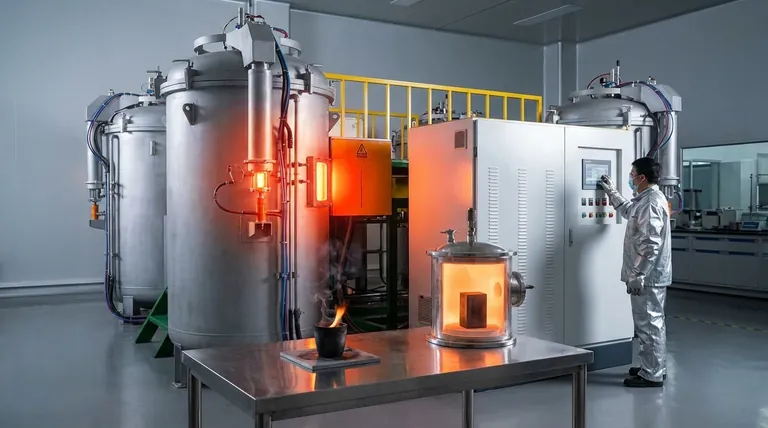
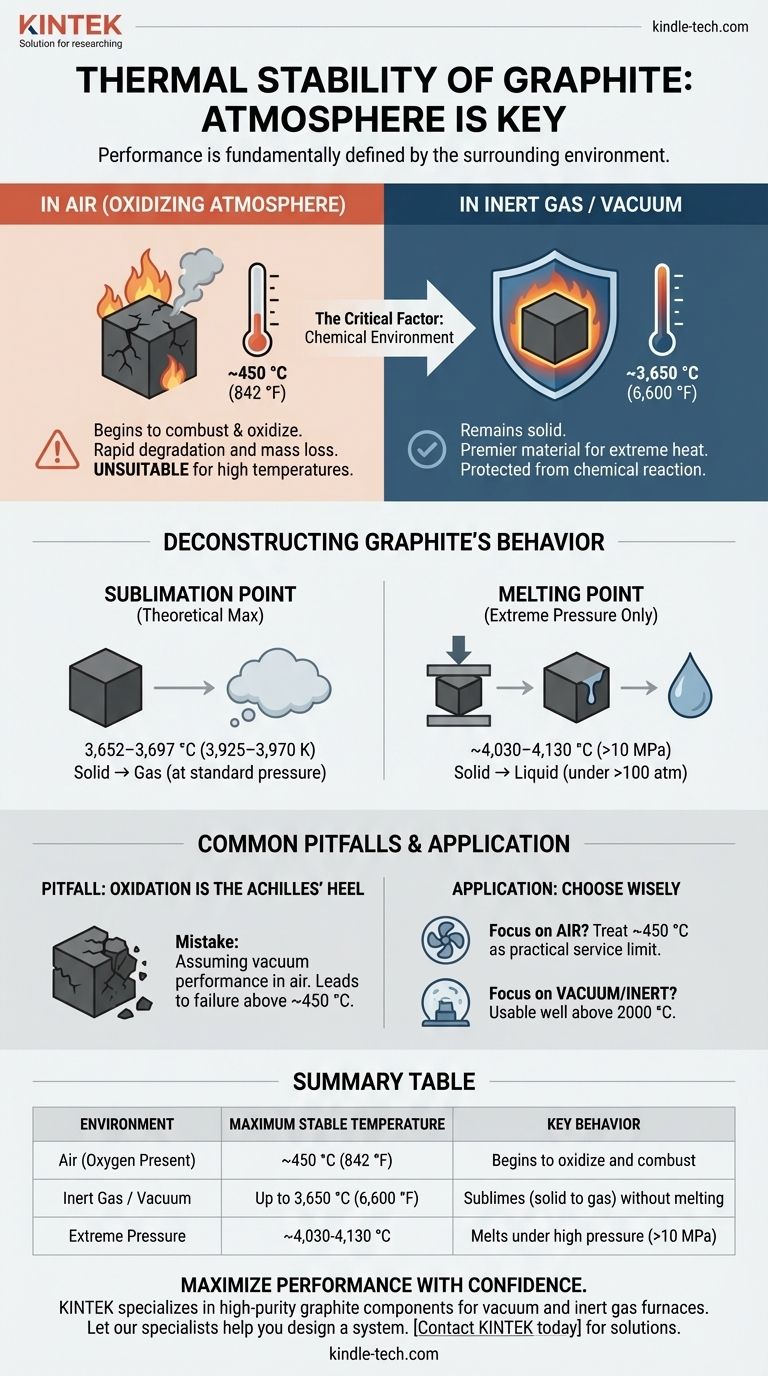
In the absence of oxygen, graphite is one of the most thermally stable materials known, remaining solid at temperatures up to its sublimation point of approximately 3,650 °C (6,600 °F). However, its stability is drastically reduced in an oxidizing atmosphere like air, where it will begin to combust at temperatures as low as 450 °C (842 °F).
