In the context of thin film deposition, a vacuum is not a perfect void. Instead, it is a highly controlled, artificially created environment where the atmospheric pressure has been reduced so significantly that it contains very few atoms or molecules. This low-pressure condition is the fundamental prerequisite for constructing high-quality, high-purity films on a substrate, one atomic layer at a time.
The purpose of a vacuum is not simply to create "emptiness," but to achieve two critical goals for thin film quality: ensuring absolute purity by removing unwanted atmospheric contaminants and enabling precise directional control of the deposition material.
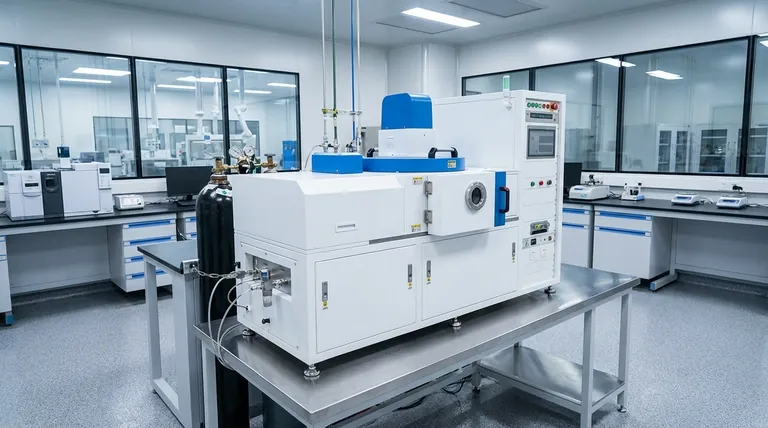

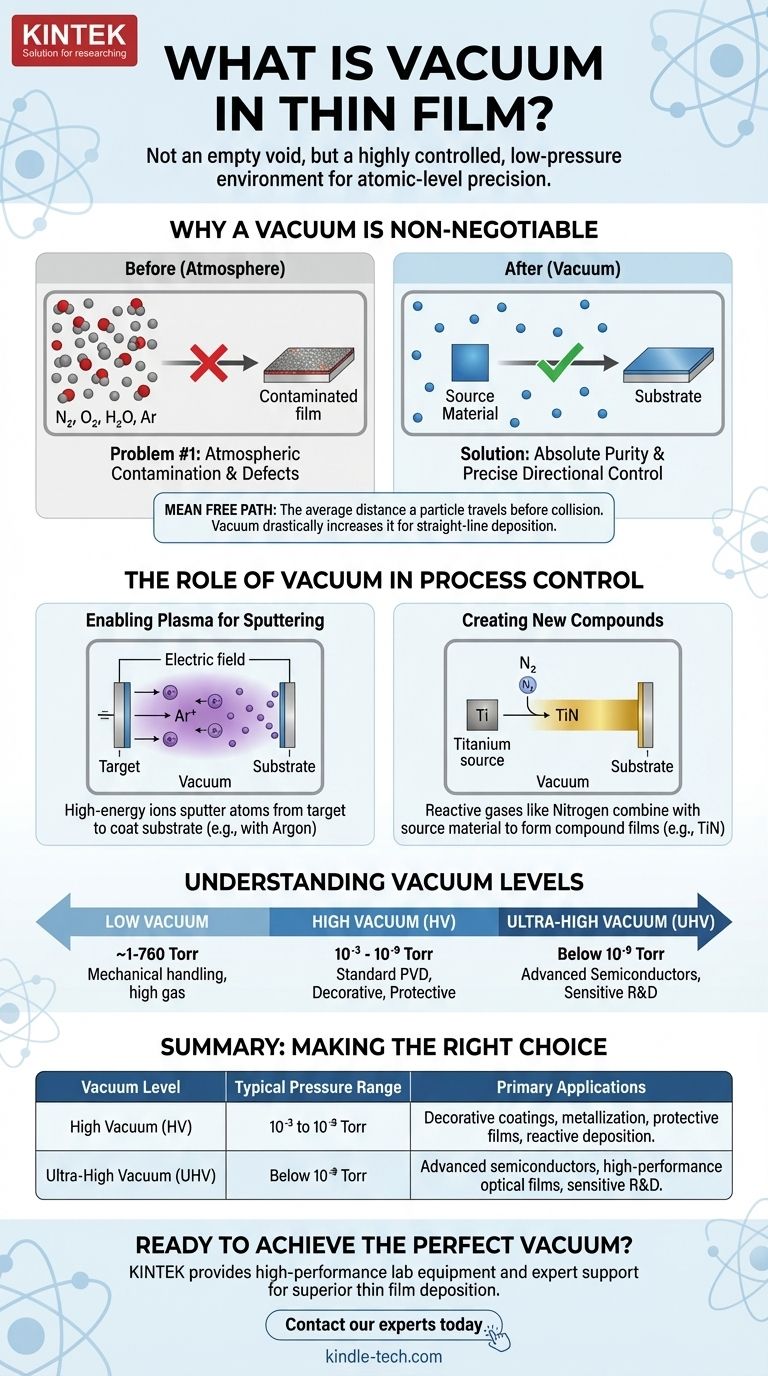
Why a Vacuum is Non-Negotiable
At sea level, we are surrounded by an atmosphere dense with particles—primarily nitrogen, oxygen, water vapor, and argon. Attempting to deposit a thin film in this environment would be like trying to paint a masterpiece in a dust storm. A vacuum chamber systematically eliminates these problems.
