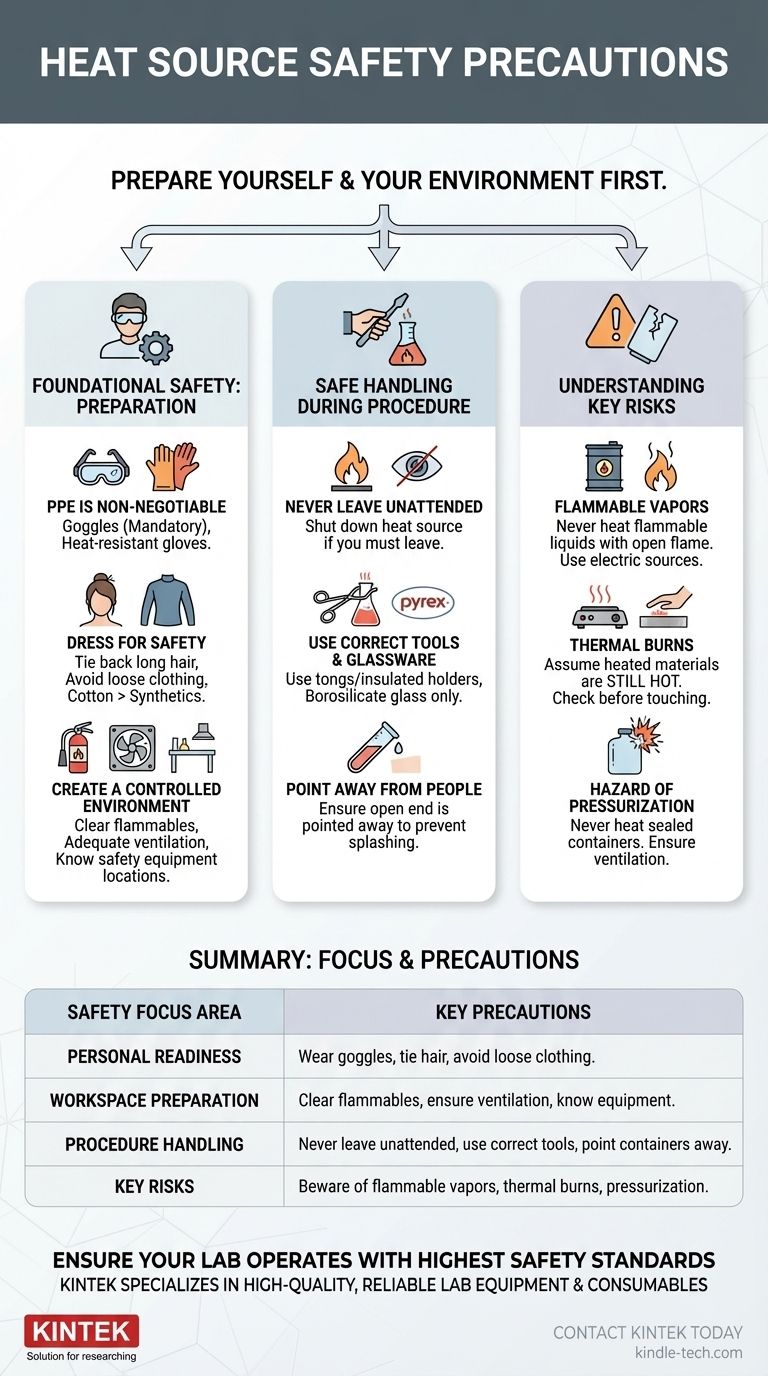
To work safely with any heat source, you must first prepare yourself and your immediate environment. This involves tying back long hair, wearing tight-fitting clothing or short sleeves to prevent accidental contact or ignition, and always wearing safety goggles to protect your eyes from splashes or projectiles.
The core principle of heat safety is not just following a list of rules, but creating a controlled environment. This means preparing yourself, your workspace, and your emergency plan before the heat is ever applied.

Foundational Safety: Preparing Yourself and Your Workspace
Proper preparation is the most critical phase of heat safety. An accident is far less likely to occur in a well-prepared environment with a well-prepared operator.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) is Non-Negotiable
Your first line of defense is what you wear. Safety goggles are mandatory to shield your eyes from chemical splashes, which can become more dangerous when heated.
Depending on the task, heat-resistant gloves are also essential. Always ensure you are using the correct personal protective equipment for the specific materials and temperatures involved.
