The "temperature of CVD diamond" is not a single value but refers to two distinct contexts: its creation and its operational limits. The process to create Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) diamond requires extremely high temperatures, typically ranging from 800°C to 2000°C. However, its performance temperature, especially when cutting, is limited by chemical reactions that occur at high heat, particularly with iron-based materials.
Understanding the difference between CVD diamond's high formation temperature and its more limited operational temperature is the key to using it effectively. Its creation defines what it can be coated on, while its operational limits define what it can cut.
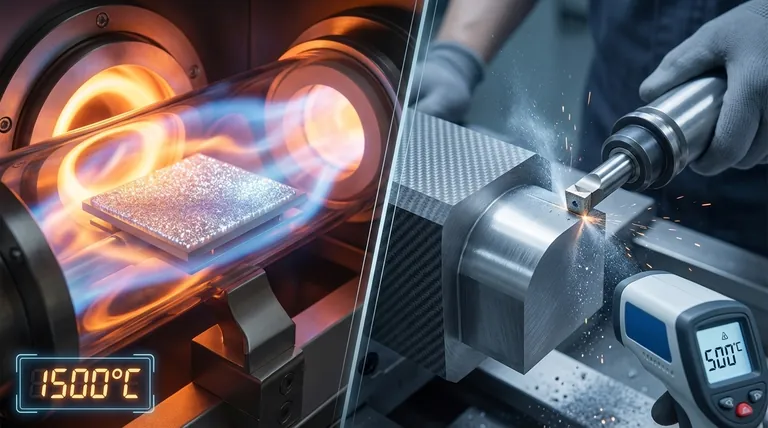
The Creation Temperature: Forging Diamond from Gas
The CVD Process Environment
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a process where a substrate is placed in a vacuum chamber and exposed to precursor gases.
For diamond, these gases are typically a mix of a carbon source (like methane) and hydrogen.
The Critical Temperature Range
To create a crystalline diamond film, the substrate must be heated to a very high temperature, generally between 800°C and 2000°C (1472°F - 3632°F).
This intense heat provides the necessary energy to break down the gas molecules and allow carbon atoms to arrange themselves into the rigid diamond crystal lattice on the substrate's surface.
Implications for Substrates
This high processing temperature is a critical constraint. The material being coated (the substrate) must be able to withstand these conditions without melting, warping, or losing its essential properties.
For example, since the CVD process temperature is higher than the tempering temperature of many steels, coating standard steel tools directly is often impractical as the tool would lose its hardness. This is why substrates are often materials like tungsten carbide or ceramics.
The Operational Temperature: Performance Under Heat
Thermal Stability in Air
Like natural diamond, CVD diamond is exceptionally stable. However, when heated in the presence of oxygen, it will begin to oxidize and convert back to graphite at temperatures around 700°C to 800°C.
This provides a general upper limit for its use in a standard atmospheric environment.
The Challenge of Cutting Ferrous Metals
Although extremely hard, CVD diamond tools are generally unsuitable for machining steel or other iron-based alloys.
The problem is not the diamond "melting" in a simple sense. At the high temperatures generated at the tool's cutting edge, the carbon in the diamond becomes highly reactive with the iron in the steel. This chemical interaction rapidly converts the diamond into softer graphite, causing catastrophic tool wear.
Success with Non-Ferrous Materials
This chemical limitation is why CVD diamond excels at cutting abrasive, non-ferrous materials.
Materials like high-silicon aluminum, carbon fiber composites, graphite, and ceramics do not react chemically with the diamond at high temperatures. This allows the tool to leverage its incredible hardness and wear resistance for a significantly longer tool life, often 2 to 10 times longer than Polycrystalline Diamond (PCD) tools.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Process Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
The very thing that creates a high-quality diamond film—intense heat—is also its biggest manufacturing limitation. The choice of what can be coated is restricted to materials that can survive the CVD chamber.
Extreme Hardness vs. Chemical Reactivity
CVD diamond’s greatest strength, its hardness, can only be leveraged in applications where its chemical weakness—reactivity with iron at high temperatures—is not a factor. This creates a clear dividing line for its ideal use cases.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To apply this knowledge effectively, you must match the thermal properties of CVD diamond to your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is coating a tool: Ensure your substrate material (e.g., tungsten carbide) can withstand the 800°C+ CVD process temperature without degrading.
- If your primary focus is machining materials: Use CVD diamond for high-speed cutting of non-ferrous metals, composites, and ceramics, but select a different tool material like Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) for steels and ferrous alloys.
By distinguishing between its formation and operational temperatures, you can harness the exceptional properties of CVD diamond for the right task.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Type | Typical Range | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Formation Temperature | 800°C - 2000°C | Defines substrate compatibility (e.g., tungsten carbide, ceramics) |
| Operational Temperature | Up to 700°C-800°C in air | Limits use with ferrous metals due to chemical reactivity |
Optimize Your Machining and Coating Processes with KINTEK
Understanding the thermal properties of CVD diamond is crucial for maximizing tool performance and longevity. Whether you're coating substrates or machining advanced materials, selecting the right tool technology is key to achieving superior results.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific laboratory and manufacturing needs. Our expertise in material science and cutting-edge solutions can help you:
- Select the right substrate materials for CVD diamond coating
- Choose optimal tooling for non-ferrous machining applications
- Enhance efficiency and extend tool life in your operations
Let our experts guide you to the ideal solution for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our specialized lab equipment and consumables can drive success in your projects.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) equipment play in the preparation of C/C composites? Expert Analysis
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- What are the methods of producing CNT? Scalable CVD vs. High-Purity Lab Techniques
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries



















