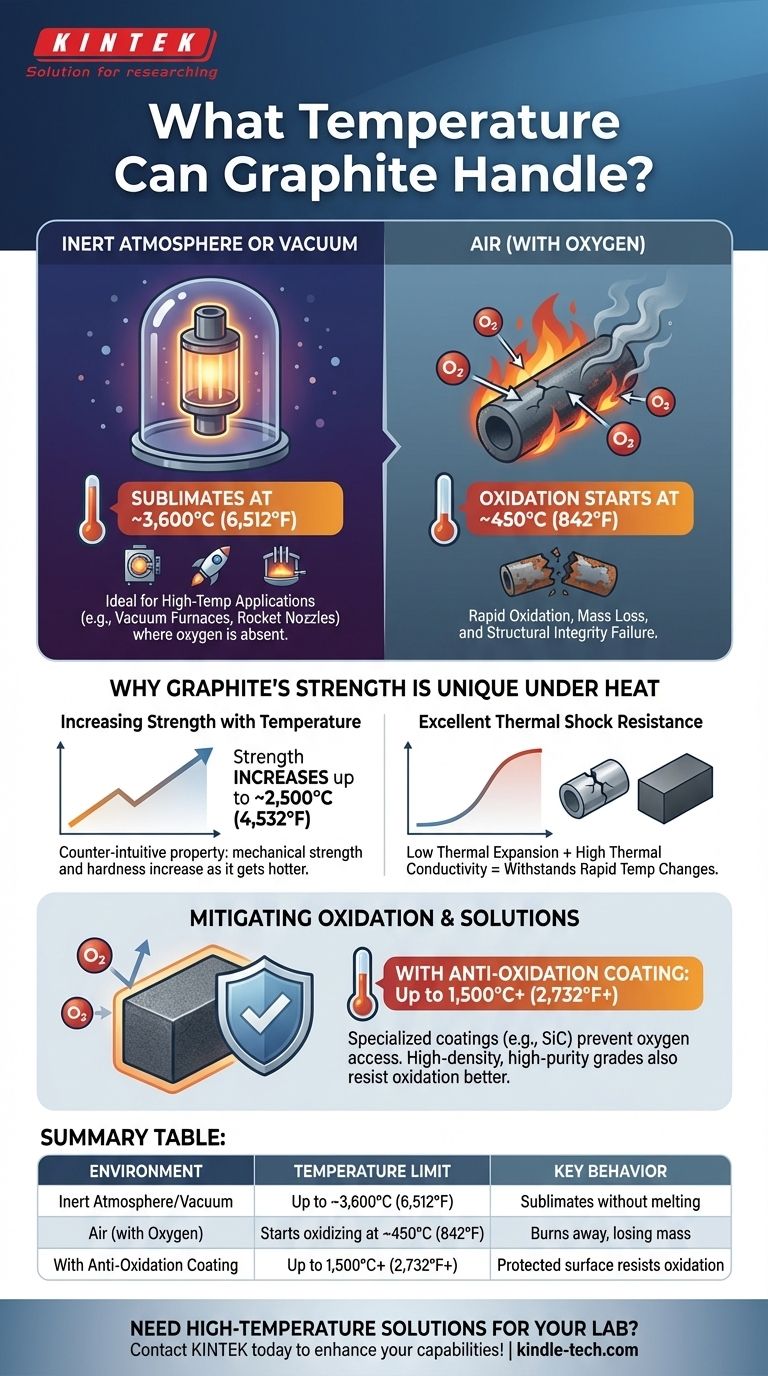
Ultimately, graphite’s maximum temperature depends entirely on its environment. In an inert atmosphere or vacuum, it is one of the most heat-resistant materials known, sublimating (turning from a solid directly to a gas) at approximately 3,600°C (6,512°F). However, in the presence of oxygen, its practical temperature limit is drastically lower, as it will begin to oxidize and burn away at temperatures as low as 450°C (842°F).
