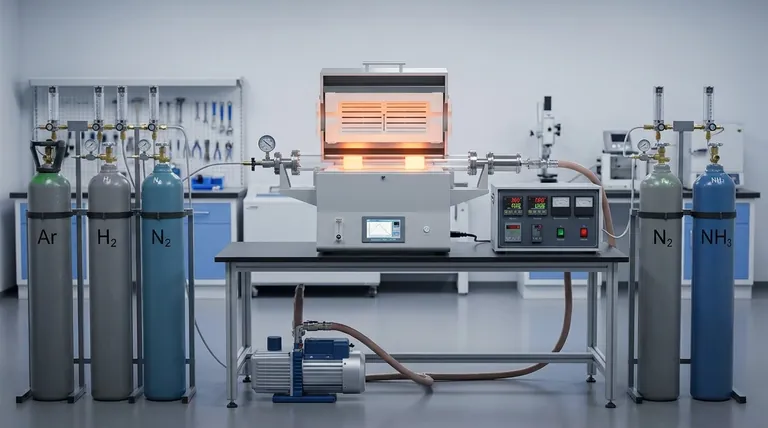
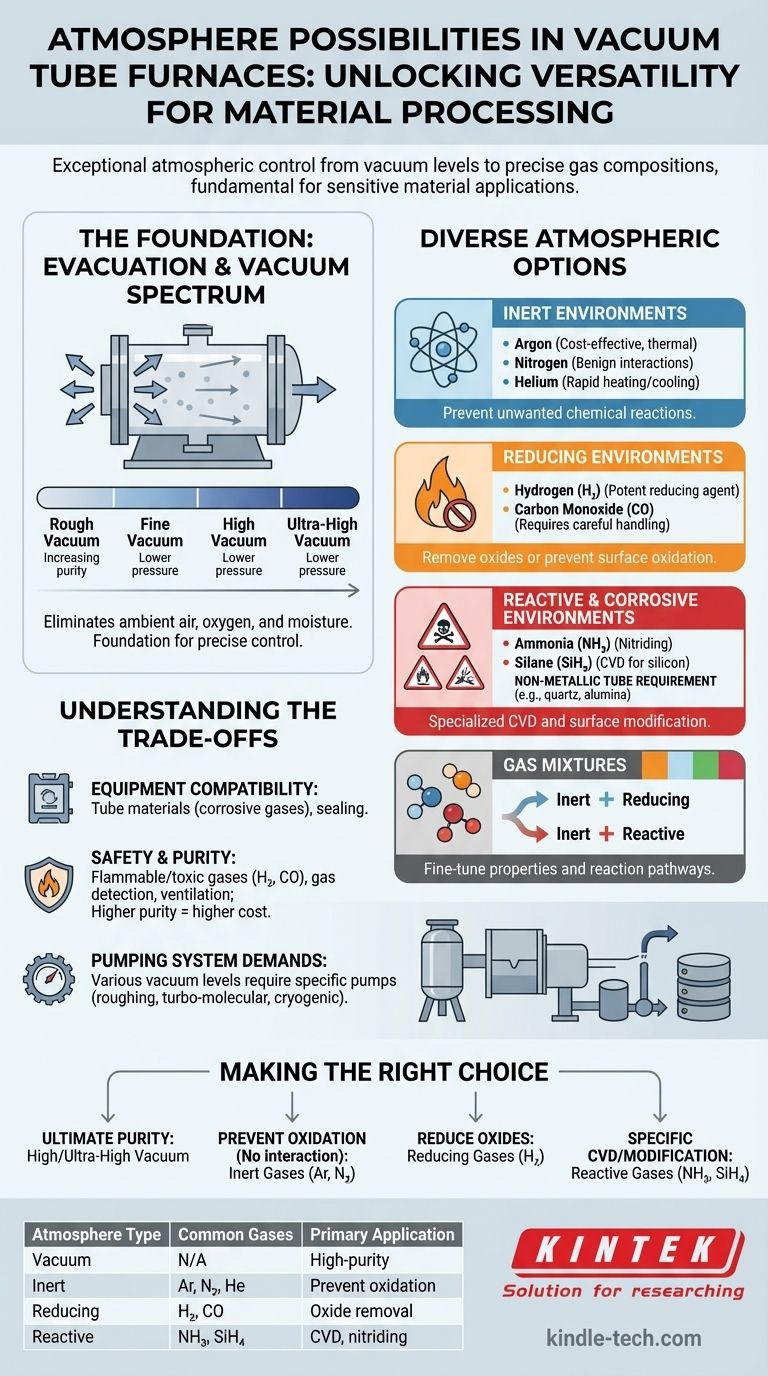
A vacuum tube furnace offers exceptional versatility in atmospheric control, allowing for a wide range of environments from various levels of vacuum to precisely controlled gas compositions. This capability is fundamental to its application in sensitive material processing.
