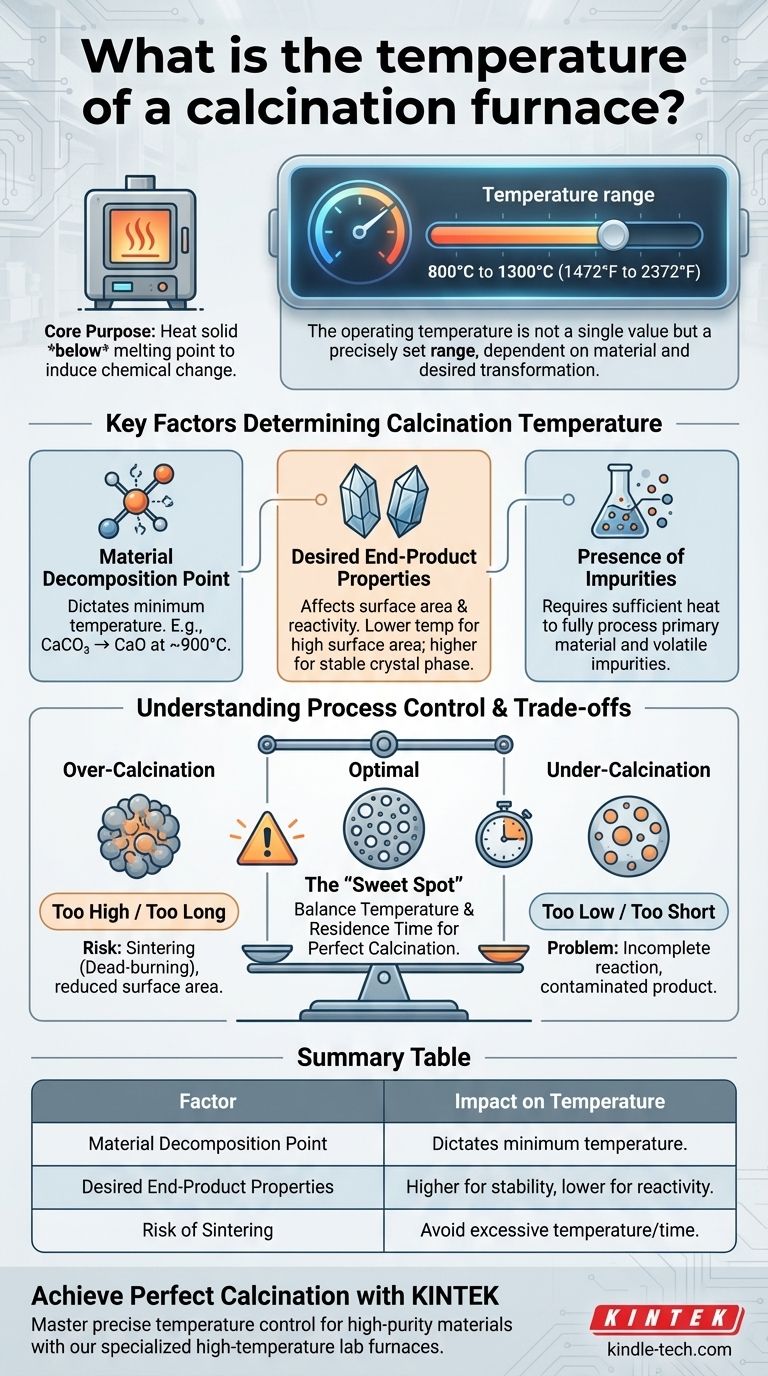
The operating temperature of a calcination furnace is not a single value but is precisely set within a typical range of 800°C to 1300°C (1472°F to 2372°F). This temperature is carefully selected based on the specific material being processed and the desired chemical or physical transformation.
The core purpose of calcination is to heat a material to a specific temperature below its melting point to induce a chemical change. Therefore, the "correct" temperature is dictated entirely by the decomposition point of the substance and the properties desired in the final product.

What is Calcination? A Primer on Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is a fundamental thermal treatment process used across industries like cement production, mineral processing, and catalyst manufacturing. Understanding its core principles is key to controlling the outcome.
The Core Principle: Heat Without Melting
The defining characteristic of calcination is heating a solid material to a high temperature without allowing it to fuse or melt.
