In short, an induction furnace can melt virtually any type of electrically conductive metal scrap. This includes a vast range of both ferrous (iron-based) and non-ferrous metals. The key isn't a limited list of usable materials, but rather the quality, cleanliness, and density of the scrap being charged into the furnace.
The versatility of an induction furnace allows it to melt almost any conductive metal. However, the success and efficiency of the process are determined not by the type of metal, but by the physical and chemical quality of the scrap material itself.

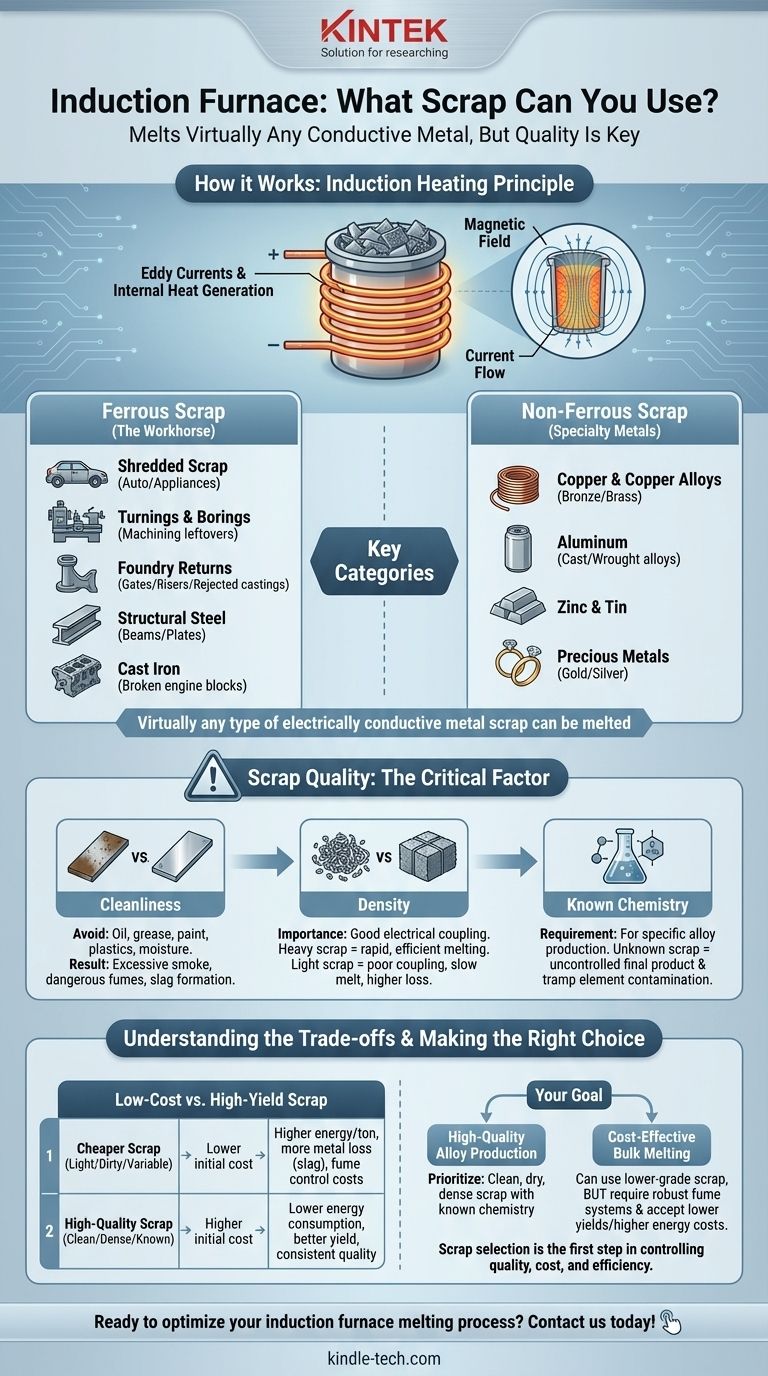
How an Induction Furnace Actually Works
To understand what scrap can be used, you must first understand the principle of induction. An induction furnace does not use external heating elements to melt metal.
The Principle of Induction Heating
Think of the furnace's coil as the primary winding of a transformer, and the metal scrap placed inside as a single-turn secondary winding. When a powerful alternating current flows through the coil, it creates a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field.
