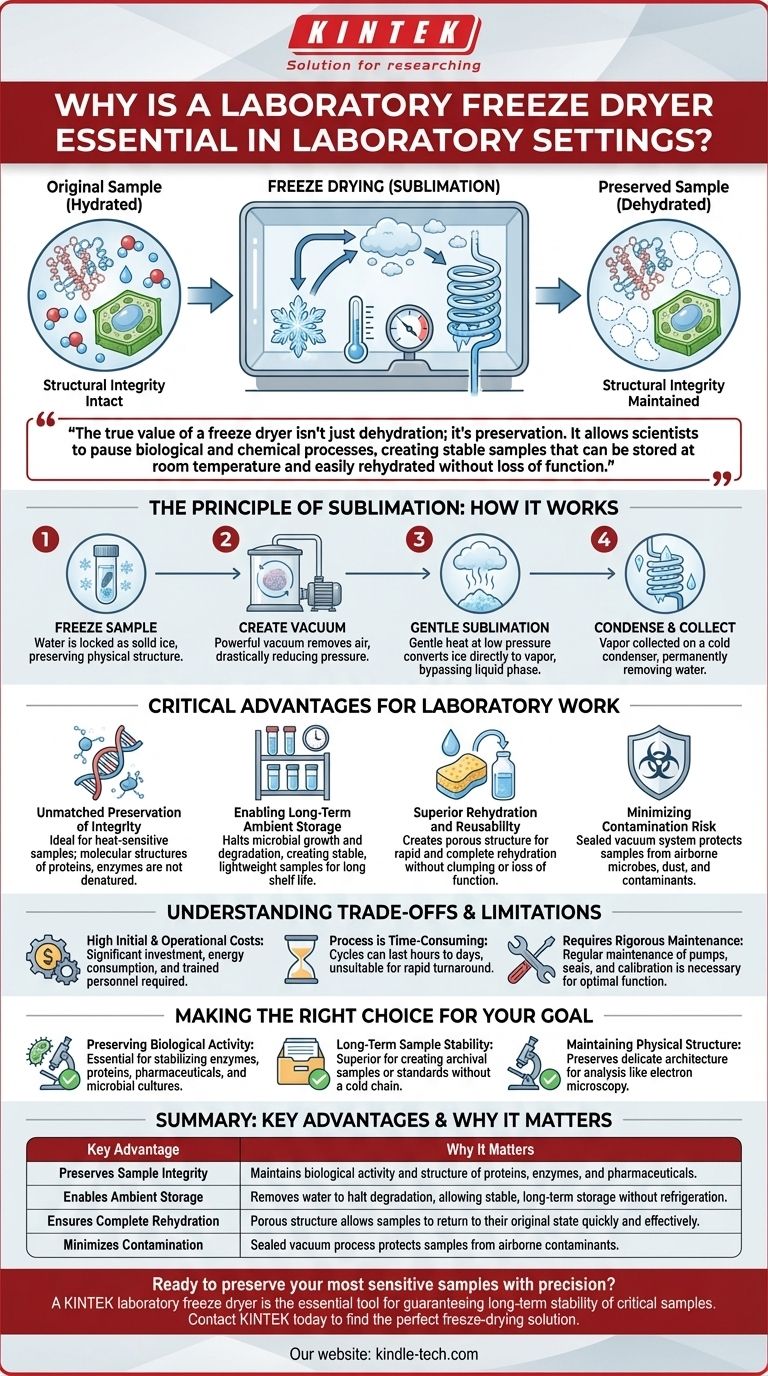
At its core, a laboratory freeze dryer is essential because it is the only method that removes water from a sample without destroying its fundamental structure. By freezing the material and then turning the ice directly into vapor through sublimation, it masterfully preserves the integrity of heat-sensitive materials like proteins, enzymes, and pharmaceuticals, ensuring their biological activity and chemical stability remain intact for long-term storage.
The true value of a freeze dryer isn't just dehydration; it's preservation. It allows scientists to pause biological and chemical processes, creating stable samples that can be stored at room temperature and easily rehydrated without loss of function.

The Principle of Sublimation: How Freeze-Drying Works
To understand why a freeze dryer is so indispensable, you must first understand its unique process. It doesn't use heat to evaporate water; instead, it uses pressure and temperature to sublimate it.
Step 1: Freezing the Sample
The process begins by thoroughly freezing the sample material. This locks the water molecules in place as solid ice crystals, which is critical for preserving the sample's physical structure.