The goal is to provide enough thermal energy to break chemical bonds and trigger a reaction, fundamentally altering the material's composition.
Driving Chemical Change
The primary function of calcination is to cause thermal decomposition. This most often involves removing a specific component from the material.
Common examples include:
- Removing water of crystallization (dehydration).
- Driving off carbon dioxide (CO₂) from carbonates, like converting limestone to lime.
- Removing other volatile organic compounds or sulfur compounds.
Achieving Physical Transformation
Beyond chemical change, calcination is also used to alter a material's physical properties.
This can involve changing the crystal structure (phase transformation) or increasing the porosity and surface area of a material, which is critical for applications like catalysts and adsorbents.
Key Factors Determining Calcination Temperature
The broad 800°C to 1300°C range exists because different materials and goals demand different conditions. The temperature is a carefully controlled variable, not an arbitrary setting.
Material Decomposition Point
This is the most critical factor. Every compound has a specific temperature at which it will decompose.
For example, calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) begins to rapidly decompose into calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂) at approximately 900°C. To produce lime, the furnace must operate at or above this temperature.
Desired End-Product Properties
Even for the same material, the final calcination temperature affects the properties of the end product.
A lower-temperature calcination might produce a material with a higher surface area and greater chemical reactivity. Conversely, a higher temperature might be needed to achieve a specific, stable crystal phase.
Presence of Impurities
The composition of the raw material, including any impurities, can influence the required temperature. The process must supply enough heat to ensure that both the primary material and any unwanted volatile impurities are fully processed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Process Control
Achieving the perfect calcination requires a delicate balance. Minor deviations in temperature can lead to significant problems with the final product.
The Risk of Over-Calcination (Sintering)
If the temperature is too high or held for too long, the material particles can begin to fuse together in a process called sintering.
Sintering dramatically reduces the material's surface area and reactivity, a condition often called "dead-burning." This is a common failure mode that produces a low-quality or unusable product.
The Problem of Under-Calcination
If the temperature is too low or the processing time is too short, the chemical reaction will be incomplete.
This results in a final product that is contaminated with the original, unreacted feed material, failing to meet purity specifications.
Temperature vs. Residence Time
Temperature is not the only variable. The amount of time the material spends in the hot zone of the furnace, known as residence time, is equally important.
A process might achieve complete calcination at a lower temperature by using a longer residence time, which can sometimes be a strategy to prevent sintering while ensuring a full reaction.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the optimal furnace temperature is a matter of defining your process objective. Your goal dictates your operating parameters.
- If your primary focus is producing a highly reactive material: You will likely operate at the lower end of the material's decomposition range to preserve maximum surface area and avoid sintering.
- If your primary focus is ensuring complete decomposition and purity: You may need to operate at a moderate temperature above the decomposition point, balancing completeness with the risk of sintering.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific crystal phase: The temperature will be dictated precisely by the target phase, often requiring very tight control at a specific point within the calcination range.
Ultimately, mastering calcination comes from understanding that temperature is the tool you use to precisely control your material's final form and function.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Temperature | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Material Decomposition Point | Dictates the minimum temperature required for the reaction. | CaCO₃ decomposes to CaO at ~900°C. |
| Desired End-Product Properties | Higher temperatures can reduce reactivity; lower temps preserve surface area. | A catalyst needs high surface area (lower temp). |
| Risk of Sintering | Excessive temperature causes particle fusion, ruining product quality. | Over-calcination leads to "dead-burning." |
Achieve Perfect Calcination with KINTEK
Mastering the precise temperature control of your calcination process is key to producing high-purity, reactive materials. Whether you're developing catalysts, processing minerals, or manufacturing advanced ceramics, the right furnace makes all the difference.
KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab furnaces designed for exacting calcination applications. Our equipment delivers the uniform heating and precise temperature control you need to avoid under-calcination and prevent destructive sintering.
Let us help you optimize your thermal processing:
- Select the right furnace for your specific material and temperature range (800°C to 1300°C+).
- Ensure complete decomposition and achieve your target crystal phases.
- Improve your product's quality and consistency with reliable, durable equipment.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss your calcination requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















