In short, induction technology can melt virtually any metal. The list includes all ferrous metals like iron and steel, non-ferrous metals like copper and aluminum, precious metals like gold and silver, and even high-performance superalloys. The key is not if a metal can be melted, but rather how its specific properties affect the efficiency of the process.
The fundamental principle of induction heating is that it works on any electrically conductive material. The real-world application, however, depends on matching the equipment's power and frequency to the unique magnetic and resistive properties of the specific metal you intend to melt.
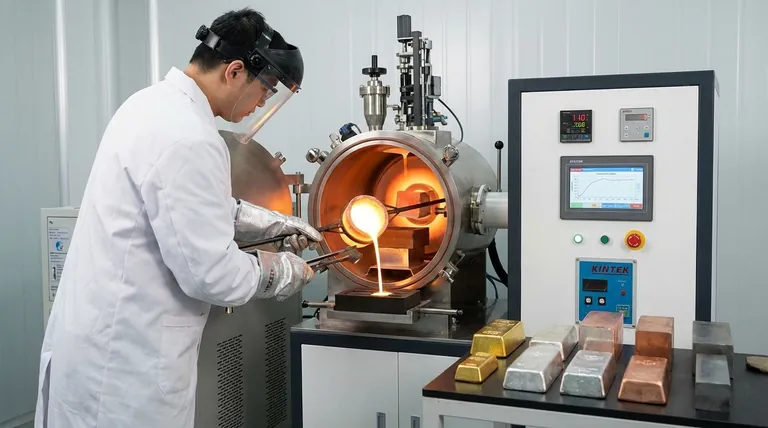

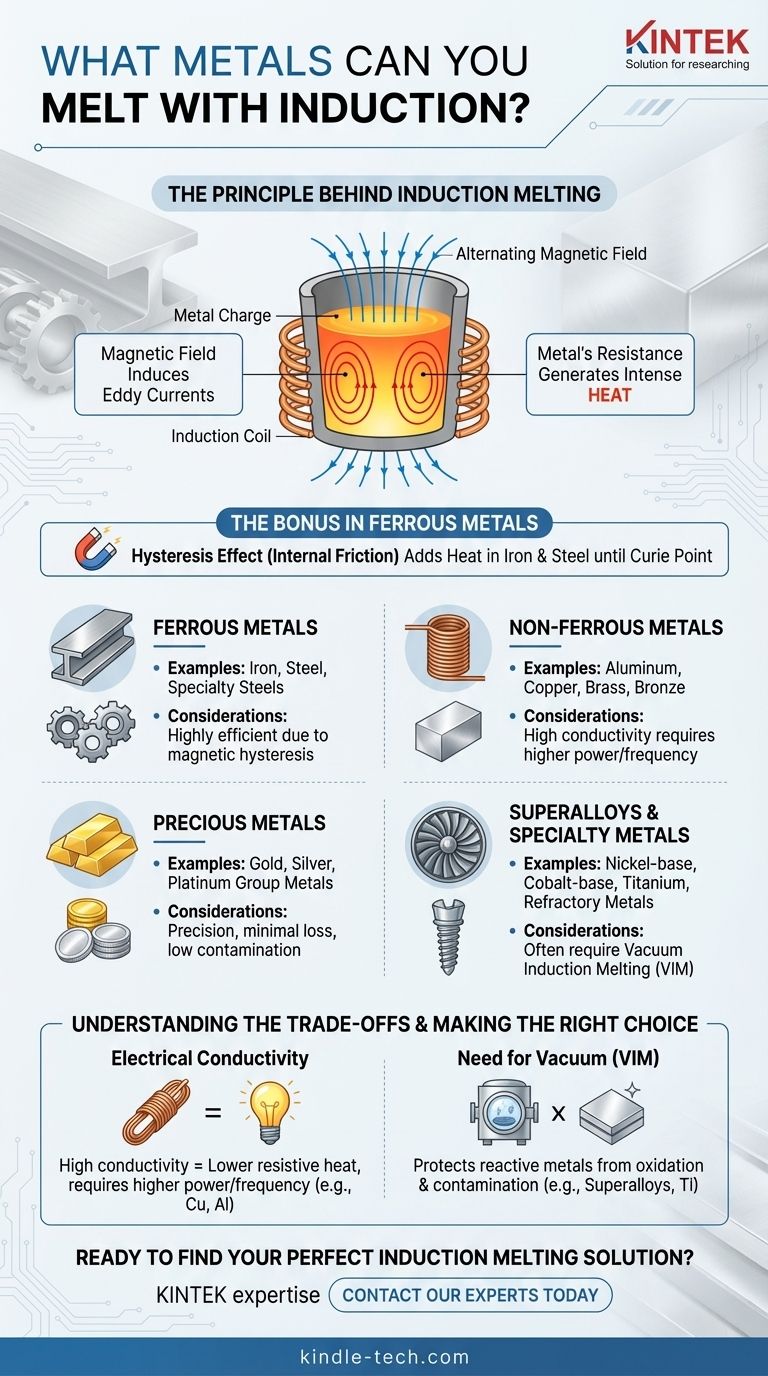
The Principle Behind Induction Melting
To understand which metals are suitable, you must first understand how induction works. It's not about external flames or heating elements; the heat is generated within the metal itself.
