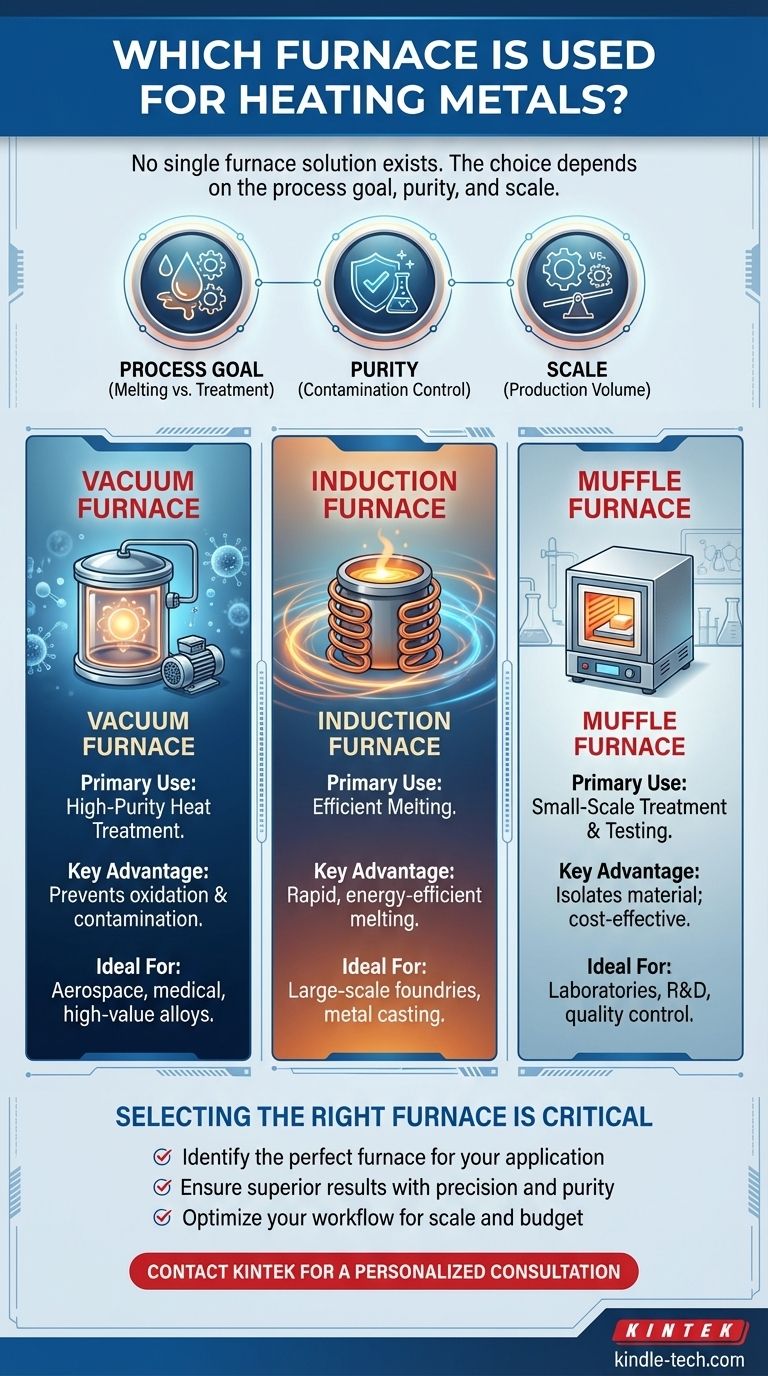
There is no single furnace for heating all metals; the correct choice depends entirely on the goal of the heating process. Different furnaces are designed for specific applications, such as melting, high-purity heat treatment, or small-scale testing. The most common types include induction, vacuum, and muffle furnaces, each with distinct advantages for particular tasks.
The selection of a metal heating furnace is a trade-off between three key factors: the process goal (melting vs. heat treatment), the required purity of the final product, and the scale of the operation. Understanding your specific need is the first step to choosing the right technology.

The Purpose of Heating Metals
Heat treatment is a fundamental process in manufacturing used to alter the physical and chemical properties of a metal. This can improve characteristics like strength, toughness, and ductility.
