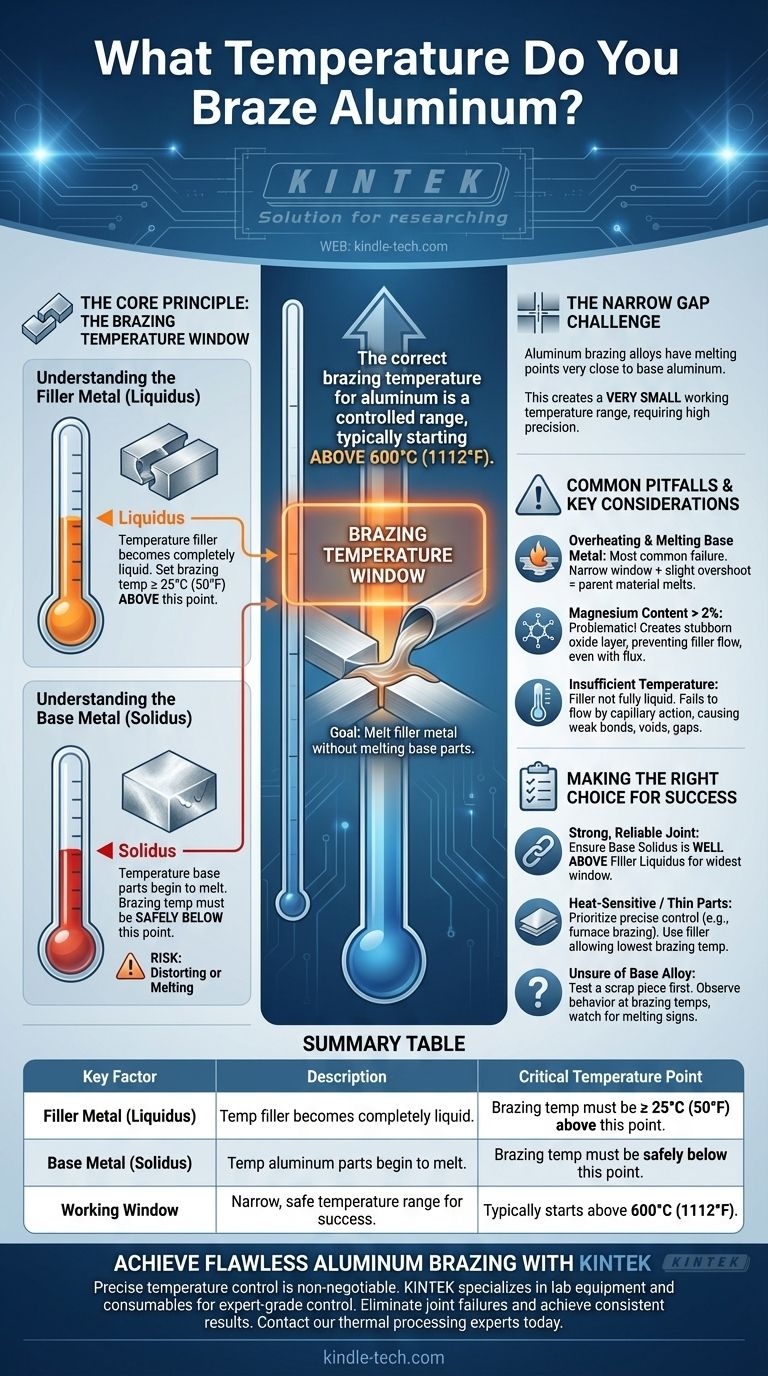
The correct brazing temperature for aluminum is not a single value, but a carefully controlled range that typically starts above 600°C (1112°F). The precise temperature is critically dependent on two factors: the specific filler alloy you are using and the base aluminum alloy you are joining. The goal is to melt the filler metal so it flows into the joint without melting the aluminum parts themselves.
Successful aluminum brazing depends on a critical temperature window. You must heat the assembly to a temperature that is above the melting point (liquidus) of your filler alloy but safely below the melting point (solidus) of the aluminum parts you are joining.

The Core Principle: The Brazing Temperature Window
Understanding aluminum brazing is about understanding the relationship between the base metal and the filler metal. Unlike steel, aluminum alloys have a very narrow gap between their brazing temperature and their melting point, demanding high precision.