Problem #1: Atmospheric Contamination
The air around us is highly reactive. Gases like oxygen and water vapor will instantly interact with the deposition materials and the substrate surface, leading to the formation of unwanted oxides and other compounds.
These impurities become embedded within the film, creating defects that degrade its desired properties. A contaminated film can have poor electrical conductivity, reduced optical transparency, or weak mechanical integrity. The vacuum removes these reactive contaminants to create a pristine environment.
Problem #2: Particle Collisions (Mean Free Path)
Mean Free Path is the average distance a particle can travel before it collides with another particle. In the dense atmosphere of a normal room, this distance is incredibly short—mere nanometers.
Under vacuum, the pressure is reduced by many orders of magnitude. This drastically increases the mean free path, often to several meters, which is much longer than the distance between the material source and the substrate in a deposition chamber.
This long, uninterrupted path is crucial. It ensures that the atoms of the deposition material travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate, arriving with enough energy to form a dense, uniform, and well-adhered film. Without it, the material would scatter randomly, creating a porous and low-quality coating.
The Role of Vacuum in Process Control
Once a vacuum has removed the undesirable atmospheric gases, the chamber becomes a blank canvas. This allows engineers to introduce specific, high-purity gases in precise amounts to control the deposition process and create new materials.
Enabling Plasma for Sputtering
In Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) techniques like sputtering, a heavy, inert gas like Argon is introduced into the vacuum chamber. An electric field then ionizes this gas, creating a plasma.
These high-energy Argon ions are directed at a source material (the "target"), bombarding it with enough force to knock off, or "sputter," atoms. These sputtered atoms then travel through the vacuum to coat the substrate. This entire process is only possible in a vacuum where Argon is the dominant gas.
Creating New Compounds with Reactive Gases
A vacuum is also essential for reactive deposition, where the goal is to form a specific chemical compound on the substrate.
For example, to create a hard, gold-colored Titanium Nitride (TiN) coating, pure titanium is sputtered in a vacuum chamber where a controlled amount of pure nitrogen gas has been introduced. The titanium and nitrogen atoms combine on the substrate surface to form the desired compound film. This level of chemical control is impossible without first establishing a clean vacuum.
Understanding Vacuum Levels
"Vacuum" is not a single state but a spectrum of pressures. The required level of vacuum is determined entirely by the sensitivity of the film being created.
A Spectrum, Not an Absolute
Vacuum quality is measured in units of pressure like Torr or millibar (mbar). Atmospheric pressure is about 760 Torr.
Different applications require different levels of "emptiness" to succeed.
Common Classifications
- Low Vacuum: ~1 to 760 Torr. Used for mechanical handling or processes where gas presence is high.
- High Vacuum (HV): 10⁻³ to 10⁻⁹ Torr. This is the workhorse range for most industrial PVD coatings, including decorative, metallization, and protective films.
- Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV): Below 10⁻⁹ Torr. This extreme level is necessary for highly sensitive research and the manufacturing of advanced semiconductor and optical components where even a few stray atoms of contamination can cause device failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The level of vacuum you need is dictated by the level of perfection your film requires.
- If your primary focus is decorative or basic protective coatings: A standard High Vacuum (HV) environment is typically sufficient to prevent major oxidation and ensure good film adhesion.
- If your primary focus is high-performance optical or electronic films: An Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) is non-negotiable to minimize the atomic contaminants that degrade optical transmission or electrical performance.
- If your primary focus is creating specific compound films (e.g., nitrides, oxides): A clean High Vacuum (HV) base pressure is the critical first step before you can precisely introduce and control your reactive gases.
Ultimately, mastering vacuum is mastering the art of controlling the atomic-scale environment to build a perfect thin film.
Summary Table:
| Vacuum Level | Typical Pressure Range | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High Vacuum (HV) | 10⁻³ to 10⁻⁹ Torr | Decorative coatings, metallization, protective films, reactive deposition (e.g., TiN). |
| Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) | Below 10⁻⁹ Torr | Advanced semiconductors, high-performance optical films, sensitive R&D. |
Ready to achieve the perfect vacuum environment for your thin film application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-performance lab equipment and expert support you need to master thin film deposition. Whether you are developing high-purity optical coatings or robust protective layers, our solutions ensure the process control and contamination-free environment essential for success.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can help you build superior thin films.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- Why is high vacuum level critical in vacuum systems for CVD diamond? Achieve Pure Crystalline Growth
- How does a continuous, single layer of graphene form from carbon species? Master the 4 Stages of Graphene Growth
- How thick is CVD diamond coating? Balancing Durability and Stress for Optimal Performance
- What is the temperature range for LPCVD? A Guide to Process Parameters by Material
- What is the general process of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Master High-Performance Thin-Film Growth
- What occurs during the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process for graphene growth? A Guide to High-Quality Synthesis
- What is the chemical vapor deposition technique involved in? A Guide to Thin-Film Synthesis
- What methods are used to deposit thin films? A Guide to PVD, CVD, and ALD Techniques



















