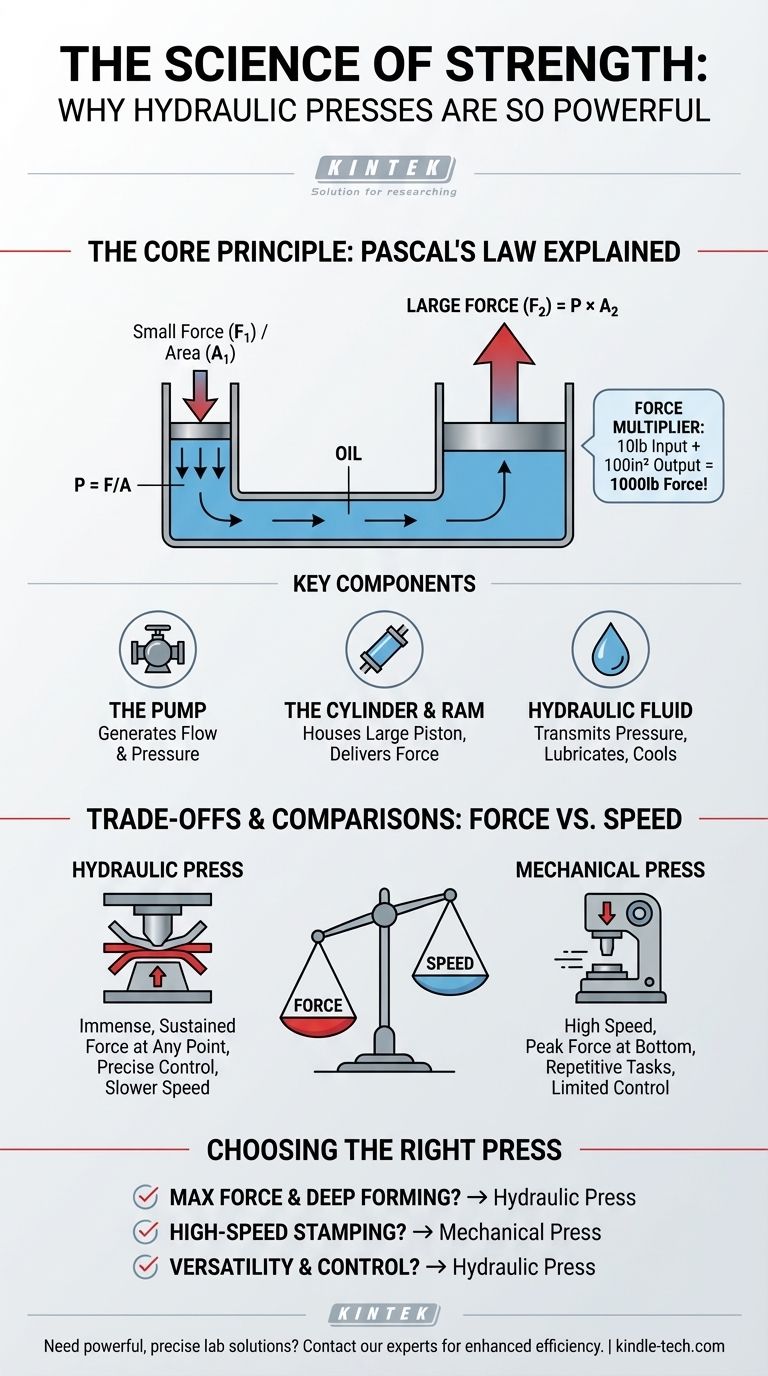
The immense strength of a hydraulic press comes from a fundamental principle of fluid dynamics known as Pascal's Law. This principle allows the system to act as a force multiplier, transforming a small initial force into an exceptionally large output force by applying pressure through an incompressible fluid, typically oil.
The core concept is force multiplication. By applying a small force to a piston in a small area, you create pressure in a closed fluid system. This same pressure then acts on a much larger piston, generating a proportionally massive output force.
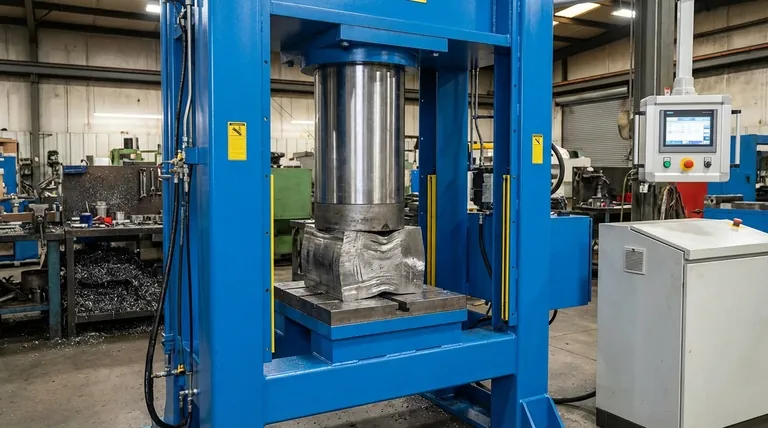

The Core Principle: Pascal's Law Explained
To understand why a hydraulic press can generate forces capable of crushing cars or forging steel, you must first understand the physics at its heart.
