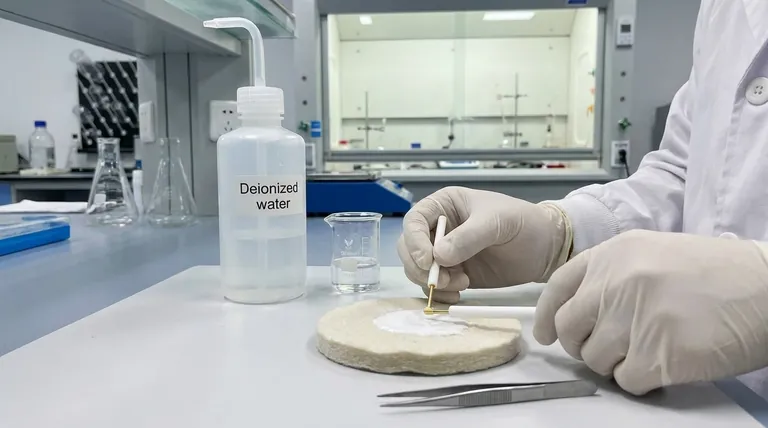
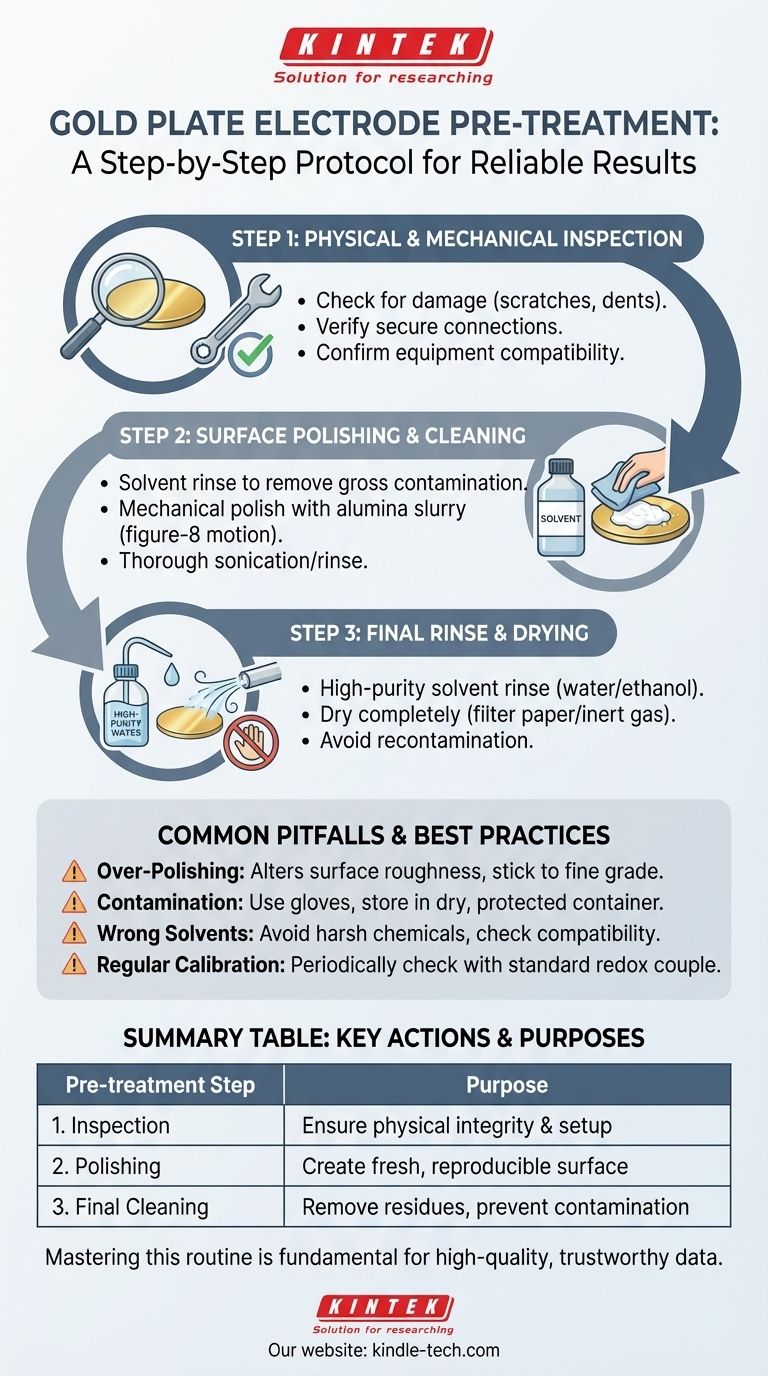
Before any experiment, a gold plate electrode must undergo a multi-step pre-treatment process to ensure its surface is clean, active, and reproducible. This procedure involves a thorough physical inspection for damage, a mechanical polishing step to create a fresh surface, and a final cleaning with high-purity solvents to remove all residues. These steps are critical for obtaining accurate and reliable electrochemical data.
The ultimate goal of pre-treatment is not just to clean the electrode, but to create a standardized and electrochemically active surface. Failing to do so is the most common source of unreliable and non-reproducible experimental results.

