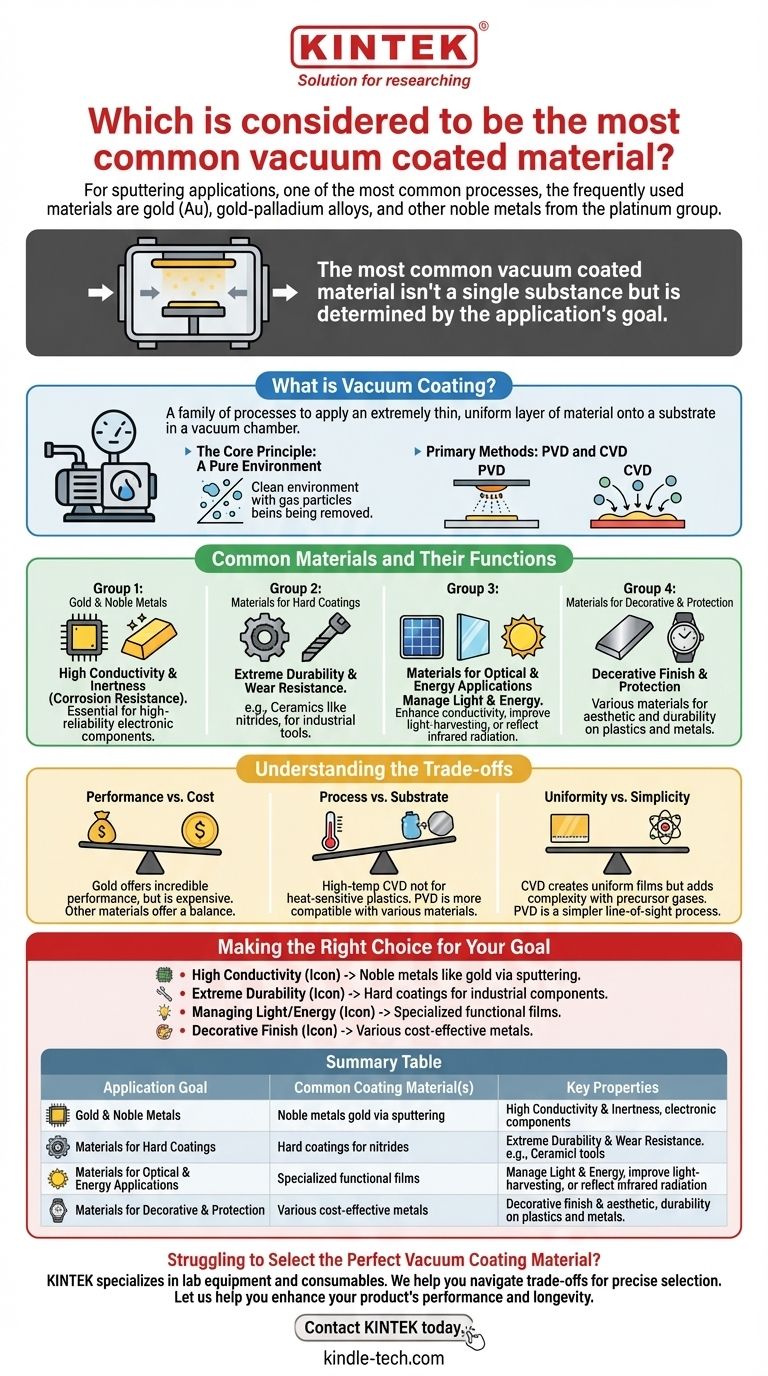
For sputtering applications, one of the most common vacuum coating processes, the most frequently used materials are gold (Au), gold-palladium alloys, and other noble metals from the platinum group. These materials are favored because they are excellent electrical conductors and are highly resistant to oxidation, ensuring the purity and performance of the deposited thin film.
The most common vacuum coated material isn't a single substance but is instead determined entirely by the application's goal. While gold is a frequent choice for high-end electronics due to its stability, the true answer depends on whether the priority is durability, conductivity, optical properties, or decoration.
What is Vacuum Coating?
Vacuum coating is a family of processes used to apply an extremely thin, uniform layer of material onto a surface, known as a substrate. The entire process takes place inside a vacuum chamber.
The Core Principle: A Pure Environment
The primary reason for using a vacuum is to remove air and other gaseous contaminants. This ensures that the coating material travels from its source to the substrate without reacting with any unintended particles, resulting in a purer and more strongly bonded film.
Primary Methods: PVD and CVD
There are two dominant techniques. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) involves physically vaporizing the solid coating material (e.g., by heating or bombarding it with ions) and allowing it to condense onto the substrate.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is different. It uses precursor gases that react or decompose on the surface of a heated substrate to form the desired solid film, allowing for highly uniform coatings even over large areas.
