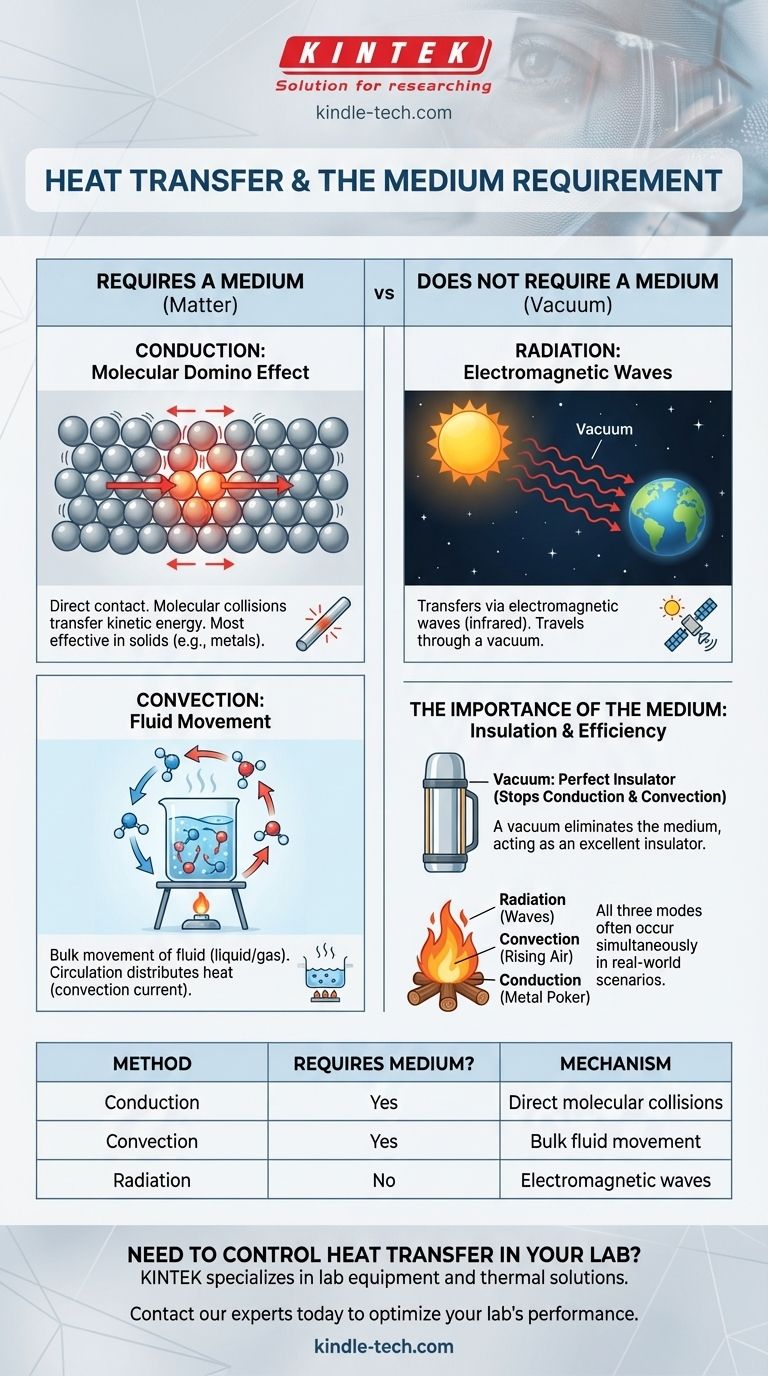
Both conduction and convection are the forms of heat transfer that require a medium. These processes rely on the interactions between particles or the bulk movement of a fluid to move thermal energy from one place to another. In contrast, thermal radiation can transfer heat through the vacuum of space, as it travels via electromagnetic waves.
The fundamental distinction between heat transfer methods is not merely the presence of a medium, but how that medium participates. Conduction uses molecular collisions, convection uses fluid movement, and radiation bypasses a medium altogether.

