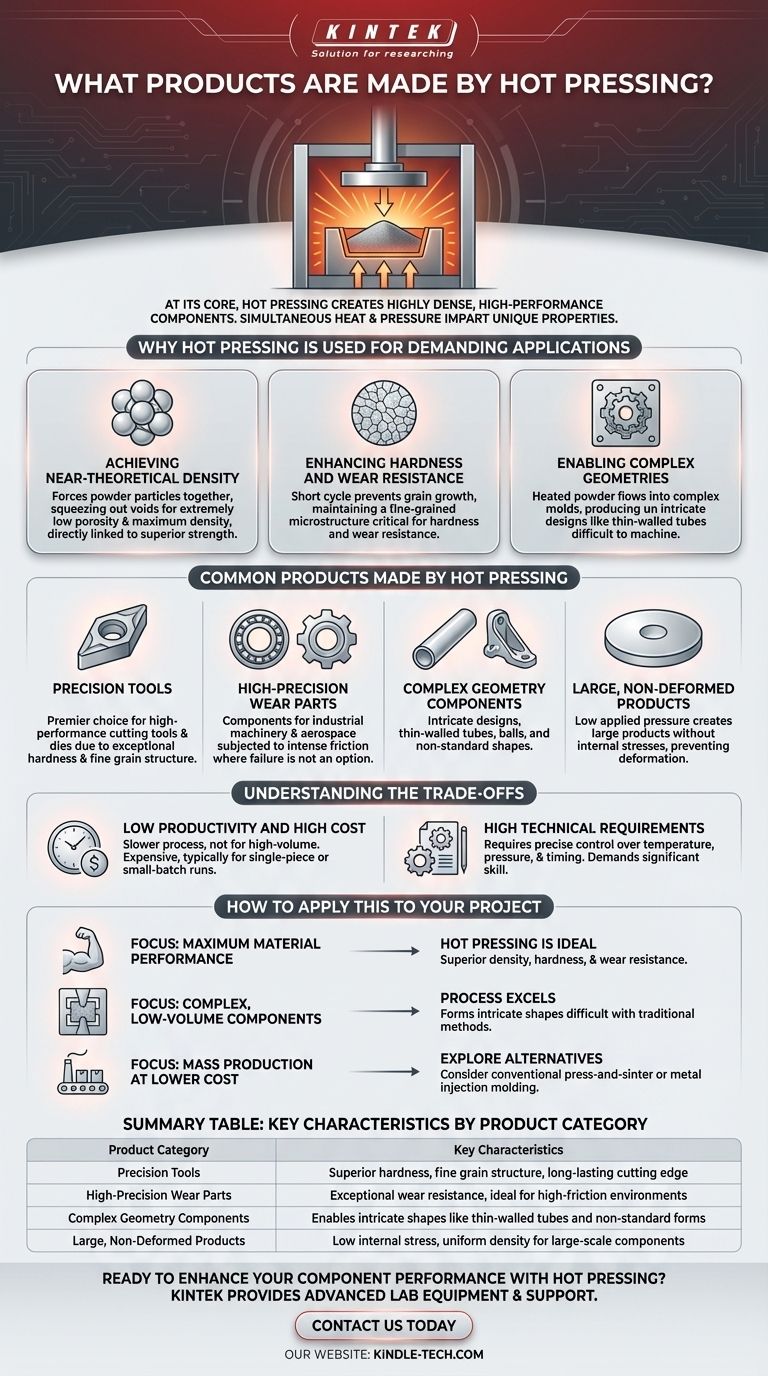
At its core, hot pressing is used to create highly dense, high-performance components where material integrity is paramount. This specialized manufacturing process is ideal for producing products like precision cutting tools, critical wear-resistant parts, and components with complex geometries, such as thin-walled tubes and cemented carbide parts.
Hot pressing is not a method for mass production. It is a targeted process chosen specifically to create components with near-perfect density and superior mechanical properties, making it essential for applications where performance and durability justify a higher cost.

