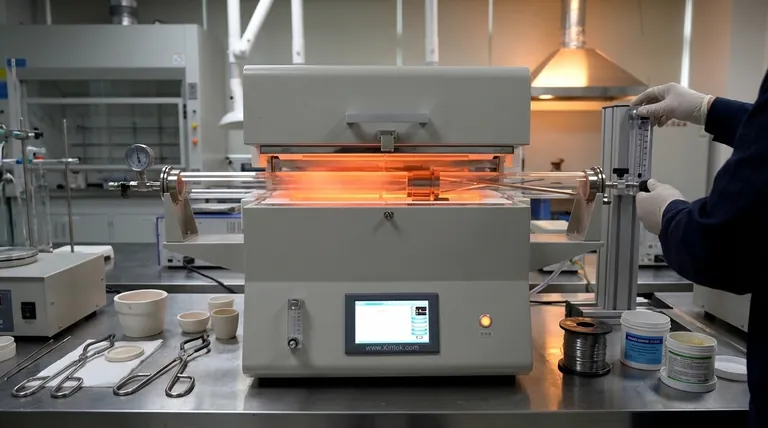
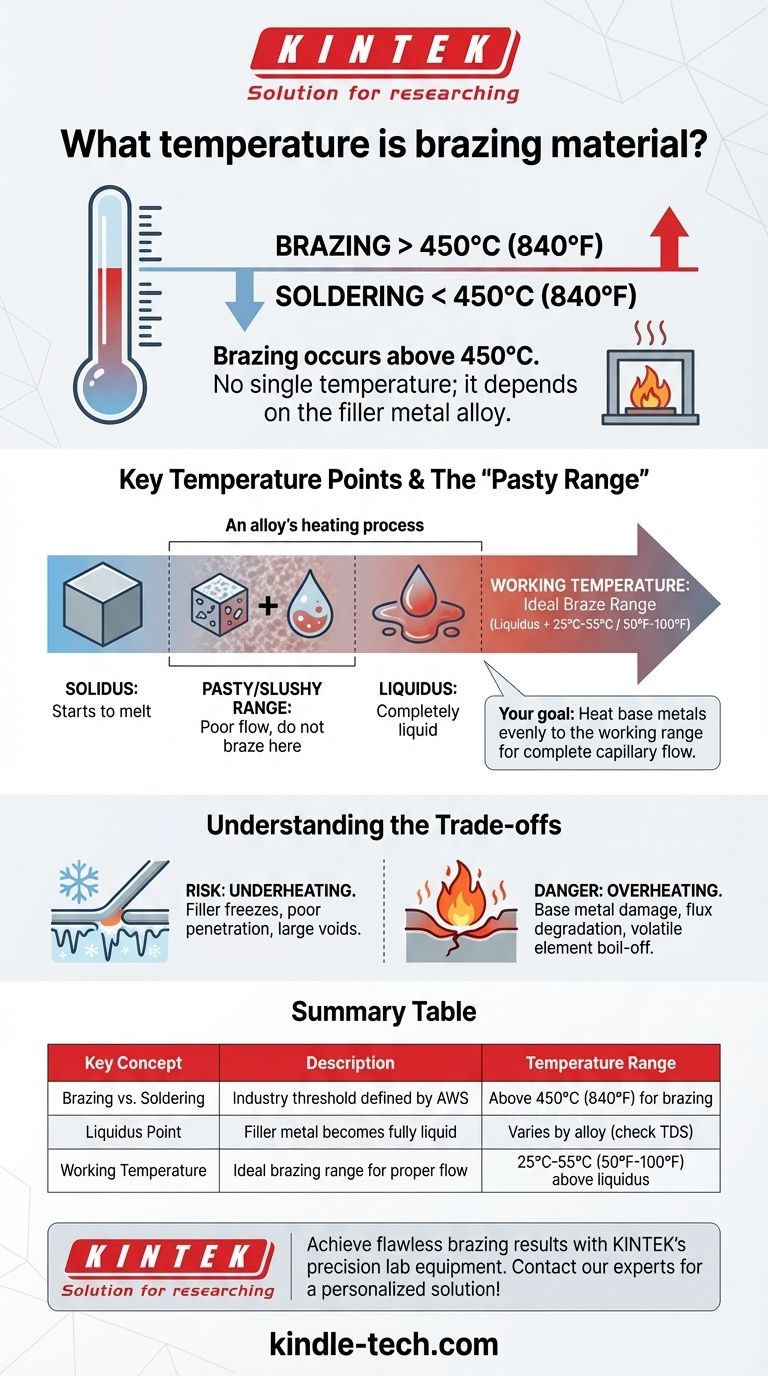
The short answer is, brazing is a metal-joining process that occurs at temperatures above 450°C (840°F), but there is no single temperature for all brazing. The exact temperature required depends entirely on the specific filler metal alloy you are using. The correct working temperature is always a range set slightly above the point where the specific filler alloy becomes fully liquid.