Vacuum tube furnaces are highly adaptable due to their ability to first evacuate the chamber, completely removing ambient air. This foundation enables the introduction of highly specific atmospheres, including different levels of vacuum, inert gases, reducing gases, and even certain reactive or corrosive gases, tailored to the material processing requirements.

The Foundation of Atmosphere Control
Evacuation as the Precursor
The primary advantage of a vacuum tube furnace is its capacity to completely remove the existing atmosphere. This evacuation step is crucial because it eliminates unwanted contaminants like oxygen and moisture, setting the stage for precise atmosphere control.
Spectrum of Vacuum Levels
Once evacuated, the furnace can operate directly under various vacuum conditions. These range from rough vacuum to fine vacuum, high vacuum, and even ultra-high vacuum, depending on the sensitivity of the process. The specific vacuum level achieved impacts material purity and surface reactions.
Diverse Atmospheric Options
Inert Environments
Following evacuation, a vacuum tube furnace can be backfilled with inert gases. These gases prevent unwanted chemical reactions with the material being processed.
- Argon: A widely used inert gas, often for its cost-effectiveness and good thermal conductivity for cooling.
- Nitrogen: Another common inert gas, used where nitrogen-material interactions are benign or desired.
- Helium: Utilized for its high thermal conductivity, beneficial for rapid heating and cooling.
Reducing Environments
Reducing atmospheres are employed to remove oxides from material surfaces or to prevent oxidation during high-temperature processes.
- Hydrogen (H₂): A potent reducing agent, often diluted with inert gases for safety.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Another reducing gas, though its use requires careful handling due to its toxicity.
Reactive and Corrosive Environments
For specialized applications, vacuum tube furnaces can handle certain reactive or corrosive gases. This capability expands the range of materials that can be processed.
- Ammonia (NH₃): Used in processes like nitriding.
- Silane (SiH₄): Important for chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of silicon-containing films.
- Non-Metallic Tube Requirement: The use of corrosive gases necessitates non-metallic tubes (e.g., quartz, alumina) to prevent damage to the furnace components.
Gas Mixtures
The furnace can also operate with carefully controlled mixtures of the gases mentioned above. This allows for fine-tuning of the atmospheric conditions to achieve specific material properties or reaction pathways.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Equipment Compatibility
The choice of atmosphere directly impacts the required furnace components. Corrosive gases, for instance, demand specific tube materials and sealing mechanisms.
Safety Considerations
Gases like hydrogen and carbon monoxide are flammable or toxic. Their use requires advanced safety interlocks, gas detection systems, and proper ventilation.
Purity and Cost
The purity of the introduced gas is critical for process integrity, especially in sensitive applications. Higher purity gases typically come with a higher cost.
Pumping System Demands
Achieving and maintaining various vacuum levels requires different types of vacuum pumps, from roughing pumps to turbo-molecular or cryogenic pumps for high vacuum.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of atmosphere in a vacuum tube furnace is a critical decision driven by the desired material properties and process requirements.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and contamination prevention: Utilize high or ultra-high vacuum.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation or unwanted reactions without chemical interaction: Employ inert gases like Argon or Nitrogen.
- If your primary focus is reducing oxides or preventing surface oxidation during processing: Use reducing gases such as Hydrogen.
- If your primary focus is specific chemical vapor deposition or surface modification: Consider reactive gases like Silane or Ammonia, ensuring the furnace has non-metallic tubes.
By understanding the full spectrum of atmospheric possibilities, you can precisely control the environment for your material processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere Type | Common Gases | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum | N/A (Evacuated) | High-purity processing, contamination prevention |
| Inert | Argon, Nitrogen, Helium | Prevent oxidation/unwanted reactions |
| Reducing | Hydrogen, Carbon Monoxide | Oxide removal, prevent surface oxidation |
| Reactive/Corrosive | Ammonia, Silane | Chemical vapor deposition (CVD), nitriding |
Unlock the full potential of your material processes with KINTEK's vacuum tube furnaces. Our expertise in lab equipment ensures you get the precise atmospheric control—from high vacuum to specialized gas mixtures—that your research or production demands. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific laboratory needs in heat treatment, synthesis, or thin-film deposition.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- What is the physical description of a tube furnace? A Detailed Breakdown of its High-Temperature Design
- What tube is used for tubular furnace? Choose the Right Material for Temperature & Atmosphere
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material



















