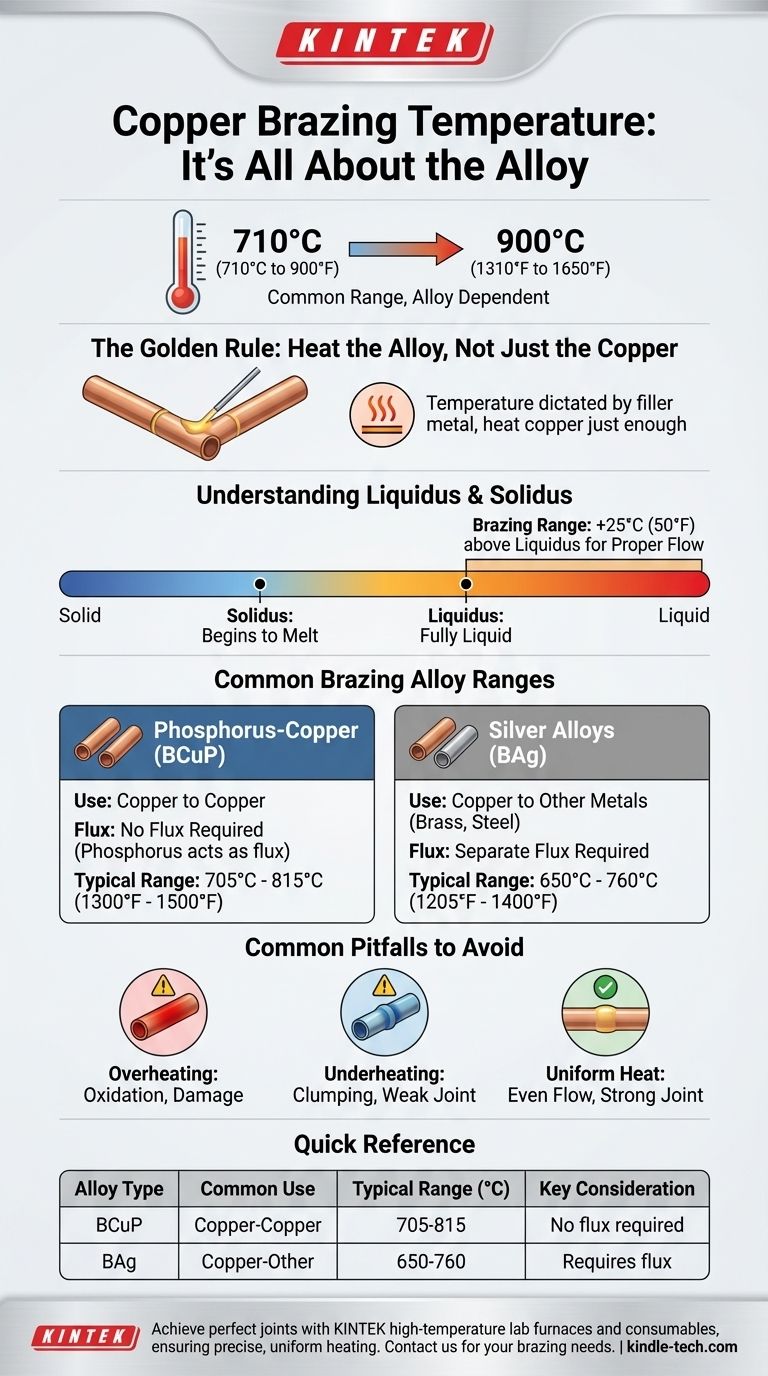
To be precise, there is no single temperature for brazing copper. The correct temperature is determined entirely by the specific brazing alloy (filler metal) you use, with most common alloys for copper requiring a temperature between 710°C and 900°C (1310°F to 1650°F). The goal is to heat the copper parts until they are hot enough to melt the filler alloy, allowing it to flow into the joint.
The core principle of brazing is that the temperature is dictated by the filler metal, not the base metal. You must heat the copper just enough to be at least 25°C (50°F) above the "liquidus" (fully melted) temperature of your specific brazing alloy, ensuring proper flow without damaging the copper itself.

Why Brazing Temperature is Alloy-Dependent
To master brazing, it's essential to understand that you are not melting the copper. You are melting a separate filler metal that acts as a powerful adhesive, joining the copper parts together at a molecular level.