A Closed System with an Incompressible Fluid
A hydraulic system is a sealed circuit filled with a fluid, usually a specialized oil. This fluid is considered incompressible, meaning its volume does not noticeably decrease under pressure. This property is critical, as it ensures that pressure applied at one point is transferred efficiently throughout the entire system.
Pressure Equals Force Divided by Area
Pascal's Law states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted equally and undiminished to every part of the fluid and the walls of its container. The formula is simple: Pressure = Force / Area. This relationship is the key to the entire operation.
Force Multiplication in Action
Imagine a simple hydraulic system with two pistons: a small input piston and a large output piston (the ram).
If you apply a 10-pound force to a small piston with an area of 1 square inch, you create a pressure of 10 pounds per square inch (PSI) throughout the fluid.
Now, that same 10 PSI of pressure acts on a large output piston with an area of 100 square inches. The resulting output force is Pressure x Area, or 10 PSI x 100 square inches, which equals 1,000 pounds of force. A small 10-pound effort has been multiplied into a powerful 1,000-pound output.
Key Components Driving the Force
This principle is put into practice using a few essential components working in unison.
The Pump
The hydraulic pump is the source of the initial force. It moves the hydraulic fluid into the cylinder, creating the flow and pressure that initiate the entire process. The pump's power determines how quickly this pressure can be built.
The Cylinder and Piston
This is where the work is done. The cylinder houses the large piston, often called the ram. As pressurized fluid enters the cylinder, it pushes against the face of this ram, generating the tremendous output force used for pressing, forming, or crushing.
The Hydraulic Fluid
The fluid (oil) is the lifeblood of the system. Its primary role is to transmit pressure, but it also serves to lubricate moving parts, prevent corrosion, and help dissipate heat generated during operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While hydraulic presses are immensely powerful, that strength comes with inherent trade-offs compared to other systems like mechanical presses.
The Inverse Relationship: Force vs. Speed
The multiplication of force comes at the cost of distance and speed. To move the large 100-square-inch piston by one inch, you must displace 100 cubic inches of fluid. This requires moving the small 1-square-inch piston a total of 100 inches. You trade a long travel distance on the input side for a short but powerful stroke on the output side.
Comparison to Mechanical Presses
Mechanical presses, which use a flywheel and crank mechanism, are often much faster for high-volume, repetitive tasks like stamping or punching. Their speed is their primary advantage. However, they only deliver their maximum force at the very bottom of the stroke.
In contrast, a hydraulic press can deliver its full, rated force at any point during its stroke. This makes it superior for applications requiring sustained pressure, such as deep-drawing, molding, or forging.
Precision and Control
Hydraulic systems offer unparalleled control. An operator can precisely manage the pressure, speed, and ram position throughout the entire cycle. This level of control is crucial for complex forming operations and for protecting delicate (and expensive) tooling.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct type of press depends entirely on the primary objective of the manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is maximum force and deep forming: A hydraulic press is the definitive choice for its ability to deliver immense, sustained pressure throughout its stroke.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, repetitive stamping: A mechanical press is almost always the more efficient tool due to its much higher cycle rate.
- If your primary focus is versatility and process control: A hydraulic press offers superior command over force, speed, and position, making it ideal for complex, varied, or delicate operations.
By understanding the principle of force multiplication, you can confidently determine which technology is the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hydraulic Press | Mechanical Press |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Force | Immense, sustained force | High force at bottom of stroke |
| Force Control | Full force at any point in stroke | Limited control |
| Speed | Slower, controlled speed | Very high speed |
| Primary Use | Deep drawing, forging, molding | High-speed stamping, punching |
Need a powerful and precise solution for your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including hydraulic systems designed for reliability and control. Whether you're involved in material testing, sample preparation, or complex forming, our expertise ensures you get the right equipment for your specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and deliver unmatched results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Automatic Laboratory Hydraulic Press for XRF & KBR Pellet Press
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in the preparation of solid electrolyte pellets? Ensure Data Accuracy
- What is the pressed powder pellet method? A Guide to Accurate FTIR Sample Preparation
- Why use KBr for IR? Achieve Clear, Unobstructed Spectra for Solid Samples
- Why are KBr pellets used in FTIR? Achieve Clear, Accurate Solid Sample Analysis
- Are hydraulic presses powered by water? Discover the critical role of hydraulic oil.



















