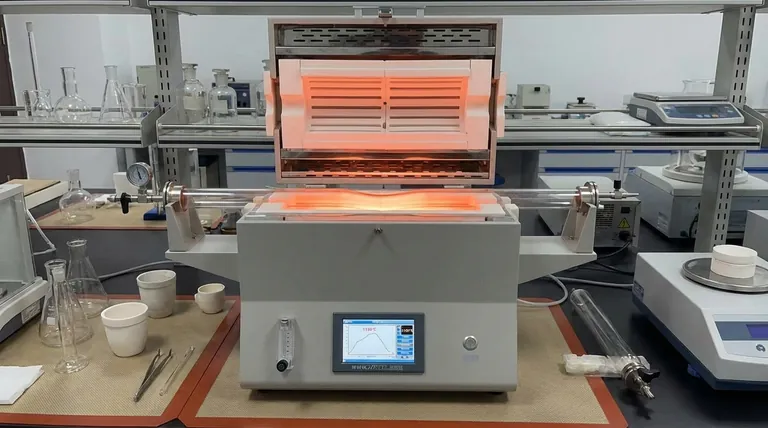
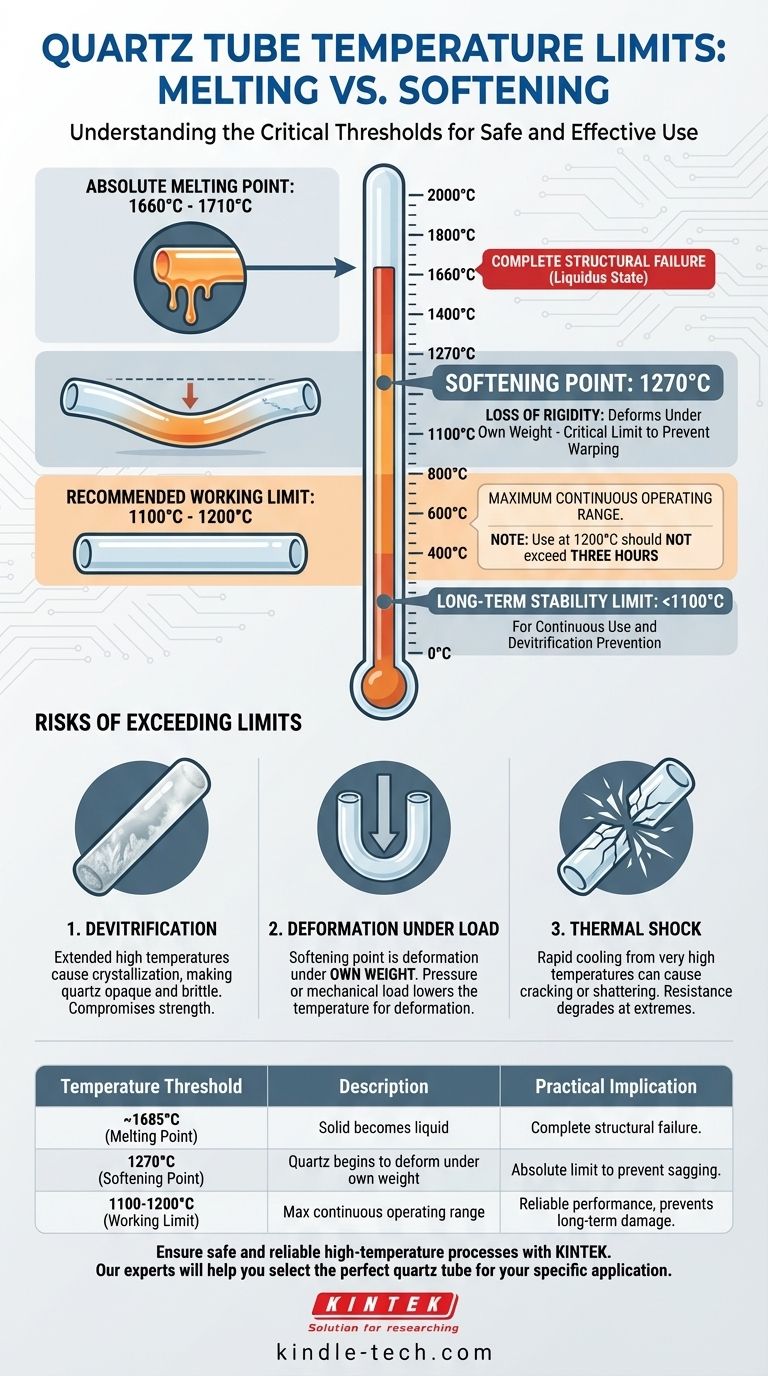
In absolute terms, a quartz tube melts at a temperature between 1660°C and 1710°C. However, this number is highly misleading for any practical purpose. The temperature at which the tube loses its structural integrity and begins to fail is significantly lower.
