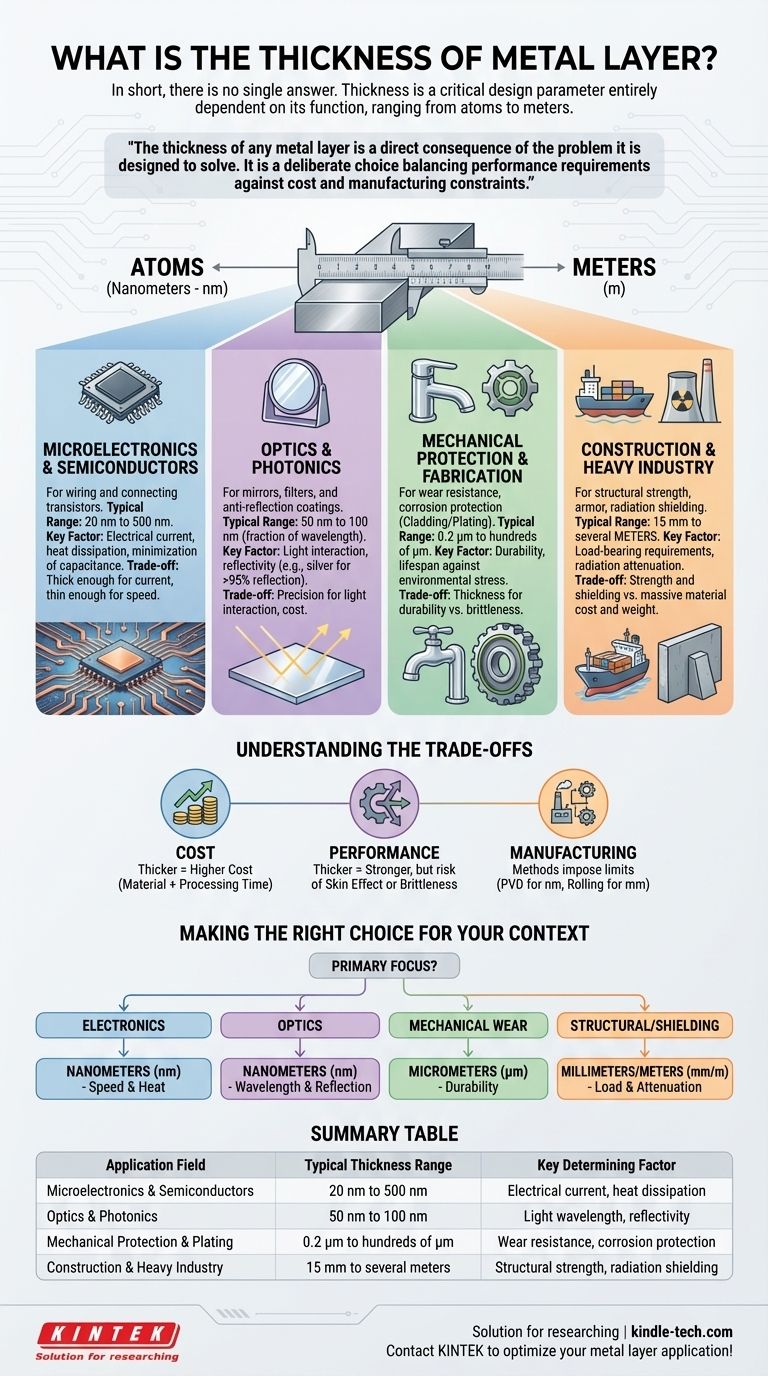
In short, there is no single answer. The thickness of a metal layer is not a fixed value but a critical design parameter that is entirely dependent on its intended function. This value can range from a few atoms thick in a semiconductor chip to several meters thick for radiation shielding in a nuclear facility.
The thickness of any metal layer is a direct consequence of the problem it is designed to solve. It is a deliberate choice balancing performance requirements—such as electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, or optical behavior—against the constraints of cost and manufacturing feasibility.