Step 2: Creating a Vacuum
The frozen sample is placed in a sealed chamber, and a powerful vacuum pump removes the surrounding air. This drastic reduction in pressure is the key to enabling sublimation at low temperatures.
Step 3: Gentle Sublimation
With the pressure extremely low, a small amount of heat is gently applied to the shelves holding the samples. This energy gives the frozen water molecules just enough energy to transition directly from a solid (ice) to a gas (water vapor), bypassing the liquid phase entirely.
Step 4: Condensation and Collection
The water vapor released from the samples is drawn away from the chamber and collected on an extremely cold condenser coil. This coil acts as a trap, turning the vapor back into ice and permanently removing it from the system.
The Critical Advantages for Laboratory Work
This elegant process of sublimation delivers several advantages that are simply unattainable with other drying methods like oven-drying or desiccation.
Unmatched Preservation of Integrity
Because the process avoids high temperatures, it is ideal for heat-sensitive samples. The molecular structures of proteins, enzymes, and other complex biologicals are not denatured, and their activity is perfectly retained.
Enabling Long-Term Ambient Storage
By removing nearly all water content, freeze-drying effectively halts microbial growth and slows the chemical degradation processes that require moisture. This creates a highly stable, lightweight sample with a long shelf life that does not require constant refrigeration.
Superior Rehydration and Reusability
The freeze-drying process creates a porous, sponge-like structure in the final product. This allows for rapid and complete rehydration, returning the sample to its original state without clumping or loss of effectiveness.
Minimizing Contamination Risk
The entire process takes place within a sealed vacuum system. This inherently protects the sample from airborne microbes, dust, and other environmental contaminants that could compromise results.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, a freeze dryer is a specialized piece of equipment with specific operational requirements and limitations that demand careful consideration.
High Initial and Operational Costs
Laboratory freeze dryers represent a significant capital investment. Furthermore, they require trained personnel to operate correctly and consume a notable amount of energy during their long cycles.
The Process is Time-Consuming
A typical freeze-drying cycle can last from several hours to several days, depending on the sample size and type. This makes it unsuitable for applications requiring rapid turnaround.
Not Suitable for All Materials
The process is generally ineffective for samples with high concentrations of fats, sugars, or certain salts. These substances can lower the freezing point of the material, making the sublimation process difficult or impossible to control.
Requires Rigorous Maintenance
To function correctly, the system relies on a perfect vacuum and extreme cold. This necessitates regular maintenance of vacuum pumps, seals, and refrigeration units, as well as periodic calibration of temperature and pressure sensors.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if a freeze dryer is essential for your work depends entirely on your preservation needs.
- If your primary focus is preserving biological activity: A freeze dryer is non-negotiable for stabilizing enzymes, proteins, pharmaceuticals, and microbial cultures.
- If your primary focus is long-term sample stability: It is the superior choice for creating archival samples or standards that can be stored for years without a cold chain.
- If your primary focus is maintaining physical structure: For materials being prepared for analysis like electron microscopy, freeze-drying preserves the delicate architecture that other methods would destroy.
Ultimately, a laboratory freeze dryer is an essential tool for any work where the integrity, activity, and structure of a sample are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Preserves Sample Integrity | Maintains biological activity and structure of proteins, enzymes, and pharmaceuticals. |
| Enables Ambient Storage | Removes water to halt degradation, allowing stable, long-term storage without refrigeration. |
| Ensures Complete Rehydration | Porous structure allows samples to return to their original state quickly and effectively. |
| Minimizes Contamination | Sealed vacuum process protects samples from airborne contaminants. |
Ready to preserve your most sensitive samples with precision?
A KINTEK laboratory freeze dryer is the essential tool for researchers and lab managers who need to guarantee the long-term stability and activity of critical samples like proteins, enzymes, and pharmaceuticals. Our freeze dryers deliver the unmatched preservation your work demands.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect freeze-drying solution for your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Vertical Pressure Steam Sterilizer for Liquid Crystal Display Automatic Type
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the function of Freeze-thaw Equipment in Au-(PNiPAAm/PVA) hydrogel? Achieve High-Speed Photothermal Actuation
- Why is a laboratory vacuum freeze dryer essential for plant extracts? Preserve Bioactivity & Structure
- What is the purpose of an evaporator? The Key Component That Creates Cooling
- What is the function of a freeze dryer in the ice-templating process? Preserving Aligned Pore Scaffolds for LAGP
- Why is a freeze dryer preferred for reduced graphene oxide (Hh-RGO) powders? Preserve Nano-Structure and Performance



