This magnetic field induces powerful eddy currents within the metal scrap. The inherent electrical resistance of the metal opposes this current flow, generating intense heat and causing the scrap to melt from the inside out.
The Primary Categories of Scrap
Because the process relies on electrical conductivity, the list of suitable materials is extensive. It is typically broken down into two main families.
Ferrous Scrap (The Workhorse)
This is the most common category of scrap melted in induction furnaces, especially in steel mills and iron foundries.
Examples include:
- Shredded Scrap: From automobiles and appliances.
- Turnings and Borings: Leftover material from machining operations.
- Foundry Returns: Gates, risers, and rejected castings from a foundry's own process.
- Structural Steel: Cuttings from beams, plates, and construction demolition.
- Cast Iron: Broken engine blocks and machinery parts.
Non-Ferrous Scrap (Specialty Metals)
Induction furnaces are also exceptionally effective for melting non-ferrous metals, which often require precise temperature control.
Examples include:
- Copper and Copper Alloys: Including bronze and brass.
- Aluminum: Both cast and wrought alloys.
- Zinc and Tin.
- Precious Metals: Such as gold and silver in specialized applications.
Why Scrap Quality is More Important Than Scrap Type
Simply knowing a furnace can melt a certain metal is only the beginning. The physical and chemical condition of that scrap is what dictates the efficiency, safety, and quality of the final product.
The Critical Need for Cleanliness
Contaminants are the primary enemy of a good melt. Oil, grease, paint, plastics, and moisture on scrap will burn off, creating excessive smoke, dangerous fumes, and potential hydrogen pickup in the metal. Sand and dirt will form slag (impurities), leading to lower metal yield.
The Role of Density
The efficiency of the induction process depends on good electrical "coupling" between the coil and the charge. Dense, heavy scrap (like cut-up solids or bales) couples very well, leading to rapid and energy-efficient melting. Light, loose scrap (like fine turnings) has poor coupling, takes longer to melt, and has more surface area exposed to oxygen, which can increase metal loss.
The Requirement of Known Chemistry
To produce a specific alloy, you must know the chemical composition of what you are melting. Charging scrap with unknown or mixed alloys makes it impossible to control the final chemistry of the product. Tramp elements (unwanted impurities) from one piece of scrap can ruin an entire batch of metal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of scrap is always a balance between cost and quality. Understanding the compromises is essential for any foundry or mill manager.
Low-Cost vs. High-Yield Scrap
Cheaper scrap is often lighter, dirtier, or has a more variable chemistry. While the initial purchase price is low, it results in higher energy consumption per ton, greater metal loss to slag, and increased costs for environmental fume control.
Contamination Risks
Using lower-grade scrap increases the risk of introducing harmful elements into your melt. For example, a small amount of lead or zinc in an iron melt can compromise the final casting's mechanical properties. This risk must be managed with careful scrap inspection and sorting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the right scrap depends entirely on the objective of your melting operation.
- If your primary focus is high-quality alloy production: Prioritize clean, dry, and dense scrap with a known and certified chemical composition.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective bulk melting: You may use lower-grade scrap, but you must invest in robust fume extraction systems and be prepared for lower metal yields and higher energy costs.
Choosing the right scrap is the first and most critical step in controlling the quality, cost, and efficiency of your entire melting process.
Summary Table:
| Scrap Category | Key Examples | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Ferrous Scrap | Shredded auto scrap, turnings, foundry returns, structural steel, cast iron | Most common; requires cleanliness and density for efficiency |
| Non-Ferrous Scrap | Copper, aluminum, zinc, precious metals (gold, silver) | Ideal for precise temperature control; known chemistry is critical |
| Scrap Quality Factors | Cleanliness, density, known chemistry | Directly impacts melting efficiency, safety, and final product quality |
Ready to optimize your induction furnace melting process? The right scrap selection is crucial for achieving high-quality results and cost efficiency. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing top-tier lab equipment and consumables tailored to your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you're melting ferrous or non-ferrous metals, our expertise ensures you get the most out of your operation. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your melting goals with reliable solutions and expert guidance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the vacuum induction method? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Advanced Alloys



















