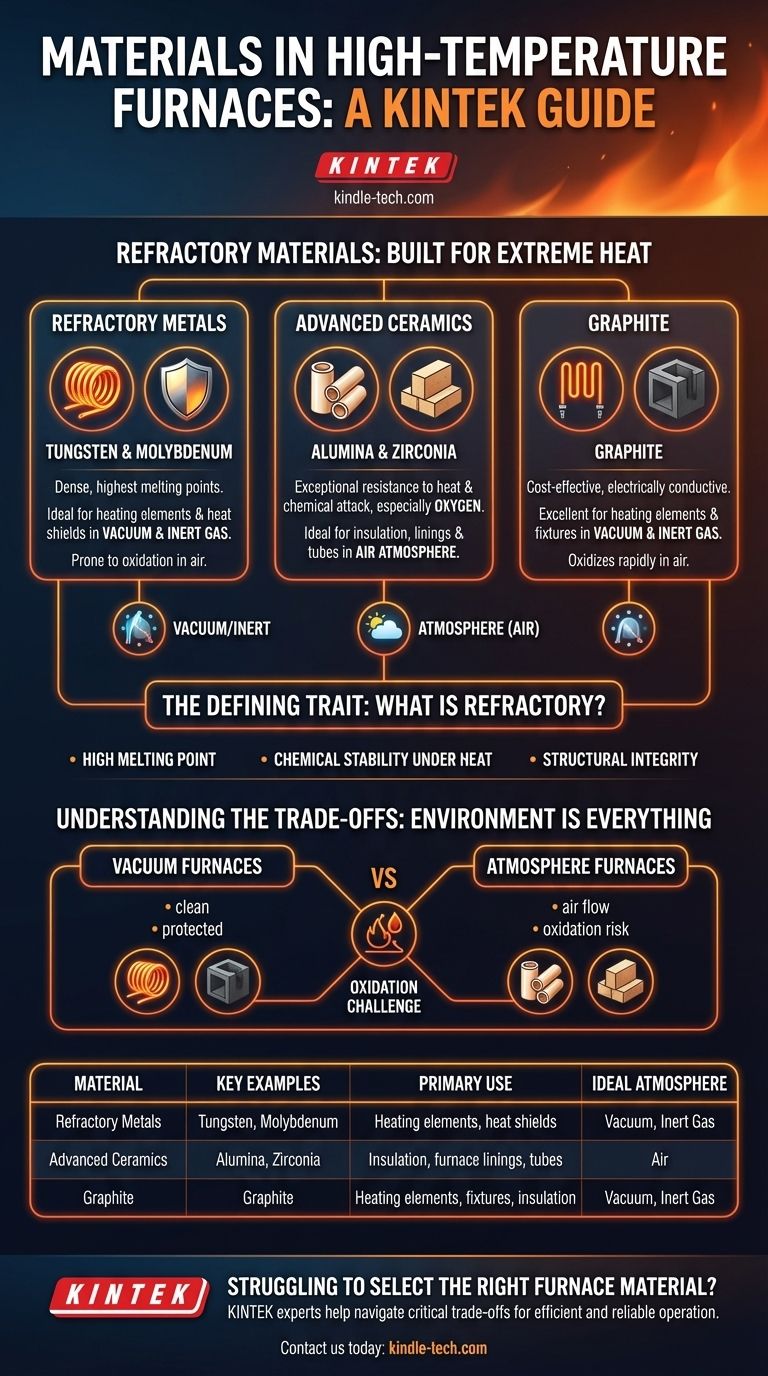
At their core, high-temperature furnaces are constructed from refractory materials. These specialized materials are chosen for their ability to withstand extreme heat and wear without breaking down. The primary categories include dense refractory metals, advanced ceramics, and specialized forms of graphite, each selected based on the furnace's intended temperature range and operating atmosphere.
The selection of a furnace material is not about finding one "best" option. It is a critical engineering decision that balances the material's melting point and chemical stability against the furnace's specific operating environment—primarily whether it operates with a vacuum, an inert gas, or in open air.

The Defining Trait: What is a Refractory Material?