How Heat is Generated
Induction furnaces create a powerful, alternating magnetic field. When an electrically conductive metal is placed inside this field, it induces strong electrical currents, known as eddy currents, to flow within the metal.
The metal's natural electrical resistance opposes these currents, which generates intense and rapid heat. This is the primary mechanism for heating all conductive metals.
The Bonus Effect in Ferrous Metals
For magnetic metals like iron and steel, a secondary heating effect called hysteresis also occurs. The rapidly changing magnetic field causes the magnetic domains within the metal to flip back and forth, creating internal friction and additional heat. This makes induction exceptionally efficient for melting iron and steel, though this effect disappears once the metal passes its Curie temperature and loses its magnetic properties.
A Guide to Meltable Metals
Induction melting is remarkably versatile, covering nearly the entire spectrum of commercially and scientifically important metals.
Ferrous Metals
This is the most common application for induction furnaces. The magnetic properties of these metals make them heat very efficiently.
- Iron (Cast Iron, Ductile Iron)
- Steel (Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, Stainless Steel)
- Specialty Steels (Tool Steel, Bearing Steel, Heat-Resistant Steel)
Non-Ferrous Metals
These metals are not magnetic but are excellent electrical conductors. They melt cleanly and quickly with the right equipment setup.
- Aluminum
- Copper
- Brass and Bronze
Precious Metals
The precision and speed of induction make it ideal for working with high-value metals, where minimizing loss and contamination is critical.
- Gold and its alloys
- Silver and its alloys
- Platinum Group Metals (Platinum, Palladium, Rhodium)
Superalloys and Specialty Metals
For aerospace, medical, and other high-tech applications, induction melting is essential, often performed in a controlled environment.
- Nickel-base superalloys
- Cobalt-base superalloys
- Titanium (requires a vacuum or inert atmosphere)
- Refractory Metals
Understanding the Trade-offs
While almost any metal can be melted, its properties present unique challenges and considerations.
The Impact of Electrical Conductivity
Counter-intuitively, metals with very high electrical conductivity, like pure copper or aluminum, can be more challenging to heat. Their low resistance means the induced eddy currents flow easily, generating less resistive heat. This often requires furnaces with higher power or different operating frequencies to compensate.
The Need for a Vacuum
Many advanced alloys and reactive metals have a high affinity for oxygen and other atmospheric gases. Melting them in open air can lead to contamination and poor material quality.
This is why Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnaces are used. They perform the melting process in a vacuum, protecting metals like superalloys, stainless steel, and aluminum from oxidation and ensuring the final product meets stringent purity standards.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your specific objective dictates the type of induction system you need.
- If your primary focus is casting standard iron and steel: A coreless induction furnace is the industry standard, offering high efficiency and reliability.
- If your primary focus is melting aluminum or copper: You will require a system properly configured for high-conductivity metals, which may involve adjustments to power and frequency.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity superalloys or reactive metals: A vacuum induction melting (VIM) furnace is essential to prevent atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is working with precious metals: Your priority will be a system that offers precise temperature control and minimizes metal loss.
Ultimately, the versatility of induction melting ensures there is a solution for nearly any metallic material, provided the technology is applied correctly.
Summary Table:
| Metal Category | Key Examples | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Metals | Iron, Steel, Stainless Steel | Highly efficient due to magnetic hysteresis effect. |
| Non-Ferrous Metals | Aluminum, Copper, Brass | Require proper power/frequency due to high conductivity. |
| Precious Metals | Gold, Silver, Platinum | Ideal for precision and minimizing loss/contamination. |
| Superalloys & Reactive Metals | Titanium, Nickel alloys | Often require a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace. |
Ready to Find Your Perfect Induction Melting Solution?
Whether you are casting standard alloys or producing high-purity superalloys, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your lab's specific needs. Our range of induction furnaces, including vacuum models, ensures precise temperature control and minimal contamination for any metal.
Let's discuss your project. Contact our experts today to enhance your melting process efficiency and material quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision



















