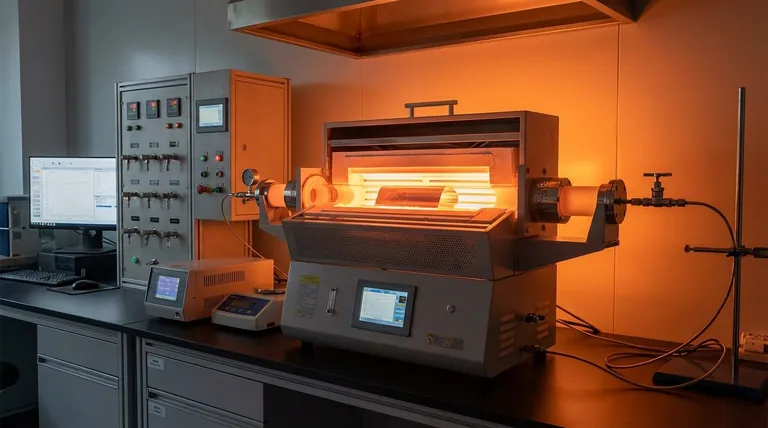
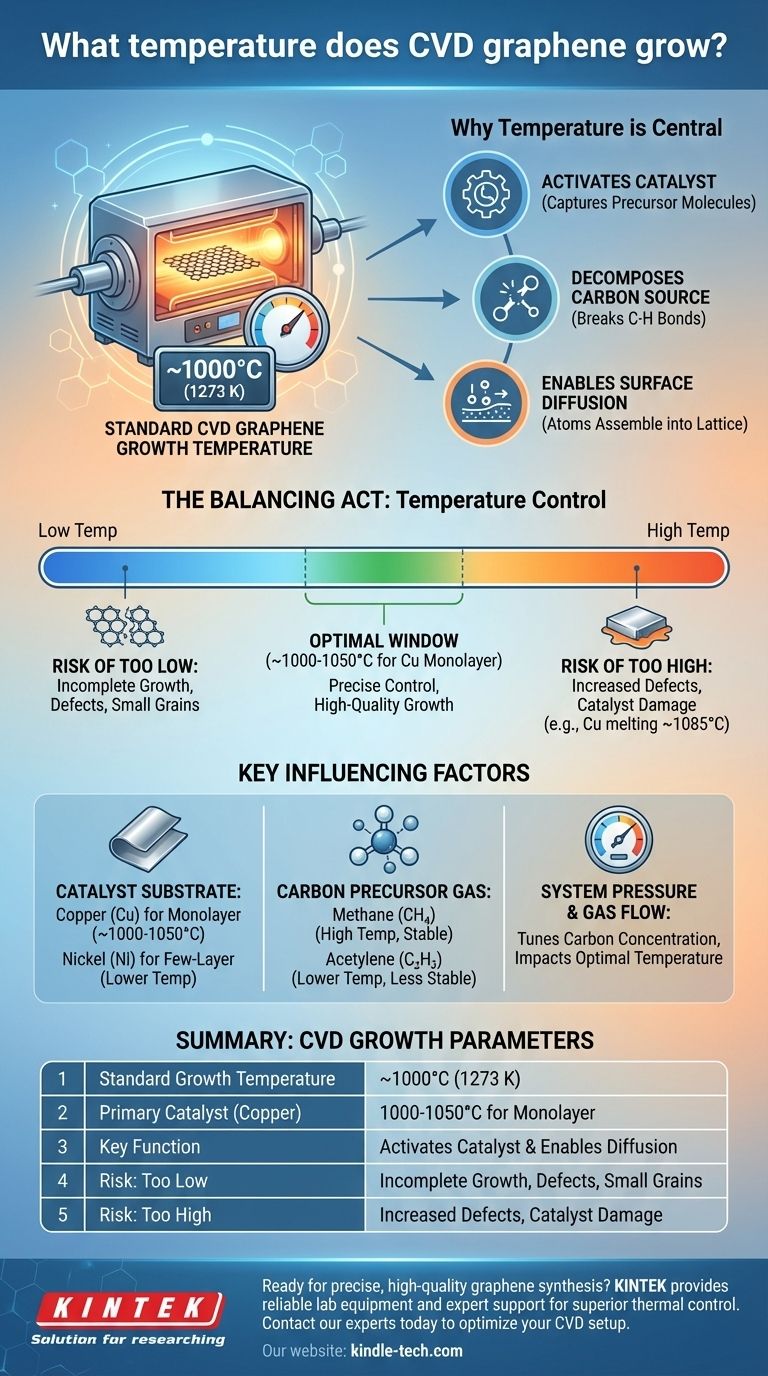
For graphene grown via Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the process is typically conducted at high temperatures, most commonly around 1000°C (1273 K). However, this is not a fixed value; the optimal temperature is highly dependent on the specific catalyst, carbon source, and desired quality of the graphene film.