Understanding the Filler Metal (Liquidus)
The liquidus is the temperature at which a filler alloy becomes completely liquid. To ensure the filler flows properly into the joint, the brazing temperature must be slightly higher than this point.
A common rule is to set the brazing temperature at least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus of the specific filler alloy being used.
Understanding the Base Metal (Solidus)
The solidus is the temperature at which the base aluminum alloy begins to melt. Your brazing temperature must always remain below the solidus of the parts you are joining.
If the temperature reaches the solidus of the base metal, you risk distorting or completely melting your workpiece. This is the primary failure mode in aluminum brazing.
Why the Gap is So Narrow
The challenge with aluminum is that its brazing alloys (typically aluminum-silicon alloys) have a melting point very close to that of the base aluminum parts. This creates a very small working temperature range, often only a few dozen degrees, requiring precise heat control.
Common Pitfalls and Key Considerations
Achieving the correct temperature is only part of the process. Certain material properties and process errors can lead to joint failure even if your temperature seems correct.
Overheating and Melting the Base Metal
This is the most common and catastrophic failure. Because the temperature window is so narrow, even a slight overshoot in temperature or uneven heating can cause the parent material to melt before the filler has properly filled the joint.
The Problem with Magnesium Content
The composition of your base aluminum alloy is critical. Alloys with a magnesium content above 2% are generally not suitable for brazing.
Magnesium creates a highly stable and stubborn oxide layer on the surface that prevents the filler metal from wetting and bonding with the base metal, even with proper fluxing.
Insufficient Temperature
Operating at too low a temperature is also a problem. The filler metal will not become fully liquid and will fail to flow completely into the joint via capillary action. This results in an incomplete, weak bond with voids and gaps.
Making the Right Choice for a Successful Braze
Your approach should be guided by the materials you are using and the precision your project requires.
- If your primary focus is a strong, reliable joint: Ensure the solidus temperature of your base alloy is well above the liquidus temperature of your filler to create the widest possible working window.
- If you are working with heat-sensitive or thin components: Prioritize precise temperature control using methods like furnace brazing and select a filler alloy that allows you to use the lowest possible brazing temperature.
- If you are unsure of your base alloy's composition: Test a scrap piece first to observe how it behaves at brazing temperatures, paying close attention to any signs of melting.
Ultimately, mastering aluminum brazing is about controlling this narrow and critical temperature window with precision.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Description | Critical Temperature Point |
|---|---|---|
| Filler Metal (Liquidus) | Temperature at which the filler alloy becomes completely liquid. | Brazing temp must be ≥ 25°C (50°F) above this point. |
| Base Metal (Solidus) | Temperature at which the aluminium parts begin to melt. | Brazing temp must be safely below this point. |
| Working Window | The narrow, safe temperature range for successful brazing. | Typically starts above 600°C (1112°F). |
Achieve Flawless Aluminum Brazing with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is non-negotiable for strong, reliable aluminium brazed joints. The narrow window between the filler metal's melting point and the base metal's melting point demands expert-grade equipment.
KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables that empower your success. Whether you are developing new products or ensuring quality in production, our range of precision furnaces and thermal processing solutions provides the exact control you need to master this critical process.
Let us help you eliminate joint failures and achieve consistent results.
Contact our thermal processing experts today to discuss your specific aluminium brazing application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vacuum drying oven preferred for Au/TiO2 catalysts? Maintain 3nm Particle Size & Peak Activity
- Can you determine the temperature of a vacuum? Unpacking the Physics of 'Empty' Space
- What are the benefits of vacuum annealing? Achieve Pristine, Oxide-Free Parts with Superior Material Properties
- What role does a high-temperature annealing furnace play in LPBF NAB? Optimize Microstructure for Industrial Performance
- How does furnace temperature precision affect Inconel 718 grain size? Master Microstructural Control
- What is high temperature brazing? Achieve Strong, Clean Metal Joints for Complex Assemblies
- What is the primary function of a resistance heating furnace? Master Magnesium Purification via Vacuum Sublimation
- What are the advantages of an arc furnace? Achieve Flexible, Low-Carbon Steel Production



















