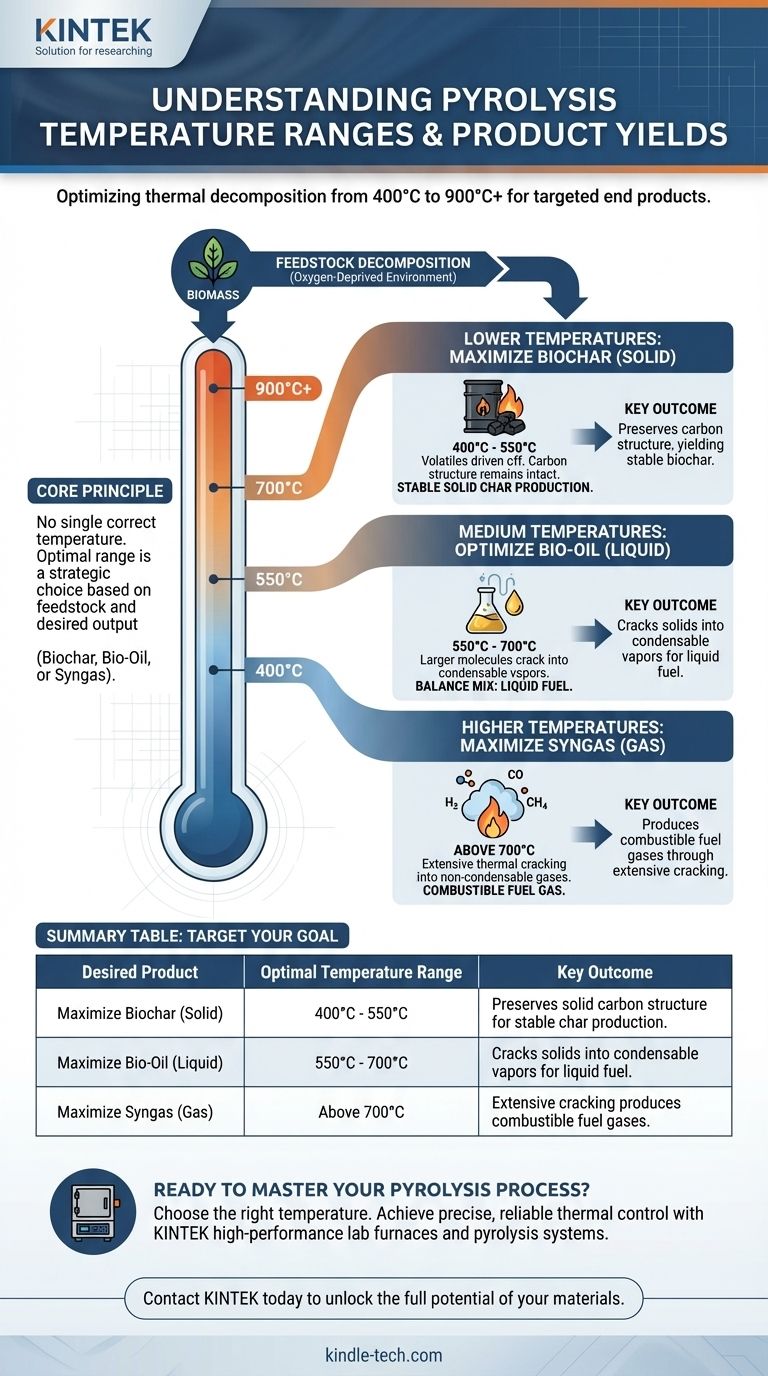
In essence, pyrolysis requires temperatures high enough to break down material without combustion, typically falling within a broad range of 400°C to 900°C (750°F to 1650°F). This process, known as thermal decomposition, occurs in an oxygen-deprived environment, ensuring the material carbonizes and transforms rather than burns. The exact temperature is not a fixed number but a critical variable tuned to the specific feedstock and the desired end products.