Why Application Determines Thickness
The term "metal layer" is used across dozens of industries, from microelectronics to heavy construction. The required thickness is dictated by the physical properties needed for the layer to perform its job successfully. A layer designed for electrical purposes has vastly different requirements than one designed for structural integrity.
For Microelectronics and Semiconductors
In integrated circuits, metal layers (like copper or aluminum) form the wiring that connects billions of transistors. Here, thickness is measured in nanometers (nm).
A typical range might be 20 nm to 500 nm. The thickness is a careful trade-off. It must be thick enough to carry the required electrical current without overheating (electromigration) but thin enough to minimize capacitance between layers, which would slow the chip down.
For Optics and Photonics
Metal layers are used to create mirrors or specialized filters. The thickness is chosen based on its interaction with light and is often a fraction of a specific wavelength.
For a highly reflective mirror, a silver or aluminum layer might be 50 nm to 100 nm thick. This is sufficient to be opaque and reflect over 95% of visible light. For anti-reflection coatings, much thinner, multi-layered films are used to create destructive interference.
For Mechanical Protection and Fabrication
In manufacturing, metal layers provide wear resistance, corrosion protection, or a base for further processing. This is often called cladding or plating.
Thickness here is measured in micrometers (µm), also known as microns. A chrome plating on a faucet for corrosion resistance might be 0.2 µm to 0.5 µm, while a hard-facing layer on an industrial tool could be hundreds of micrometers thick.
For Construction and Heavy Industry
In large-scale applications, metal layers provide structural strength, armor, or containment. Thickness is measured in millimeters (mm) or centimeters (cm).
The steel plate hull of a cargo ship can be 15 mm to 25 mm thick. The steel and lead layers in a nuclear reactor's containment vessel can be several meters thick to provide radiation shielding.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost, Performance, and Process
Choosing a layer's thickness is never done in a vacuum. It involves a critical balance of competing factors that every engineer must consider.
Cost vs. Thickness
Thicker layers almost always mean higher costs. This is due not only to the increased amount of raw material (like gold or platinum) but also to the longer processing time required for deposition, plating, or rolling.
Performance Degradation
While thicker can mean stronger, it can also harm performance. In high-frequency electronics, a phenomenon called the "skin effect" causes current to flow only on the outer surface of a conductor, making a thick wire act like a thin one and wasting material. An overly thick coating can also be brittle and prone to cracking.
Manufacturing Limitations
The method used to create the layer imposes its own limits. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is excellent for creating uniform, nanometer-scale films but is too slow and expensive for millimeter-thick layers. Rolling and welding are efficient for thick plates but lack the precision for optical coatings.
Making the Right Choice for Your Context
To determine the relevant thickness, you must first identify the primary function of the layer within your specific field.
- If your primary focus is electronics or semiconductors: Thickness will be in nanometers, dictated by signal speed, current density, and heat dissipation.
- If your primary focus is optics: Thickness will be in nanometers, determined by the target wavelength of light for reflection, absorption, or interference.
- If your primary focus is mechanical wear or corrosion: Thickness will be in micrometers, chosen for durability and lifespan against a specific environmental stress.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity or shielding: Thickness will be in millimeters or centimeters, calculated based on load-bearing requirements or radiation attenuation properties.
Ultimately, the thickness of a metal layer is a precise answer to a specific engineering question.
Summary Table:
| Application Field | Typical Thickness Range | Key Determining Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Microelectronics & Semiconductors | 20 nm to 500 nm | Electrical current, heat dissipation |
| Optics & Photonics | 50 nm to 100 nm | Light wavelength, reflectivity |
| Mechanical Protection & Plating | 0.2 µm to hundreds of µm | Wear resistance, corrosion protection |
| Construction & Heavy Industry | 15 mm to several meters | Structural strength, radiation shielding |
Struggling to determine the optimal metal layer thickness for your specific application? The right thickness is critical for performance, cost, and manufacturability. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise material deposition and analysis, serving industries from microelectronics to heavy manufacturing. Our experts can help you select the right equipment and processes to achieve your desired layer properties. Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and optimize your metal layer application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition


















