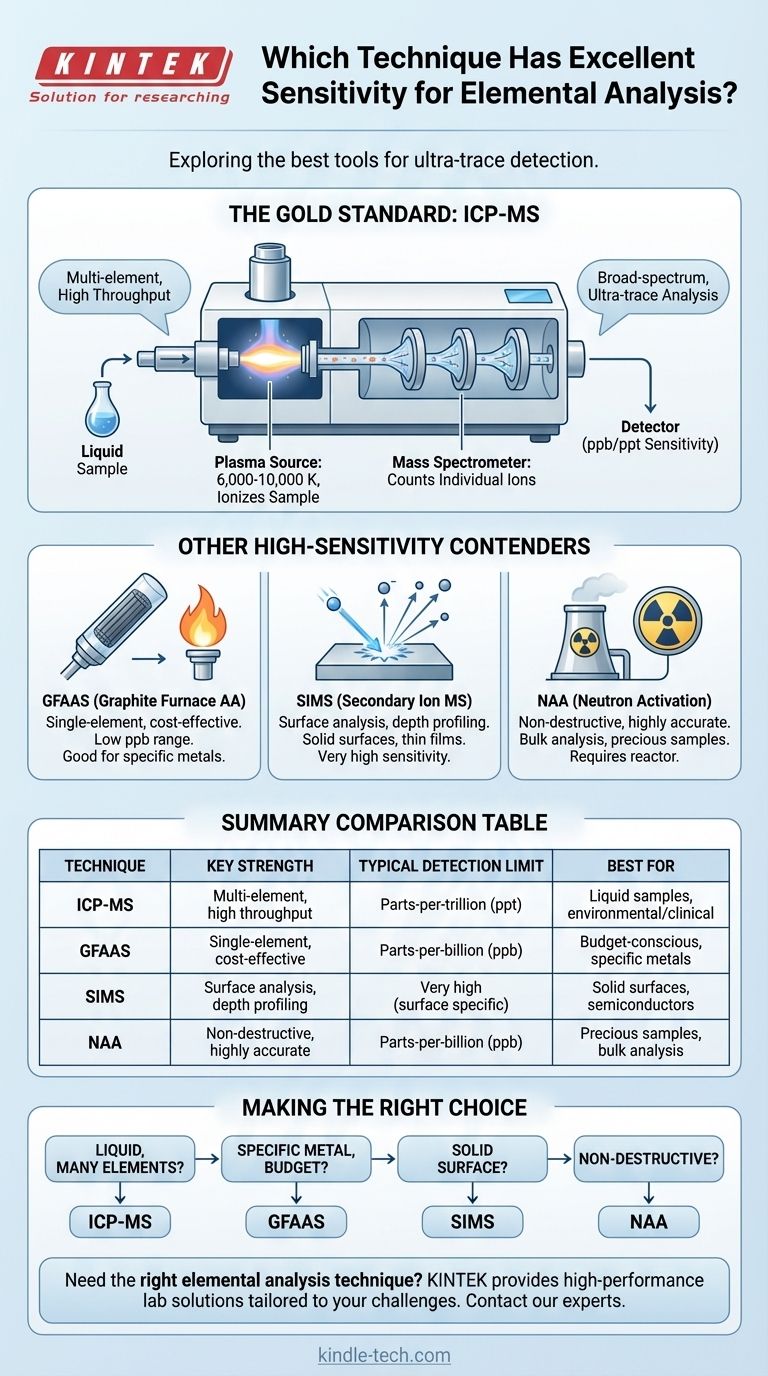
For exceptional, broad-spectrum elemental analysis, the technique with the highest sensitivity is Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). It combines a high-temperature plasma source that effectively ionizes a sample with a mass spectrometer that can count individual ions. This combination allows ICP-MS to routinely detect most elements in the periodic table down to part-per-billion (ppb) and even part-per-trillion (ppt) concentration levels.
The search for "excellent sensitivity" is a search for the right tool for a specific job. While ICP-MS is the undisputed leader for multi-element, ultra-trace analysis, other techniques like GFAAS or SIMS offer comparable sensitivity for more specialized applications, often with different trade-offs in cost and complexity.

Why ICP-MS Sets the Standard for Sensitivity
ICP-MS is a powerful and destructive technique that excels at determining the elemental composition of a sample, typically introduced as a liquid. Its remarkable sensitivity comes from a two-stage process.
The Power of the Plasma
The "ICP" portion uses a stream of argon gas energized by radiofrequency waves to create a plasma torch reaching temperatures of 6,000 to 10,000 Kelvin.
When a sample is introduced into this plasma, it is almost instantaneously dried, vaporized, and then atomized. The extreme energy strips electrons from these atoms, creating a dense cloud of positively charged ions. This ionization process is incredibly efficient for over 70 different elements.
The Precision of the Mass Spectrometer
The "MS" portion extracts these ions into a high vacuum, where they are guided by electric fields into a mass analyzer. This device acts as a highly sophisticated filter, separating the ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio.