The Role of the Filler Metal
Brazing works through a process called capillary action. The molten filler metal is drawn into the tight gap between the two copper pieces, creating a strong, leak-proof seal once it cools and solidifies.
This means the only thing that needs to melt is the filler metal, which is specifically designed to have a lower melting point than the copper it is joining.
Understanding Liquidus and Solidus
Every brazing alloy has two critical temperature points specified by the manufacturer:
- Solidus: The temperature at which the alloy begins to melt.
- Liquidus: The temperature at which the alloy becomes completely liquid.
For the alloy to flow properly and create a strong joint, it must be heated past its liquidus temperature.
The "25°C Above Liquidus" Rule
The guideline to heat the joint at least 25°C (50°F) above the liquidus temperature is critical. This slight superheating ensures the filler alloy is fully fluid and has low viscosity, allowing it to wet the copper surfaces and be pulled completely through the joint by capillary action.
Common Brazing Alloy Ranges for Copper
The alloy you choose depends on what you are joining. Different alloys have different temperature requirements.
Phosphorus-Copper Alloys (BCuP)
These are the most common alloys for joining copper to copper. A key advantage is that the phosphorus acts as a fluxing agent, meaning no separate flux is needed for copper-to-copper joints.
A typical example is a BCuP-5 alloy (15% silver), which has a brazing range of 705°C - 815°C (1300°F - 1500°F).
Silver Alloys (BAg)
These alloys are used for joining copper to other metals, such as brass, bronze, or steel. They contain silver, which improves flow and ductility.
Unlike BCuP alloys, silver alloys require a separate flux to clean the metals and ensure a good bond. A common BAg alloy might have a brazing range of 650°C - 760°C (1205°F - 1400°F).
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Achieving the correct temperature is a balance. Both too much and too little heat will result in a failed joint.
The Danger of Overheating
If you heat the copper far beyond the alloy's required temperature, you risk creating heavy, flaky oxides on the copper surface. This oxidation can prevent the filler metal from bonding correctly. In extreme cases, you could even begin to melt or damage the copper parts.
The Problem with Underheating
Failing to reach the alloy's proper brazing temperature is the most common mistake. If the base metal is too cool, the filler alloy will "clump" and fail to flow. It won't wet the copper surfaces, resulting in a weak joint with gaps and voids.
The Importance of Uniform Heat
You must heat the entire joint area evenly. If one part is hot and the other is cool, the filler metal will only flow toward the hotter area, creating an incomplete and unreliable joint. Focus your torch on the copper parts, not the filler rod.
Determining the Correct Temperature for Your Project
Always refer to the manufacturer's technical data sheet for your specific brazing alloy. However, these general guidelines will help you select the right material for the job.
- If your primary focus is joining copper to copper: Choose a phosphorus-copper (BCuP) alloy and confirm its specific brazing range, which will likely be between 700°C and 900°C.
- If your primary focus is joining copper to a different metal: Use a silver-based (BAg) alloy with the correct flux, and consult its data sheet for a temperature range, typically between 620°C and 845°C.
- If you are unsure of your alloy: Do not proceed. Identify the alloy or purchase a new one with a clear technical data sheet to ensure you are using the correct temperature and creating a safe, strong joint.
Ultimately, matching your technique to the requirements of your chosen filler metal is the key to a perfect braze.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Alloy Type | Common Use | Typical Brazing Range (°C) | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phosphorus-Copper (BCuP) | Copper to Copper | 705°C - 815°C | No flux required for copper-copper joints |
| Silver Alloys (BAg) | Copper to Other Metals (e.g., steel, brass) | 650°C - 760°C | Requires separate flux for proper bonding |
Achieve perfect, strong brazed joints every time with the right equipment and expertise. KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab furnaces and consumables, providing the precise, uniform heating essential for successful copper brazing. Whether you're in R&D or production, our solutions ensure you meet the exact temperature requirements of your specific brazing alloy. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's brazing and materials joining needs. Get in touch via our Contact Form
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process
- Why is a quartz tube furnace utilized in the thermal oxidation of MnCr2O4 coatings? Unlock Precise Selective Oxidation
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.



