The core issue is not graphite's melting point—it doesn't truly melt under normal pressure—but the stark difference between its theoretical heat limit in a vacuum and its practical heat limit in air due to oxidation.

The Two Extremes: Inert vs. Oxygen Environments
The answer to "what temperature can graphite handle?" is a tale of two completely different scenarios. The presence or absence of oxygen is the single most important factor.
In an Inert Atmosphere or Vacuum
Graphite does not have a melting point at atmospheric pressure. Instead, when heated to extreme temperatures without oxygen, it sublimates.
This process begins around 3,600°C (6,512°F). This makes it an exceptional material for applications like vacuum furnace components, rocket nozzles, and electrodes in arc furnaces where oxygen is not present.
In the Presence of Oxygen (Air)
This is the limiting factor for most common applications. When exposed to oxygen, graphite begins to oxidize, a chemical reaction that is essentially a slow burn, converting the carbon into CO and CO2 gas.
This oxidation process can begin at temperatures as low as 450°C (842°F). The rate of oxidation accelerates rapidly as the temperature increases, meaning the graphite component will lose mass and structural integrity.
Why Graphite's Strength Is Unique Under Heat
Unlike metals, which soften and lose strength as they get hotter, graphite exhibits a remarkable and counter-intuitive property.
Increasing Strength with Temperature
Graphite's mechanical strength and hardness actually increase with temperature. This effect continues up to approximately 2,500°C (4,532°F), where its strength can be up to twice its value at room temperature.
This makes it an ideal structural material for high-temperature applications, provided the oxidation issue is managed.
Excellent Thermal Shock Resistance
Graphite has a very low coefficient of thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity. This combination means it can withstand rapid and extreme changes in temperature without cracking, a phenomenon known as thermal shock.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Solutions
Choosing graphite requires acknowledging its primary weakness and knowing how to mitigate it.
The Oxidation Problem
The tendency to oxidize is graphite's main disadvantage. For any application in air above 500°C, you cannot use standard graphite and expect it to survive. The material will simply burn away.
Mitigating Oxidation with Coatings
To overcome this limitation, graphite can be treated with anti-oxidation coatings. Materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or specialized ceramic paints form a protective barrier.
These coatings prevent oxygen from reaching the graphite surface, significantly increasing its effective operating temperature in air, sometimes up to 1,500°C (2,732°F) or higher depending on the coating's quality.
The Role of Grade and Density
The exact temperature at which oxidation begins is also influenced by the graphite's physical properties. Higher-density, higher-purity isostatic graphite will resist oxidation better than a lower-density, porous grade of graphite.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the right approach, you must first define your operating environment.
- If your primary focus is use in a vacuum or inert gas: Graphite is an outstanding choice, remaining stable and strong up to its sublimation point of approximately 3,600°C.
- If your primary focus is use in open air below 450°C: Standard graphite grades are perfectly suitable and cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature use in air (above 500°C): You must either use graphite with an anti-oxidation coating or select a different ceramic material.
Understanding the critical impact of the surrounding atmosphere is the key to successfully using graphite in any high-temperature design.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Temperature Limit | Key Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Inert Atmosphere / Vacuum | Up to ~3600°C (6512°F) | Sublimates without melting |
| Air (with Oxygen) | Starts oxidizing at ~450°C (842°F) | Burns away, losing mass |
| With Anti-Oxidation Coating | Up to 1500°C+ (2732°F+) | Protected surface resists oxidation |
Need high-temperature solutions for your lab? Graphite's performance depends heavily on the right environment and protective measures. At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including high-temperature components and materials designed for your specific applications. Whether you're working with vacuum furnaces, inert atmospheres, or require oxidation-resistant materials, our experts can help you select the right graphite products or alternatives.
Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's high-temperature capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why can graphite conduct heat? Unlocking Its Anisotropic Thermal Properties
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C
- What is the graphite furnace used for? Achieve Extreme Heat Up to 3000°C in a Controlled Environment
- Is a graphite melting point high or low? Discover Its Extreme Thermal Resilience



















