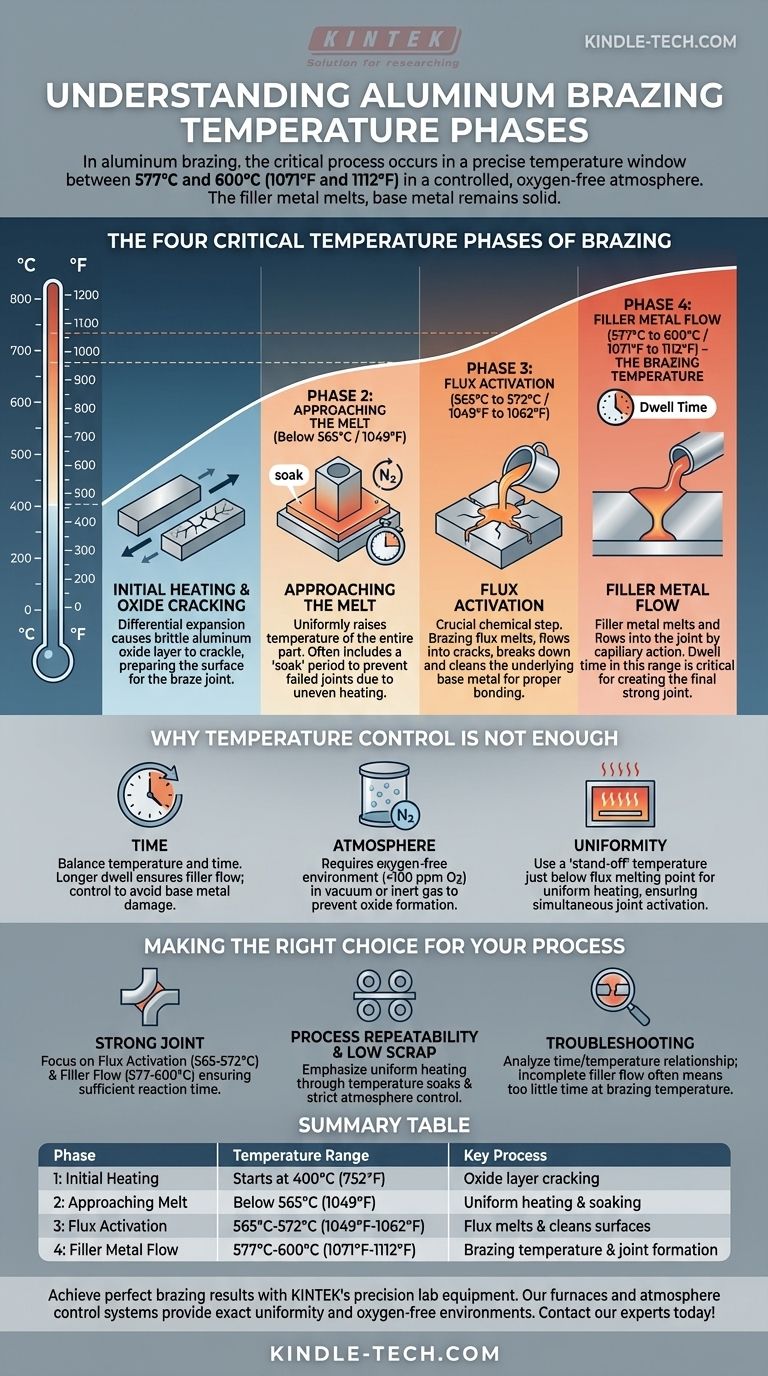
The Four Critical Temperature Phases of Brazing
Brazing isn't simply heating a part until metal flows. It is a structured process where specific chemical and physical changes happen at defined temperature ranges. For a typical aluminum brazing cycle, this process is broken into four phases.
Phase 1: Initial Heating and Oxide Cracking (Starts at 400°C / 752°F)
As the assembly is heated, the different metals—the base material and the filler metal—expand at different rates. This differential expansion causes the brittle, naturally occurring aluminum oxide layer on the surface to crackle and break.
This initial cracking is the first step in preparing the surface for the braze joint.
Phase 2: Approaching the Melt (Below 565°C / 1049°F)
During this heating stage, all components of the assembly remain in their solid form. The primary goal here is to raise the temperature of the entire part uniformly, often with a "soak" period to ensure even heat distribution.
Proper soaking prevents one area from reaching the brazing temperature before another, which could lead to a failed joint.
Phase 3: Flux Activation (565°C to 572°C / 1049°F to 1062°F)
This is a crucial chemical step. In this narrow temperature range, the brazing flux melts. The liquid flux flows into the cracks in the oxide layer, breaking it down and cleaning the underlying base metal.
Without this step, the filler metal cannot properly "wet" or bond to the base metal, resulting in a weak or non-existent joint.
Phase 4: Filler Metal Flow (577°C to 600°C / 1071°F to 1112°F)
This is the brazing temperature. The filler metal, which has a lower melting point than the base metal, becomes liquid. Capillary action pulls the molten filler into the gap between the parts, creating the final, strong brazed joint.
The time spent in this temperature range, known as dwell time, is a critical process parameter.
Why Temperature Control Is Not Enough
Achieving the correct temperature is essential, but it is only one piece of a larger puzzle. The most successful brazing operations master the relationship between temperature and other key variables.
The Role of Time
The balance between temperature and time is paramount. A longer dwell time at the peak brazing temperature can help ensure the filler metal has fully flowed, potentially reducing scrap parts.
However, this must be carefully controlled to avoid damaging the base metals.
The Importance of Atmosphere
Brazing requires an environment free of oxygen. Oxygen rapidly forms oxides on hot metal surfaces, which prevents the filler metal from bonding.
The process must be performed in a vacuum or a controlled atmosphere of an inert gas like pure nitrogen, with extremely low levels of oxygen (<100 ppm) and humidity.
The Need for Uniformity
A "stand-off" or "soak" temperature is often used just below the flux melting point. Holding the assembly at this temperature allows the entire part, regardless of its thickness or geometry, to reach a uniform temperature.
This ensures that when the final heating to brazing temperature occurs, the entire joint activates and flows at the same time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your approach to temperature control should be dictated by your end goal, whether it's maximizing joint strength or ensuring process consistency.
- If your primary focus is a strong, complete joint: Pay close attention to the flux activation (565-572°C) and filler metal flow (577-600°C) stages, ensuring sufficient time for each reaction to complete.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and low scrap: Emphasize uniform heating through temperature soaks and maintain strict control over the furnace atmosphere or vacuum level.
- If you are troubleshooting failed joints: Analyze the relationship between your time and temperature settings, as incomplete filler flow is often caused by too little time at the correct brazing temperature.
Ultimately, mastering brazing is about mastering the entire thermal profile, not just a single temperature value.
Summary Table:
| Phase | Temperature Range | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1: Initial Heating | Starts at 400°C (752°F) | Oxide layer cracking |
| 2: Approaching Melt | Below 565°C (1049°F) | Uniform heating & soaking |
| 3: Flux Activation | 565°C-572°C (1049°F-1062°F) | Flux melts & cleans surfaces |
| 4: Filler Metal Flow | 577°C-600°C (1071°F-1112°F) | Brazing temperature & joint formation |
Achieve perfect brazing results with KINTEK's precision lab equipment. Our industrial furnaces and atmosphere control systems provide the exact temperature uniformity and oxygen-free environment required for flawless aluminum brazing cycles. Whether you're focused on joint strength or process repeatability, KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables that serve your laboratory's most demanding thermal processing needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your brazing process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- What are the tubes in a furnace called? Understanding the Role of the Working Tube
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning



