A detector at the end of the path then counts the number of ions for each specific mass that strike it. By counting individual ions, the instrument can quantify elements present at extraordinarily low concentrations.
Other High-Sensitivity Contenders
While ICP-MS is the dominant force, it is not the only option for trace elemental analysis. Understanding the alternatives is key to making an informed decision.
Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption (GFAAS)
GFAAS offers excellent sensitivity, often in the low part-per-billion range, rivaling ICP-MS for certain elements.
Instead of a plasma, it uses a small graphite tube that is resistively heated to atomize a tiny amount of sample. It is a single-element technique, meaning you must analyze for each element sequentially, making it much slower than ICP-MS for multi-element surveys.
Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (SIMS)
For analyzing solid surfaces, SIMS is often considered the most sensitive technique available.
A focused beam of primary ions bombards the sample surface, sputtering away atoms and creating "secondary ions." These ejected ions are then analyzed by a mass spectrometer. SIMS is unique in its ability to provide depth profiles, analyzing elemental composition as a function of depth into the material with nanometer-scale resolution.
Neutron Activation Analysis (NAA)
NAA is a nuclear technique that offers high sensitivity for a wide range of elements. It is also uniquely non-destructive.
The sample is placed in a nuclear reactor and irradiated with neutrons, making some of its constituent elements radioactive. As these newly radioactive isotopes decay, they emit characteristic gamma rays, which act as a fingerprint to identify and quantify the original elements. Its major limitation is the required access to a nuclear reactor.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Sensitivity vs. Practicality
High sensitivity always comes with compromises. Choosing the right technique requires balancing analytical needs with practical constraints.
Cost and Complexity
ICP-MS and SIMS instruments represent a significant capital investment, often costing several hundred thousand dollars, and require skilled operators. GFAAS is a far more affordable alternative, but with lower sample throughput. NAA is dependent on access to very specialized, expensive nuclear facilities.
Sample Throughput
ICP-MS is extremely fast for analyzing many elements at once, capable of producing a full elemental survey in minutes. In contrast, GFAAS is slow, as each element requires a separate analysis with its own specific lamp and temperature program.
Matrix Effects and Interferences
No technique is perfect. ICP-MS can suffer from isobaric interferences (ions of different elements with the same mass) and polyatomic interferences (molecules formed in the plasma that have the same mass as the element of interest). Modern instruments use collision/reaction cells to mitigate these issues, but they add complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements should guide your decision. There is no single "best" technique for every problem.
- If your primary focus is a rapid, ultra-trace survey of many elements in a liquid (e.g., environmental water testing, clinical research): ICP-MS is the unparalleled choice for speed and comprehensive detection.
- If your primary focus is measuring one or a few specific metals with high sensitivity on a limited budget: GFAAS provides excellent detection limits at a fraction of the cost of an ICP-MS.
- If your primary focus is analyzing the elemental composition of a solid surface, thin film, or semiconductor: SIMS is the specialized, high-sensitivity technique designed specifically for this purpose.
- If your primary focus is a bulk, highly accurate analysis of a precious or irreplaceable sample that cannot be destroyed: NAA is the ideal method, provided you have access to the necessary facilities.
Ultimately, selecting the correct technique comes from a clear understanding of your analytical question and the inherent strengths of each tool.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Key Strength | Typical Detection Limit | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICP-MS | Multi-element, high throughput | Parts-per-trillion (ppt) | Liquid samples, environmental/clinical analysis |
| GFAAS | Single-element, cost-effective | Parts-per-billion (ppb) | Budget-conscious, specific metal analysis |
| SIMS | Surface analysis, depth profiling | Very high (surface specific) | Solid surfaces, semiconductors, thin films |
| NAA | Non-destructive, highly accurate | Parts-per-billion (ppb) | Precious samples, bulk analysis |
Need the right elemental analysis technique for your lab?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific analytical challenges. Whether you require the ultra-trace capabilities of ICP-MS or the specialized surface analysis of SIMS, our experts can help you select the ideal solution to achieve superior sensitivity and accuracy.
Contact us today to discuss your laboratory needs and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and quality control processes.
Get in touch with our experts now
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab Electrochemical Workstation Potentiostat for Laboratory Use
- Assemble Lab Cylindrical Press Mold
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- Does casting change material properties? Understand the Microstructural Impact on Performance
- What are the products of pyrolysis? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What kind of gas is used in the sputtering process? Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition
- What are some examples of applications that require ultra-low freezers? Protect Your Most Valuable Samples
- What are the safety precautions for brazing? Protect Yourself from Heat, Fumes, and Fire
- What precautions should be taken when brazing? A Guide to Safe Fume, Fire, and Chemical Handling
- What is the future for biomass? A Strategic Shift to High-Value Fuels and Products
- What is the purpose of using an infrared drying oven? Optimize Copper-Plated Graphite Composite Powder Quality



