The Essential Pre-treatment Protocol
A systematic approach ensures the electrode is in optimal condition. The process can be broken down into three core stages: inspection, polishing, and final cleaning.
Step 1: Physical and Mechanical Inspection
Before any cleaning, perform a careful visual and physical check.
Inspect the electrode surface for any obvious physical damage, such as deep scratches, dents, or deformation. A compromised surface can lead to inconsistent current distribution and flawed results.
Verify all connections are secure. A loose connection between the electrode and the holder or lead wire can introduce significant noise and experimental error.
Confirm equipment compatibility. Check that the electrode's size, shape, and connection method are appropriate for your electrochemical cell and holder to ensure a proper fit and secure setup.
Step 2: Surface Polishing and Cleaning
This is the most critical stage for creating a fresh, reproducible surface.
Begin with a solvent rinse. If the electrode has visible dirt or residue, gently wipe it with a soft cloth moistened with pure water, ethanol, or acetone. This removes gross contamination before polishing.
Perform mechanical polishing. Place a small amount of alumina polishing powder (starting with a larger grit like 1.0 µm and finishing with 0.05 µm) onto a polishing cloth. Moisten the cloth with deionized water to create a slurry.
Use a figure-'8' motion. Hold the electrode vertically against the polishing pad and move it in a figure-'8' or circular pattern. This ensures the surface is polished evenly without creating directional grooves.
Rinse thoroughly. After polishing, sonicate or rinse the electrode extensively with deionized water to remove all alumina particles. A final rinse with ethanol can help remove any remaining organic residue.
Step 3: Final Rinse and Drying
The final step ensures no contaminants remain from the cleaning process itself.
Use high-purity solvents. Rinse the electrode one last time with fresh deionized water and then ethanol to displace the water.
Dry the surface completely. Gently dry the electrode with filter paper or a stream of inert gas. Ensure it is perfectly dry before immersing it in the electrolyte to avoid unwanted dilution or side reactions.
Avoid recontamination. Never touch the electrode surface with your bare hands after cleaning, as skin oils will immediately contaminate it.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
Proper pre-treatment is a skill. Awareness of common mistakes is key to mastering the technique and ensuring long-term electrode health.
The Risk of Over-Polishing
While polishing is essential, excessive or overly aggressive polishing can alter the electrode's surface roughness or even change its geometric area over time, affecting quantitative measurements. Stick to the finest grade of polish necessary to achieve a clean, mirror-like finish.
Contamination from Handling and Storage
The most pristine surface can be instantly ruined by improper handling. Always use clean gloves or tweezers. After an experiment, immediately rinse the electrode and store it in a dry, protected container away from corrosive fumes (especially those containing sulfur or chlorine).
Choosing the Right Solvents
While water, ethanol, and acetone are generally safe for gold, avoid harsh organic solvents or strong acids unless specified by a particular protocol. These can attack the electrode's insulating body (e.g., PEEK or Teflon) or mounting materials.
The Need for Regular Calibration
For highly precise measurements, the electrode's performance should be periodically checked using a standard electrochemical system, such as the ferricyanide/ferrocyanide redox couple. This helps verify that the pre-treatment protocol is effective and the electrode is behaving as expected.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The required rigor of pre-treatment depends on the sensitivity of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is routine screening or qualitative analysis: A thorough cleaning with solvents and a careful inspection may be sufficient, especially if the electrode was stored properly.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis or sensitive measurements: A full mechanical polishing protocol is non-negotiable to ensure a reproducible surface area and active state for every experiment.
- If you are using a new or long-stored electrode: Always perform the complete inspection and mechanical polishing protocol to remove any passive layers and establish a reliable baseline for its performance.
Mastering this pre-treatment routine is a fundamental step toward achieving high-quality, trustworthy electrochemical data.
Summary Table:
| Pre-treatment Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Inspection | Check for damage, verify connections | Ensure physical integrity and proper setup |
| 2. Polishing | Use alumina slurry in a figure-8 motion | Create a fresh, reproducible surface |
| 3. Final Cleaning | Rinse with high-purity solvents (water/ethanol) | Remove all residues and prevent contamination |
Achieve peak performance and data reliability in your lab. Proper electrode pre-treatment is fundamental to successful electrochemistry. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including electrodes and polishing supplies, to support your precise laboratory needs. Let our experts help you optimize your processes. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Gold Electrochemical Sheet Electrode Gold Electrode
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Graphite Disc Rod and Sheet Electrode Electrochemical Graphite Electrode
People Also Ask
- What are the key aspects of maintaining and caring for a gold plate electrode? Preserve Performance and Extend Lifespan
- What is the material and purity of a gold disc electrode? Ensuring Precision in Electrochemical Analysis
- What is the proper post-treatment and storage procedure for a gold disc electrode? Ensure Reliable Electrochemical Data
- How should a gold disc electrode be maintained for long-term use? A Guide to Consistent Performance
- What is the typical role of a gold disc electrode in an electrochemical setup? Your Guide to a Precise Working Electrode



