Dress for Safety, Not for Style
The guidance to tie back long hair and avoid loose clothing is about preventing the most common and dangerous type of accident: fire. Loose hair, baggy sleeves, or dangling accessories can easily catch fire or knock over equipment.
Always opt for tight-fitting sleeves or roll them up securely. Natural fibers like cotton are often safer than synthetics, which can melt onto your skin if they ignite.
Create a Controlled Environment
Your workspace must be clear of all unnecessary items, especially flammable materials like paper, solvents, or excess chemicals.
Ensure you have adequate ventilation, as heating substances can produce harmful fumes. Crucially, know the location and proper use of safety equipment like the fire extinguisher, fire blanket, and first-aid kit before you begin.
Safe Handling During a Procedure
Once you are prepared, your focus must shift to the active handling of the heat source and the materials being heated.
Never Leave a Heat Source Unattended
This is the cardinal rule of working with heat. An unwatched procedure can quickly escalate into a fire or other hazardous situation. If you must leave the area, shut down the heat source completely.
Use the Correct Tools and Glassware
Always handle hot objects with the appropriate tools, such as tongs or insulated holders. Never use your hands, even if you are wearing gloves not specifically rated for high temperatures.
Furthermore, use only glassware designed for heating, such as borosilicate glass (e.g., Pyrex or Kimax). Standard glass can shatter from thermal shock when heated, creating a significant hazard.
Point Materials Away From People
When heating a substance in a test tube or other container, always ensure the open end is pointed away from yourself and anyone else in the vicinity. This prevents injury in the event of an unexpected splash or rapid boiling.
Understanding the Key Risks
Being aware of what can go wrong is essential for preventing it. Heat introduces specific hazards that are not present at room temperature.
The Danger of Flammable Vapors
Many organic solvents are highly flammable, and their vapors can ignite from a distant spark or heat source. Never heat flammable liquids with an open flame. Use a controlled electric source like a heating mantle or a steam bath instead.
The Risk of Thermal Burns
Direct contact with a flame or hotplate is an obvious danger. A more subtle risk comes from heated materials, like metal and glass, which can look cool long after the heat has been removed. Always assume objects that have been heated are still hot until you can verify otherwise.
The Hazard of Pressurization
Never heat a completely sealed container. As the substance inside heats up, it expands, creating immense pressure that can cause the container to explode violently. Always ensure the system is open to the atmosphere or properly vented.
A Simple Checklist for Heat Safety
Use these points to guide your actions and ensure you are working safely and effectively.
- If your primary focus is personal readiness: Ensure you are wearing appropriate PPE (goggles, at minimum), have secured loose hair and clothing, and are mentally focused on the task.
- If your primary focus is workspace preparation: Clear all flammable materials from the area, confirm proper ventilation, and verify the location of all safety equipment.
- If your primary focus is the procedure itself: Never leave the heat source unattended, use the correct tools for handling, and point all containers away from people.
Ultimately, safety is an active process, not a passive one; it requires your constant and deliberate attention.
Summary Table:
| Safety Focus Area | Key Precautions |
|---|---|
| Personal Readiness | Wear safety goggles, tie back long hair, avoid loose clothing. |
| Workspace Preparation | Clear flammable materials, ensure ventilation, know safety equipment location. |
| Procedure Handling | Never leave heat source unattended, use correct tools (tongs), point containers away from people. |
| Key Risks | Beware of flammable vapors, thermal burns, and pressurization in sealed containers. |
Ensure your lab operates with the highest safety standards. Proper equipment is fundamental to safe procedures. KINTEK specializes in high-quality, reliable lab equipment and consumables, including safe heating apparatus, designed to meet the rigorous demands of laboratory environments. Let us help you build a safer, more efficient workspace.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your lab's specific needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your safety protocols.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- At what temperature is conventional pyrolysis done? Unlock the Right Temperature for Your Desired Product
- What is the flash sintering process? Revolutionize Your Materials Processing in Seconds
- What temp does THC bind with oil? Mastering the Two-Stage Process for Perfect Potency
- Why is biochar controversial? Balancing Climate Promise with Real-World Risks
- What is the range of RF sputtering? Expanding Your Thin Film Capabilities Beyond Metals
- What role does convection play in heat transfer? Understanding Heat Movement in Fluids
- What are the key differences between incineration and gasification? Explore Waste Management Solutions
- Does sintering increase conductivity? Yes, by transforming powders into dense, conductive solids.



