The core principle to understand is that temperature is the primary lever for controlling the chemical reactions in CVD graphene synthesis. It must be high enough to break down the carbon precursor and activate the metal catalyst, but controlled carefully to prevent defects and unwanted multi-layer growth.

Why Temperature is the Central Parameter in CVD Growth
Temperature isn't just about making the furnace hot; it governs the fundamental physical and chemical steps that allow individual atoms to assemble into a high-quality graphene sheet.
Activating the Catalyst
High temperatures are necessary to make the metallic substrate, typically copper or nickel, catalytically active. This means the metal surface can effectively capture and break apart the precursor gas molecules.
Decomposing the Carbon Source
The carbon-containing precursor gas, most often methane (CH₄), is very stable. The thermal energy provided by the furnace is required to break the strong carbon-hydrogen bonds, releasing reactive carbon atoms or species.
Enabling Surface Diffusion
Once carbon atoms are on the catalyst surface, they must have enough energy to move around, or diffuse. This mobility allows them to find each other and arrange themselves into the stable, hexagonal lattice structure that defines graphene.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Temperature Control
Selecting the right temperature is a balancing act. Deviating from the optimal window in either direction has significant consequences for the quality of the final product.
The Risk of Too Low a Temperature
If the temperature is insufficient, the precursor gas will not decompose efficiently. This leads to a very slow or incomplete growth process, resulting in a graphene film with many holes, defects, and small grain sizes.
The Risk of Too High a Temperature
Excessive heat can be equally damaging. It can increase the rate of defect formation within the graphene lattice. Furthermore, for a catalyst like copper, temperatures approaching its melting point (1085°C) can cause surface roughening or even sublimation, which disrupts uniform growth.
Key Factors That Influence Optimal Temperature
The ideal growth temperature is not a universal constant. It is intrinsically linked to the other parameters of the CVD process, as outlined in a typical furnace setup.
The Catalyst Substrate
Different metals have different properties. Copper has low carbon solubility, which self-limits the growth to a single layer, making it ideal for high-quality monolayer graphene, typically grown around 1000-1050°C. Nickel, with its higher carbon solubility, can be used at slightly lower temperatures but often produces few-layer graphene.
The Carbon Precursor Gas
The stability of the gas matters. Methane (CH₄) requires high temperatures (~1000°C) to decompose. Other precursors, like acetylene (C₂H₂), are less stable and can be used for lower-temperature growth processes.
System Pressure and Gas Flow
The pressure inside the reactor and the flow rates of the gases also play a role. These factors determine the concentration of carbon atoms available on the catalyst surface at any given moment, and the optimal temperature is tuned in conjunction with them to achieve controlled growth.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct temperature is ultimately defined by the specific outcome you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is the highest quality single-layer graphene: You will almost certainly work with a copper foil catalyst near 1000°C, requiring precise control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow.
- If your primary focus is few-layer graphene or faster growth: Using a nickel catalyst may allow for slightly lower temperatures and is less sensitive, but quality control for single layers is more difficult.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with other materials: You must investigate specialized low-temperature CVD methods (e.g., Plasma-Enhanced CVD), which operate at lower temperatures but often compromise on crystalline quality.
Ultimately, temperature is the master variable that orchestrates the complex interplay of chemistry and physics required to synthesize graphene.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Typical Range / Key Point |
|---|---|
| Standard Growth Temperature | ~1000°C (1273 K) |
| Primary Catalyst (Copper) | 1000-1050°C for monolayer graphene |
| Key Function | Activates catalyst & enables carbon atom diffusion |
| Risk: Too Low | Incomplete growth, defects, small grains |
| Risk: Too High | Increased defects, catalyst damage (e.g., Cu melting ~1085°C) |
Ready to achieve precise, high-quality graphene synthesis?
The exact temperature for your CVD process is critical for success. KINTEK specializes in providing the reliable lab equipment and expert support you need to master this delicate balance. Whether you're working with copper for monolayers or exploring other catalysts, our furnaces and consumables are designed for the precise thermal control required for superior graphene growth.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can optimize your CVD setup for your specific research goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning



