The practical thermal stability of graphite is not a single number but is fundamentally defined by its surrounding atmosphere. While its theoretical limit is exceptionally high, its real-world performance is almost always dictated by its reaction with oxygen.

Deconstructing Graphite's Thermal Behavior
To truly understand graphite's performance under heat, we must look beyond a single temperature and consider the underlying physics and its inherent chemical nature.
The Sublimation Point: Its Theoretical Maximum
Under standard atmospheric pressure, graphite does not melt. Instead, it sublimes—transforming directly from a solid into a gas.
This sublimation occurs at an extremely high temperature, typically cited between 3,652–3,697 °C (3,925–3,970 K). This is the absolute upper limit of its stability as a solid material.
The Melting Point: Only Under Extreme Pressure
Graphite only exhibits a liquid phase under very high pressure, in the range of 10 MPa (~100 atmospheres) or more. Under these specific conditions, its melting point is even higher than its sublimation point, estimated to be around 4,030–4,130 °C (4,300–4,400 K). For most practical applications, this is not a relevant scenario.
The Foundation of Stability
At a fundamental level, graphite's thermal resilience comes from its thermodynamic stability. At standard temperature and pressure, graphite is the most stable form (allotrope) of carbon. Diamond, for instance, is slightly less stable and will, with sufficient energy input, revert to graphite.
The Critical Factor: Operating Atmosphere
The most significant variable controlling graphite's usable temperature range is the chemical environment. The theoretical sublimation point is only achievable under specific conditions.
In an Inert Environment or Vacuum
When used in a vacuum or surrounded by an inert gas like argon or nitrogen, graphite is protected from chemical reaction. In these applications, such as furnace elements or crucibles for metallurgy, it can be reliably used at temperatures approaching its sublimation point, making it a premier material for extreme heat.
In the Presence of Oxygen (Air)
In an oxidizing atmosphere like air, the story is completely different. Graphite readily reacts with oxygen to form carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO₂).
This oxidation process begins to occur at a meaningful rate around 450-500 °C. As temperatures rise further, the rate of oxidation increases dramatically, causing the material to degrade and lose mass. This makes graphite unsuitable for long-term, high-temperature use in air.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the limitations of graphite is as important as knowing its strengths. Misjudging the operating environment is the most common cause of failure.
Oxidation is the Achilles' Heel
The single greatest mistake is assuming the performance of graphite in a vacuum can be achieved in air. Engineers must design systems to either provide an inert environment or accept a much lower maximum operating temperature of around 450 °C.
Purity and Structure Matter
The exact temperature at which oxidation begins can be influenced by the graphite's physical properties. Materials with higher porosity, greater surface area, or lower purity may begin to oxidize at slightly lower temperatures than highly crystalline, pure forms of graphite.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice must be dictated by the operating environment of your application.
- If your primary focus is operating in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is one of the most stable and effective materials available, usable for applications well above 2000 °C.
- If your primary focus is operating in air: You must treat graphite's practical service limit as approximately 450 °C to avoid rapid degradation from oxidation.
Ultimately, harnessing the incredible thermal potential of graphite depends entirely on protecting it from its chemical environment.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Maximum Stable Temperature | Key Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Air (Oxygen Present) | ~450°C (842°F) | Begins to oxidize and combust |
| Inert Gas / Vacuum | Up to 3,650°C (6,600°F) | Sublimes (solid to gas) without melting |
| Extreme Pressure | ~4,030-4,130°C | Melts under high pressure (>10 MPa) |
Maximize your high-temperature processes with confidence.
Graphite's performance is unparalleled in controlled environments. KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including graphite components designed for vacuum and inert gas furnaces. Whether you're in materials research, metallurgy, or semiconductor manufacturing, our expertise ensures you select the right materials for your specific thermal and atmospheric conditions.
Let our specialists help you design a system that fully leverages graphite's exceptional thermal stability. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and discover the right solutions for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the maximum working temperature of graphite? Unlock High-Temp Performance with the Right Atmosphere
- How well does graphite transfer heat? Unlock Superior Thermal Management for Your Electronics
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- Why is graphite so hard to melt? The Secret Lies in Its Atomic Structure
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C



