The core principle to understand is that there is no single "correct" temperature for pyrolysis. The optimal temperature is a strategic choice determined by the chemical makeup of your starting material and whether you aim to maximize the output of solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, or combustible syngas.

Why Temperature is the Critical Control Parameter
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of controlled deconstruction. Temperature acts as the primary tool that dictates how, and to what extent, the chemical bonds within a material are broken down.
The Foundational Temperature Threshold
For organic materials like biomass, the process doesn't begin in earnest until a certain heat threshold is met. Different components of the material decompose at different temperatures.
For example, in wood or agricultural waste, hemicellulose begins breaking down around 250-400°C. Cellulose, a more stable component, requires 310-430°C, while resilient lignin needs temperatures between 300-530°C to fully decompose.
This is why effective pyrolysis operations must exceed at least 400°C to ensure the primary components of the feedstock are fully processed.
Defining Pyrolysis Regimes by Temperature
The broader temperature range can be understood as different operational zones, each favoring a different outcome. A process defined as medium temperature pyrolysis, for instance, operates between 600°C and 700°C.
This implies the existence of lower and higher temperature regimes. Choosing a regime is the most important decision in designing a pyrolysis process, as it directly influences the final product distribution.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Temperature vs. Product Yield
The final output of pyrolysis is a mix of solids (biochar), liquids (bio-oil), and gases (syngas). Changing the temperature directly shifts the ratio of these three products.
Favoring Solid Char Production
Lower temperatures, generally in the 400-550°C range, tend to maximize the yield of biochar. At this heat level, the volatile components are driven off, but the underlying carbon structure remains largely intact, creating a stable, solid char.
Optimizing for a Balanced Output
As temperatures increase into the medium range (around 550-700°C), the larger organic molecules begin to break down further, or "crack," into smaller, condensable vapors. Upon cooling, these vapors form the liquid fraction known as bio-oil. This range often produces a more balanced mix of char and oil.
Maximizing Gas Production (Syngas)
Pushing temperatures above 700°C provides enough energy to crack the molecules even further into very small, non-condensable gaseous compounds like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane. This mixture is known as syngas, which can be used as a fuel. At these high temperatures, char and oil yields are significantly reduced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct temperature is a strategic decision based entirely on your desired end product. Use the following as a guide.
- If your primary focus is producing stable biochar: Operate at the lower end of the pyrolysis range, typically 400-550°C, to preserve the solid carbon structure.
- If your primary focus is generating liquid bio-oils: Target the medium temperature range, approximately 550-700°C, to encourage the cracking of solids into condensable vapors.
- If your primary focus is maximizing fuel gas (syngas): Use high temperatures, generally above 700°C, to ensure the extensive thermal cracking of all fractions into small gas molecules.
Ultimately, mastering pyrolysis is about precisely controlling temperature to dictate the chemical transformation and achieve your specific material or energy goal.
Summary Table:
| Desired Product | Optimal Temperature Range | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Maximize Biochar (Solid) | 400°C - 550°C | Preserves solid carbon structure for stable char production. |
| Maximize Bio-Oil (Liquid) | 550°C - 700°C | Cracks solids into condensable vapors for liquid fuel. |
| Maximize Syngas (Gas) | Above 700°C | Extensive cracking produces combustible fuel gases. |
Ready to Master Your Pyrolysis Process?
Choosing the right temperature is just the first step. Achieving precise, reliable thermal control is essential for consistent results and maximizing your ROI.
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and pyrolysis systems designed for researchers and engineers like you. We provide the equipment you need to accurately target any temperature regime—from 400°C to well above 900°C—ensuring you can optimize for biochar, bio-oil, or syngas with confidence.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect pyrolysis solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the function of alumina tubes and alumina wool in a pyrolysis furnace? Optimize Your Biochar Production Quality
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- Why is a high-purity alumina lining required for high-temperature tube furnaces? Ensure Accurate Biomass Research
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?



