Understanding Heat Transfer Through a Medium
To grasp why some methods require a medium, we must look at their physical mechanisms. Both conduction and convection are fundamentally tied to the behavior of matter.
Conduction: The Molecular Domino Effect
Conduction is heat transfer through direct contact. It occurs when more energetic particles vibrate and collide with their less energetic neighbors, transferring kinetic energy.
This process is like a line of dominoes. The first domino doesn't travel to the end of the line; it simply tips over and transfers its energy to the next one, creating a chain reaction.
Conduction can happen in solids, liquids, and gases, but it is most effective in solids with tightly packed particles, like metals.
Convection: The Movement of a Heated Fluid
Convection is heat transfer through the bulk movement of fluids (liquids or gases). When a part of a fluid is heated, it expands, becomes less dense, and rises.
Cooler, denser fluid then sinks to take its place, gets heated, and rises in turn. This continuous circulation, called a convection current, distributes heat throughout the fluid.
A classic example is a pot of boiling water. The water at the bottom is heated by conduction from the stove, then rises via convection, transferring heat to the rest of the water.
The Exception: Heat Transfer Without a Medium
The third method of heat transfer operates on a completely different principle, allowing it to work where the others cannot.
Radiation: Heat as an Electromagnetic Wave
Thermal radiation transfers heat in the form of electromagnetic waves, primarily in the infrared spectrum. All objects with a temperature above absolute zero emit thermal radiation.
Unlike conduction or convection, these waves do not need any matter to propagate. They can travel through the emptiness of a vacuum.
This is how the Sun's energy travels 93 million miles through the vacuum of space to warm the Earth. It's also the heat you feel from a glowing campfire or a hot electric burner from a distance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
The requirement of a medium has critical real-world implications for insulation, heating, and engineering design.
How a Medium Dictates Efficiency
The type of medium dramatically affects the rate of heat transfer. For conduction, dense materials like metals are excellent conductors, while materials like wood or foam are poor conductors, making them good insulators.
For convection, the viscosity and thermal properties of the fluid determine how effectively currents can form and transfer heat. This is why forced-air heating systems (using a fan to force convection) heat a room much faster than passive radiators.
The Role of a Vacuum as an Insulator
Because conduction and convection require a medium, a vacuum is the perfect insulator against them. By removing the particles, you remove the mechanism for transfer.
This is the principle behind a thermos or a double-paned window. The vacuum layer between the inner and outer walls nearly eliminates heat transfer by conduction and convection, keeping the contents hot or cold.
When All Three Occur at Once
In most real-world scenarios, all three modes of heat transfer happen simultaneously. Consider a campfire:
- Radiation is the heat you feel on your face as you stand near the fire.
- Convection is the hot air and smoke rising above the flames.
- Conduction is the heat that travels up a metal poker you leave in the coals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding these mechanisms allows you to control heat flow based on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is insulation: Your goal is to stop conduction and convection, which is why a vacuum or materials that trap air (a poor conductor) are so effective.
- If your primary focus is rapidly heating a fluid: Convection is your most powerful tool, as it uses the movement of the medium itself to efficiently distribute heat.
- If your primary focus is transferring heat across a distance without contact: Radiation is your only option, as it does not rely on a physical medium.
Mastering how each method uses, or bypasses, a medium is the key to designing any effective thermal system.
Summary Table:
| Heat Transfer Method | Requires a Medium? | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Conduction | Yes | Direct molecular collisions and energy transfer. |
| Convection | Yes | Bulk movement of a heated fluid (liquid or gas). |
| Radiation | No | Transfer via electromagnetic waves (e.g., infrared). |
Need to Control Heat Transfer in Your Lab?
Whether you're designing an efficient heating system or require precise thermal insulation for an experiment, understanding these principles is critical. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise to help you master thermal processes. From high-temperature furnaces to custom insulation solutions, we support your laboratory's unique needs.
Contact our thermal experts today to discuss how we can help optimize your lab's performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- What are the advantages of torch brazing? Discover the Superior Control of Modern Brazing
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space



















