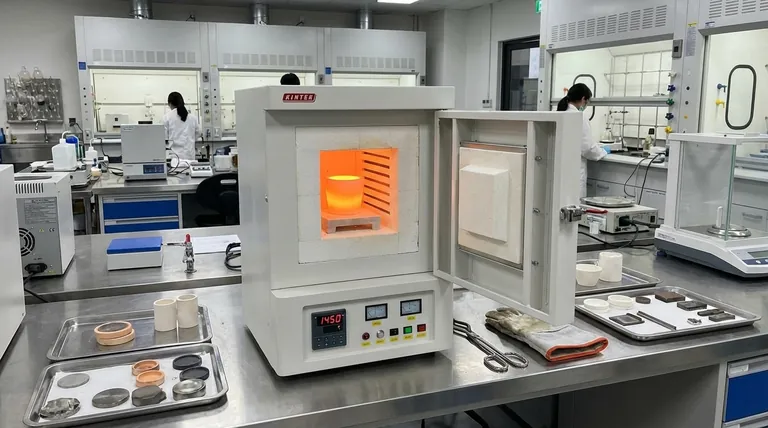
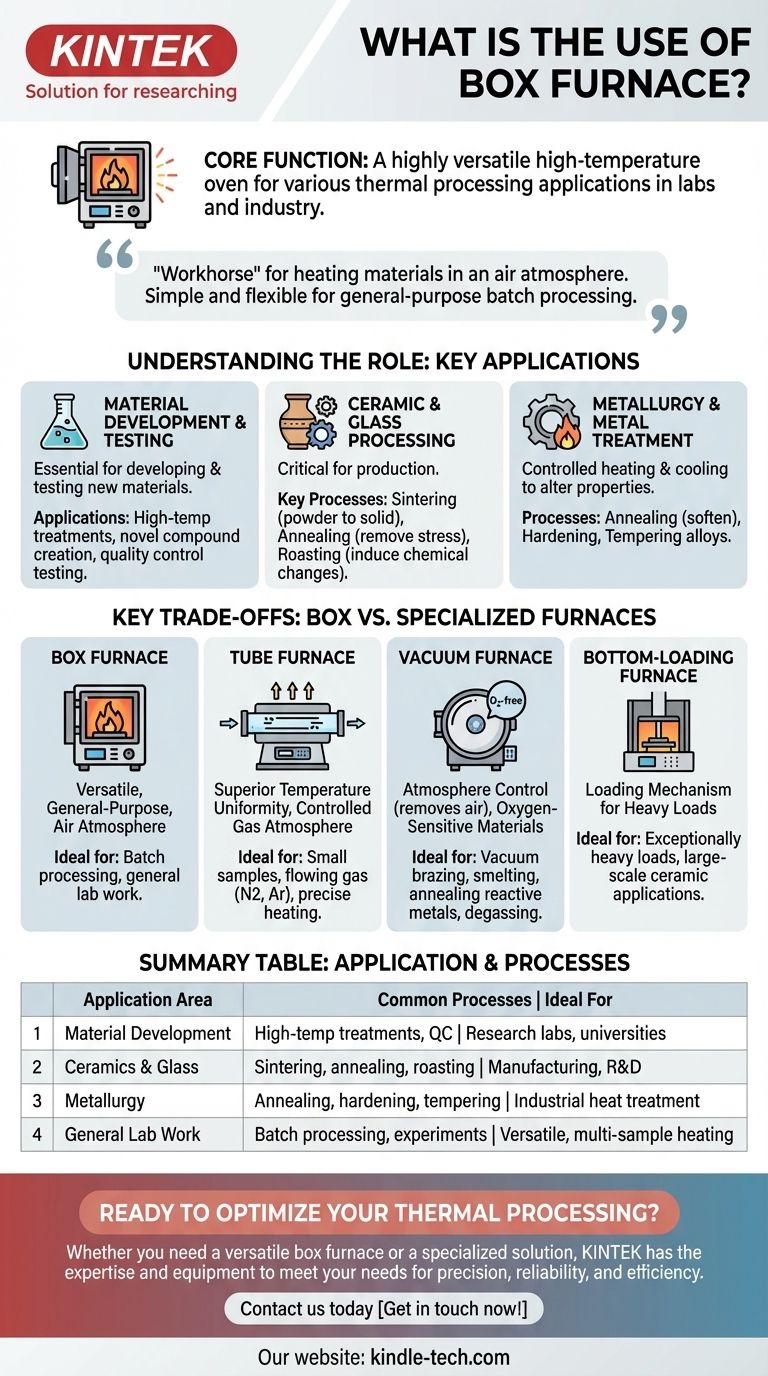
At its core, a box furnace is a highly versatile high-temperature oven used for a vast range of thermal processing applications. Found in nearly every materials science lab and industrial setting, it is used for tasks like powder roasting, ceramic sintering, heat treating metals, and general high-temperature experiments across industries from electronics and metallurgy to chemical engineering and building materials.