The technical melting point of quartz is a poor guide for its real-world use. For any high-temperature application, the softening point of 1270°C is the critical limit you must respect to prevent deformation and failure.

The Critical Difference: Melting vs. Softening
Understanding the material science of quartz (fused silica, SiO₂) is essential for using it safely and effectively. There isn't a single temperature limit, but rather a series of thresholds that dictate its behavior.
The Melting Point: 1660-1710°C
This is the true liquidus temperature. At this point, the silicon dioxide transitions from a solid to a liquid state, representing a complete loss of structure. Reaching this temperature means total component failure.
The Softening Point: 1270°C
This is the most important number for practical applications. The softening point is the temperature at which quartz loses its rigidity and begins to deform under its own weight. It is no longer a true solid and behaves more like a highly viscous liquid.
Pushing a quartz tube to this temperature will cause it to sag, bend, or warp, compromising your equipment or experiment.
The Recommended Working Limit: Below 1200°C
For reliable performance, you must operate well below the softening point. The maximum continuous operating temperature for a quartz tube is typically around 1100-1200°C.
As a specific guideline, use at 1200°C should not exceed three hours. This time limit helps prevent the cumulative stress and structural changes that occur even below the softening point.
Common Pitfalls and Why You Can't Push the Limit
Exceeding the recommended working temperatures, even if you stay below the softening point, introduces significant risks that can lead to catastrophic failure.
Risk of Devitrification
When held at high temperatures for extended periods, the amorphous structure of quartz glass can begin to crystallize. This process, called devitrification, makes the quartz opaque and extremely brittle once it cools, severely compromising its strength.
Deformation Under Load
Remember that the softening point is where the tube deforms under its own weight. If your application involves any pressure differential or mechanical load, deformation will begin at an even lower temperature.
Increased Risk of Thermal Shock
While quartz has excellent thermal shock resistance, this property degrades at extreme temperatures. Rapid cooling from a very high operating temperature can easily cause the tube to crack or shatter.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure safety and success, select your operating temperature based on the demands of your specific application.
- If your primary focus is a short-duration process (under 3 hours): You can operate cautiously up to 1200°C, but you must monitor for any signs of sagging or deformation.
- If your primary focus is long-term stability or continuous use: Your maximum operating temperature should not exceed 1100°C to ensure longevity and prevent devitrification.
- If your application involves any pressure or mechanical stress: You must significantly reduce your maximum temperature to maintain a wide safety margin below the 1270°C softening point.
Ultimately, respecting the material's practical working limits is the key to leveraging the unique properties of quartz safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Threshold | Description | Practical Implication |
|---|---|---|
| ~1685°C (Melting Point) | Solid quartz becomes a liquid. | Complete structural failure. Avoid at all costs. |
| 1270°C (Softening Point) | Quartz begins to deform under its own weight. | The absolute maximum limit to prevent sagging and warping. |
| 1100-1200°C (Working Limit) | Maximum recommended continuous operating range. | For reliable performance and to prevent long-term damage like devitrification. |
Ensure your high-temperature processes are safe and reliable with the right equipment from KINTEK.
Choosing the correct quartz tube for your specific temperature and duration requirements is critical to preventing costly failures and ensuring experiment integrity. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance to match the right materials to your laboratory's needs.
Let our experts help you select the perfect quartz tube for your application. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and ensure optimal performance and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?



