The goal isn't always to melt the metal. Often, the objective is to bring it to a precise temperature to change its internal structure, enhancing its versatility and durability for a specific application.
Key Types of Furnaces for Metal Heating
Different furnaces excel at different tasks. The primary distinction lies in how they generate heat, the environment they create, and the scale at which they operate.
Vacuum Furnaces: For High Purity and Precision
A vacuum furnace is used to heat metals to very high temperatures with minimal risk of contamination. The entire process takes place inside a vacuum chamber, which removes oxygen and other atmospheric gases.
This lack of oxygen is critical as it prevents oxidation and other reactions that can compromise the metal's quality. This makes the process cleaner and more efficient for high-value applications.
Vacuum furnaces offer extremely uniform temperatures and precise computer control, ensuring repeatable performance for sensitive heat treatment processes.
Induction Furnaces: For Efficient Melting
An induction furnace is a clean and energy-efficient furnace used to melt a wide variety of metals. It is commonly used for melting steel, iron, copper, zinc, and aluminum in large quantities.
Instead of traditional heating elements, it uses electromagnetic induction to generate heat directly within the metal itself, leading to rapid and efficient melting.
Muffle Furnaces: For Small-Scale Treatment and Testing
A muffle furnace isolates the material being heated from the heating elements. They are often used for heat-treating steel to alter its carbon content and improve strength.
Due to their typically smaller size, muffle furnaces are more common in laboratory settings for testing metal parts rather than for large-scale industrial production.
A Note on Heating Elements
The maximum temperature a furnace can achieve is determined by its heating elements.
Elements like resistance wire are common, but for higher temperatures, materials such as silicon carbide (SiC), molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2), graphite, or molybdenum are used. These advanced elements allow some furnaces to reach temperatures well over 2000°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace requires balancing the needs of your specific project. No single furnace is superior in all aspects; each represents a different set of compromises.
Purity and Contamination Control
The vacuum furnace is the undisputed leader for applications requiring the highest purity. By removing reactive gases, it provides an inert environment that other furnace types cannot match.
Process Goal: Melting vs. Treatment
If the goal is to melt metal for casting or alloying, an induction furnace is the most direct and efficient tool.
If the goal is heat treatment to alter properties without melting, vacuum and muffle furnaces are the primary choices, with the decision depending on scale and purity requirements.
Production Scale
Induction furnaces are built for high-volume melting. In contrast, muffle furnaces are best suited for individual parts or small test batches. Vacuum furnaces occupy a middle ground, often used for high-value batches where precision is paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct furnace, start by defining your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is melting large quantities of metal efficiently: An induction furnace is the industry standard and most effective choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity heat treatment with precise temperature control: A vacuum furnace is the necessary tool to prevent contamination and ensure quality.
- If your primary focus is testing, lab work, or heat-treating small parts: A muffle furnace provides a practical and cost-effective solution.
By matching the furnace technology to your specific application, you ensure optimal results in both quality and efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Furnace | High-Purity Heat Treatment | Prevents oxidation & contamination | Aerospace, medical, high-value alloys |
| Induction Furnace | Efficient Melting | Rapid, energy-efficient melting | Large-scale foundries, metal casting |
| Muffle Furnace | Small-Scale Treatment & Testing | Isolates material; cost-effective | Laboratories, R&D, quality control |
Need Help Selecting the Right Furnace?
Choosing the correct furnace is critical to your project's success, quality, and efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment you need.
We help you:
- Identify the perfect furnace for your specific application—melting, heat treatment, or testing.
- Ensure superior results with equipment designed for precision, purity, and durability.
- Optimize your workflow with solutions tailored to your production scale and budget.
Don't leave your metal's properties to chance. Let our experts guide you to the ideal solution.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the refractory material in a muffle furnace? Discover the High-Temperature Ceramic System
- What does a muffle furnace do? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is the effect of calcination temperature on the properties of nanoparticles? Master the Trade-Off for Optimal Performance
- How long does heating take on a muffle furnace? Unlock the Key Factors for Your Lab's Efficiency
- What is the primary use of furnace in the chemical industry? Master Thermal Treatment for Material Transformation



