Why Hot Pressing is Used for Demanding Applications
Hot pressing is a powder metallurgy process where pressing and sintering (heating to bond the material) occur simultaneously in a single step. This combination of high temperature and pressure imparts unique and valuable characteristics to the final product.
Achieving Near-Theoretical Density
The simultaneous application of heat and pressure forces powder particles together, effectively squeezing out the voids or pores that are common in other manufacturing methods.
This results in a product with extremely low porosity and a density that approaches the material's theoretical maximum. This high density is directly linked to superior strength and performance.
Enhancing Hardness and Wear Resistance
The hot pressing cycle is often relatively short. This prevents the microscopic grains within the material from growing too large through a process called recrystallization.
Maintaining a fine-grained microstructure is critical for materials like cemented carbide, as it significantly enhances the product's hardness and resistance to wear, making it ideal for tools and high-friction parts.
Enabling Complex Geometries
During hot pressing, the heated powder material exhibits good fluidity, allowing it to fill complex mold shapes.
This makes it possible to produce intricate designs, such as thin-walled tubes, balls, and other non-standard shapes, that would be difficult or costly to machine from a solid block of material.
Common Products Made by Hot Pressing
The unique benefits of the process make it suitable for a specific range of high-value products where standard manufacturing falls short.
Precision Tools
The exceptional hardness and wear resistance achieved through hot pressing make it a premier choice for manufacturing high-performance cutting tools and dies. The fine grain structure ensures a durable, long-lasting cutting edge.
High-Precision Wear Parts
Any component subjected to intense friction and wear can benefit from hot pressing. This includes parts for industrial machinery, aerospace applications, and other environments where component failure is not an option.
Large, Non-Deformed Products
Because the applied pressure is relatively low compared to cold pressing, hot pressing can be used to create large products without introducing the internal stresses that can lead to deformation or warping.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is not a universal solution. Its specialized nature comes with clear limitations that are critical to understand.
Low Productivity and High Cost
Hot pressing is a slower, more deliberate process than other manufacturing methods. It is not suitable for high-volume production, making it a more expensive option typically reserved for single-piece or small-batch runs.
High Technical Requirements
The process requires precise control over temperature, pressure, and timing. Operating the equipment demands significant technical skill and expertise to achieve consistent, high-quality results.
Limitations in Part Length
While excellent for complex shapes, the process can struggle with very long or slender parts. Achieving a uniform density along the entire length of a long component can be challenging, potentially creating weak points.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Choosing a manufacturing process depends entirely on balancing the performance requirements of the final product with the realities of production cost and volume.
- If your primary focus is maximum material performance: Hot pressing is the ideal choice for creating parts with superior density, hardness, and wear resistance.
- If you are producing complex, low-volume components: The process excels at forming intricate shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional machining or casting.
- If your goal is mass production at a lower cost: You should explore alternative methods like conventional press-and-sinter powder metallurgy or metal injection molding.
Ultimately, choosing hot pressing is a strategic decision to prioritize absolute material integrity and performance over production speed and cost.
Summary Table:
| Product Category | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Precision Tools | Superior hardness, fine grain structure, long-lasting cutting edge |
| High-Precision Wear Parts | Exceptional wear resistance, ideal for high-friction environments |
| Complex Geometry Components | Enables intricate shapes like thin-walled tubes and non-standard forms |
| Large, Non-Deformed Products | Low internal stress, uniform density for large-scale components |
Ready to enhance your component performance with hot pressing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables to support your high-performance manufacturing needs. Whether you're developing precision tools, wear-resistant parts, or complex components, our expertise in materials science and processing can help you achieve superior density, hardness, and durability.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your hot pressing applications and deliver the material integrity your projects demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Electric Heated Hydraulic Vacuum Heat Press for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace facilitate the consolidation of (Cu–10Zn)-Al2O3 nanocomposites?
- What is the significance of precise temperature control in melt infiltration? Achieve High-Performance Li-Alloy Electrodes
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results



