A material is classified as "refractory" based on its ability to maintain its physical and chemical integrity at very high temperatures. This capability is not a single property but a combination of several key traits.
High Melting Point is Non-Negotiable
The most fundamental requirement is an exceptionally high melting point. The material used for the furnace's hot zone must remain solid and structurally stable well above the furnace's maximum operating temperature.
Chemical Stability Under Heat
A refractory material cannot react with the process atmosphere (e.g., air, nitrogen, argon) or the material being heated (the "workpiece"). Any chemical reaction would contaminate the workpiece and degrade the furnace itself.
Structural Integrity at Extreme Temperatures
Beyond just not melting, these materials must resist physical deformation, wear, and corrosion when hot. They exhibit slow diffusion rates, meaning their atoms do not readily migrate, which helps them maintain their shape and strength.
Key Material Categories in Furnace Construction
High-temperature furnaces are complex systems, often using different refractory materials for different components like heating elements, insulation, and structural supports.
Refractory Metals (Tungsten & Molybdenum)
These metals form the backbone of many ultra-high-temperature vacuum furnaces. They are incredibly dense, hard, and boast some of the highest melting points of all elements.
Tungsten and molybdenum are the most common choices for heating elements and heat shields inside a vacuum or inert gas environment.
Advanced Ceramics (Alumina, Zirconia)
Ceramics are compounds that are exceptionally resistant to heat and chemical attack, particularly from oxygen. This makes them ideal for applications where metals would fail.
They are frequently used as insulation, furnace linings, and structural components like tubes in tube furnaces, especially those that operate in an air atmosphere.
Graphite
Graphite is a form of carbon that can withstand extreme temperatures and is an excellent conductor of electricity, allowing it to be used as a heating element.
It is a common, cost-effective choice for heating elements, insulation, and structural fixtures in vacuum or inert atmosphere furnaces where oxidation is not a concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Environment is Everything
The choice between metals, ceramics, and graphite is almost entirely dictated by the furnace's internal atmosphere, as this determines the risk of oxidation.
The Problem of Oxidation
Refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum have a critical weakness: low resistance to oxidation. When exposed to oxygen at high temperatures, they react rapidly and are destroyed.
This is the single most important factor limiting their use. They cannot be used as heating elements in furnaces that operate in air.
Vacuum vs. Atmosphere Furnaces
This trade-off directly leads to two different design philosophies.
Vacuum furnaces remove the oxygen, creating an environment where refractory metals and graphite can operate safely at extreme temperatures. This is why they are standard for processes like vacuum sintering and coating.
Atmosphere furnaces that operate in air must rely on materials that are inherently stable in oxygen, making advanced ceramics the required choice for hot zone components.
Cost and Machinability
Practical considerations also play a role. Graphite is often less expensive and easier to machine into complex shapes than brittle ceramics or extremely hard refractory metals, making it a preferred choice for fixtures and supports in non-oxidizing environments.
Matching Material to Application
To make an informed decision, you must align the material's strengths with your primary processing goal.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures in a vacuum: Refractory metals like tungsten and molybdenum are the standard for heating elements and shielding.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing in an air atmosphere: Advanced ceramics are required for insulation, process tubes, and structural components due to their resistance to oxidation.
- If your primary focus is a cost-effective solution for non-oxidizing environments: Graphite is an excellent and versatile choice for both structural components and heating elements.
Understanding these material trade-offs allows you to select not just a furnace, but the right tool for your specific scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Use | Ideal Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refractory Metals | Tungsten, Molybdenum | Heating elements, heat shields | Vacuum, Inert Gas |
| Advanced Ceramics | Alumina, Zirconia | Insulation, furnace linings, tubes | Air |
| Graphite | Graphite | Heating elements, fixtures, insulation | Vacuum, Inert Gas |
Struggling to select the right furnace material for your high-temperature application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the critical trade-offs between refractory metals, ceramics, and graphite to ensure your furnace operates efficiently and reliably in your specific environment. Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your requirements and let us provide the ideal solution for your scientific or industrial goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What factors influence the general design of a tube furnace? Match Your Process with the Perfect System
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis



