A box furnace is the foundational "workhorse" for heating materials in an air atmosphere. Its value lies in its simplicity and flexibility for general-purpose batch processing, but specialized tasks may require different types of furnaces.

Understanding the Box Furnace's Role
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, is defined by its simple design: an insulated chamber with a front-loading door, capable of reaching high temperatures, often up to 1550°C or more. This design makes it ideal for processing multiple samples or objects at once in a "batch" style.
Material Development and Testing
In research institutes and universities, the box furnace is an essential tool for developing and testing new materials. Its stable, uniform heating is perfect for controlled experiments.
Applications include high-temperature material treatments, creating novel compounds, and quality control testing where a material's response to heat is evaluated.
Ceramic and Glass Processing
The ceramics and glass industries rely heavily on box furnaces for critical production steps. The large chamber can accommodate various shapes and sizes.
Key processes include sintering, where powdered materials are heated to form a solid mass, annealing glass to remove internal stresses, and roasting powders to induce chemical changes.
Metallurgy and Metal Treatment
In metallurgy, precisely controlled heating and cooling cycles are used to alter the physical and chemical properties of metals.
Box furnaces are frequently used for annealing, a process that softens metals and improves their ductility, as well as for hardening and tempering various alloys.
Key Trade-offs: Box Furnace vs. Specialized Furnaces
While versatile, the standard box furnace is not the optimal tool for every thermal process. Understanding its limitations clarifies when a more specialized furnace is required.
vs. Tube Furnace
A tube furnace uses a cylindrical heating chamber. It is designed for superior temperature uniformity over a smaller area and is ideal for processes requiring a controlled gas atmosphere.
If your process involves flowing a specific gas (like nitrogen or argon) over a sample or requires extremely precise heating of a small sample, a tube furnace is the superior choice.
vs. Vacuum Furnace
The defining difference is atmosphere control. A standard box furnace operates in ambient air (containing oxygen), which can be reactive at high temperatures.
A vacuum furnace removes the atmosphere, making it essential for processes involving oxygen-sensitive materials. This includes vacuum brazing, smelting, annealing reactive metals, and degassing components for electronics.
vs. Bottom-Loading Furnace
The distinction here is the loading mechanism. A bottom-loading furnace features a hearth that raises into the heating chamber from below.
This design is advantageous for processing very heavy loads that are difficult to slide into a front-loading chamber. It is also common in the ceramic industry for applications that benefit from specific heating and cooling profiles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace is critical for achieving reliable and repeatable results. Your choice should be dictated by the specific requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose lab work or batch heat-treating in air: The standard box furnace is your most flexible and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is processing small samples with high temperature uniformity or in a controlled gas flow: A tube furnace is better suited for your needs.
- If your primary focus is processing oxygen-sensitive materials, performing vacuum brazing, or degassing parts: A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is treating exceptionally heavy loads or specific large-scale ceramic applications: A bottom-loading furnace offers significant operational advantages.
Ultimately, understanding the core function of each furnace type empowers you to select the right tool to ensure the success of your process.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Common Processes | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Material Development | High-temperature treatments, quality control | Research labs, universities |
| Ceramics & Glass | Sintering, annealing, roasting powders | Manufacturing, R&D |
| Metallurgy | Annealing, hardening, tempering metals | Industrial heat treatment |
| General Lab Work | Batch processing, high-temperature experiments | Versatile, multi-sample heating |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing?
Whether you need a versatile box furnace for general lab work or a specialized solution for controlled atmospheres or heavy loads, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your needs. Our range of high-temperature furnaces is designed to deliver precision, reliability, and efficiency for your specific applications.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the 3 official methods in determining ash and water content? A Guide to Proximate Analysis
- What are the different types of ash analysis? Dry vs. Wet Ashing Methods Explained
- What is the difference between a muffle furnace and an incubator? Choose the Right Tool for Your Lab
- How do you measure ash content? Choose the Right Method for Accurate Results
- What is the purpose of the muffle furnace? Achieve Contaminant-Free High-Temperature Processing



