Key Applications and Benefits
This technology is used across countless industries to add value to products. Common applications include creating hard, durable coatings for engine components, low-emissivity coatings on glass for energy savings, and depositing conductive metal patterns for microchips and solar cells.
Common Materials and Their Functions
The material selected for vacuum coating is chosen to impart a specific property to the substrate's surface. Different goals require fundamentally different materials.
Gold (Au) and Noble Metals
As mentioned, gold and other noble metals are the standard for sputter coating. Their primary advantages are high conductivity and chemical inertness (resistance to corrosion and oxidation).
This makes them essential for high-reliability electronic components, such as microchips and electrical contacts, where consistent performance over time is critical.
Materials for Hard Coatings
For industrial applications requiring extreme durability, different materials are used. While not explicitly named in the references, hard coatings for engine components typically involve ceramics like nitrides.
These materials are deposited to dramatically increase the surface hardness and wear resistance of tools and mechanical parts, extending their operational life.
Materials for Optical and Energy Applications
Coatings are critical in managing light and energy. Thin-film solar cells use vacuum deposition to apply layers that enhance conductivity and improve light-harvesting properties.
Similarly, specialty coatings on architectural glass can reflect infrared radiation, improving a building's energy efficiency. These functional films are engineered for specific optical or electrical behaviors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material and process is a balancing act between the desired outcome, the substrate being coated, and the cost.
Performance vs. Cost
Gold offers incredible performance for electronics, but it is expensive. For decorative applications on plastic or metal, other materials can provide a similar appearance at a fraction of the cost. The final choice always depends on whether the high performance justifies the expense.
Process vs. Substrate
The chosen process must be compatible with the substrate. For example, high-temperature CVD processes are unsuitable for heat-sensitive plastics. PVD methods like sputtering are often performed at lower temperatures, making them compatible with a wider range of materials.
Uniformity vs. Simplicity
CVD is renowned for its ability to create exceptionally uniform films over large and complex surfaces. However, it involves precursor gases and chemical reactions, which can add complexity. PVD is often a more direct, line-of-sight process that is simpler for certain applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the "best" material is the one that solves your specific engineering or design problem.
- If your primary focus is high conductivity and corrosion resistance: Noble metals like gold, applied via sputtering, are the industry standard for high-performance electronics.
- If your primary focus is extreme durability and wear resistance: Hard coatings are applied to industrial components to extend their lifespan.
- If your primary focus is managing light or energy: Specialized functional films are engineered for products like low-emissivity glass and thin-film solar cells.
- If your primary focus is decorative finish and protection: A wide variety of materials can be used on substrates from metal to plastic to achieve the desired aesthetic and durability.
The material and process are selected to achieve a specific functional outcome, transforming the surface properties of the final product.
Summary Table:
| Application Goal | Common Coating Material(s) | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| High-End Electronics & Conductivity | Gold (Au), Gold-Palladium Alloys | Excellent electrical conductivity, high corrosion/oxidation resistance |
| Extreme Durability & Wear Resistance | Ceramics (e.g., Nitrides) | High surface hardness, increased wear resistance for tools & components |
| Optical & Energy Management | Specialized Functional Films | Enhanced light-harvesting, infrared reflection for energy efficiency |
| Decorative Finishes & Protection | Various Cost-Effective Metals | Desired aesthetic appearance and surface protection |
Struggling to Select the Perfect Vacuum Coating Material for Your Project?
Choosing the right material and process is critical to achieving the desired surface properties, whether it's superior conductivity for your microchips, extreme durability for engine components, or specific optical performance for your glass products.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for vacuum coating processes. We understand that the success of your application depends on precise material selection and reliable equipment. Our expertise can help you navigate the trade-offs between performance, cost, and substrate compatibility.
Let us help you enhance your product's performance and longevity.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our solutions can bring value to your laboratory or production line.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- Evaporation Boat for Organic Matter
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the application of furnace brazing? Achieve Strong, Complex, and Clean Assemblies
- Which factors must be controlled during sintering? Master Temperature, Atmosphere, and Material for Optimal Results
- What are the advantages of electric arc furnace over blast furnace? Boost Efficiency & Sustainability
- What is the requirement of heat treatment? Unlock Your Material's Full Potential
- How does an annealing furnace influence alpha-Fe2O3 nanofilms in DSSCs? Optimize Photoanode Efficiency
- Why is nitrogen used in sintering? Balancing Cost, Oxidation Control, and Material Properties
- How does a high-temperature laboratory furnace modify Li–Al LDH during catalyst pretreatment? Enhance Catalytic Activity
- What is the function of a vacuum furnace? Achieve High-Purity, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing



