Your goal is not to achieve a single magic number, but to heat the base metals evenly so the entire joint area reaches the ideal working range for your specific filler alloy. This ensures the alloy melts, flows completely via capillary action, and forms a strong, permanent bond.

The Defining Line: Brazing vs. Soldering
To understand brazing temperature, it's crucial to distinguish it from its lower-temperature counterpart, soldering. The distinction is a clear, industry-defined threshold.
The 450°C (840°F) Rule
The American Welding Society (AWS) defines brazing as a process using a filler metal that melts and flows at a temperature above 450°C (840°F).
Soldering, by contrast, uses a filler metal that melts below this 450°C (840°F) threshold. This fundamental difference in temperature dictates the types of alloys used, the strength of the final joint, and the equipment required.
Why "One Temperature" Doesn't Exist
The question of brazing temperature is not about a single value but about understanding the melting behavior of a specific alloy. This behavior is defined by two critical temperature points.
Introducing Solidus and Liquidus
Every brazing alloy has two key temperatures listed on its technical data sheet:
- Solidus: The temperature at which the alloy begins to melt.
- Liquidus: The temperature at which the alloy becomes completely liquid.
For a successful braze, you must heat the assembly above the alloy's liquidus temperature.
The "Pasty" or "Slushy" Range
The temperature zone between the solidus and liquidus is known as the "pasty" or "slushy" range. In this state, the alloy is a mixture of solid and liquid and will not flow properly.
Attempting to braze in this range results in poor joint penetration and is a common cause of joint failure.
The Target: Working Temperature
The correct brazing temperature, often called the "working temperature," is a range that starts above the liquidus point.
As a general rule, the ideal brazing temperature is 25°C to 55°C (50°F to 100°F) above the liquidus temperature of your filler metal. This slight excess temperature ensures the alloy is fully fluid, compensates for minor heat loss at the joint, and promotes rapid, complete flow through capillary action.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Controlling temperature is a balancing act. Both too little and too much heat will compromise the integrity of your work.
The Risk of Underheating
If the base metals are not hot enough, the filler metal will "freeze" on contact. This prevents it from being drawn into the joint.
The result is a joint with poor penetration, large voids, and almost no mechanical strength. The filler will ball up on the surface rather than "wetting" the metal and flowing smoothly.
The Danger of Overheating
Excessive heat is just as damaging. Overheating can cause several critical problems:
- Base Metal Damage: Warping, distortion, or metallurgical damage like excessive grain growth can weaken the parts you are trying to join.
- Flux Degradation: Flux is essential for cleaning the metal and enabling flow, but it has a limited active life at high temperatures. Excessive heat will burn it away before the brazing alloy can do its job.
- Filler Metal Damage: Some alloys contain volatile elements (like zinc or cadmium). Overheating can boil these elements out of the alloy, changing its chemical composition, creating toxic fumes, and degrading its performance.
How to Determine the Right Temperature for Your Project
Choosing the correct temperature is a matter of consulting your materials and observing the process. A successful braze depends on heating the parts, not the filler metal itself.
- If your primary focus is choosing a filler metal: Start by checking the heat tolerance of your base metals, then select a brazing alloy with a working range that will not damage them.
- If your primary focus is setting up your equipment: Always consult the Technical Data Sheet (TDS) provided by the filler metal manufacturer. It will specify the exact solidus, liquidus, and recommended brazing temperature range.
- If your primary focus is troubleshooting a failed joint: The most common issue is non-uniform heating. Ensure your technique brings the entire mass of the joint area evenly up to the target temperature before you apply the filler rod.
Mastering brazing temperature is about controlling a thermal process, not just reaching a specific number on a gauge.
Summary Table:
| Key Concept | Description | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Brazing vs. Soldering | Industry threshold defined by AWS | Above 450°C (840°F) for brazing |
| Liquidus Point | Temperature where filler metal becomes fully liquid | Varies by alloy (check TDS) |
| Working Temperature | Ideal brazing range for proper flow | 25°C-55°C (50°F-100°F) above liquidus |
Achieve flawless brazing results with KINTEK's precision lab equipment. Whether you're working with high-temperature alloys or sensitive base metals, our furnaces and heating systems provide the exact temperature control and uniform heating you need for strong, reliable joints.
We specialize in serving laboratories with durable, high-performance equipment for all your metal-joining and heat treatment applications.
Ready to optimize your brazing process? Contact our experts today for a personalized solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How to clean a tube furnace? A Step-by-Step Guide for Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- How do a quartz tube reactor and atmosphere furnace collaborate in Co@NC pyrolysis? Master Precision Synthesis



















